Mäder
|
Mäder
|
||
|---|---|---|
| coat of arms | Austria map | |
|
|
||
| Basic data | ||
| Country: | Austria | |
| State : | Vorarlberg | |
| Political District : | Feldkirch | |
| License plate : | FK | |
| Surface: | 3.23 km² | |
| Coordinates : | 47 ° 21 ' N , 9 ° 37' E | |
| Height : | 414 m above sea level A. | |
| Residents : | 4,102 (January 1, 2020) | |
| Postal code : | 6841 | |
| Area code : | 05523 | |
| Community code : | 8 04 12 | |
| NUTS region | AT342 | |
| Address of the municipal administration: |
Alte Schulstr. 7 6841 Mäder |
|
| Website: | ||
| politics | ||
| Mayor : | Rainer Siegele ( ÖVP ) | |
|
Local council : (2015) (24 members) |
||
| Location of Mäder in the Feldkirch district | ||
 Aerial view of the municipality of Mäder from the east |
||
| Source: Municipal data from Statistics Austria | ||
Mäder is a municipality in Austria in Vorarlberg in the Feldkirch district with 4102 inhabitants (as of January 1, 2020).
geography
Geographical location
Mäder is located in the Vorarlberg Rhine Valley , directly north of the Kummenberg and 16 km south of the shores of Lake Constance, directly on the eastern bank of the Alpine Rhine and is therefore a community on the border with Switzerland . The center of the village is at an altitude of 414 m above sea level. A. The entire municipality lies in the Rhine Valley plain, there are no significant natural elevations.
Expansion of the municipal area
The municipality extends from north to south over 2.7 km, from west to east over 2.9 km. Mäder is bounded by the Rhine in the west and by the Egelseegraben in the east . The northern border is a straight line with no topological background, the southern border also runs arbitrarily, over some stretches along a road and in the area of the settlements of Neuburg and Kutzen partly across existing residential buildings.
With a municipal area of 3.23 km² and a population density of 1270 inhabitants per square kilometer, Mäder is not only the seventh smallest in terms of area, but also the most densely populated municipality in Vorarlberg.
Neighboring communities
| Altach | ||
| Oberriet |

|
|
| Koblach | Götzis |
geology
The Alpine Rhine Valley is an atypical for the Alps, filled with young loose rock and several hundred meters deep. 14,000 years ago this tub was still filled with water and thus part of Lake Constance , but was then gradually filled with sediments from the Rhine and its tributaries, especially the Ill and Frutz , so that about 4000 years ago the Rhine delta as far as Lustenau advanced and the area of Mäder silted up. The soil in Mäder is therefore a typical alluvial soil made of coarse to fine alluvial material.
Nature reserves and natural monuments
A former gravel pit in the north corner of the municipality was placed under landscape protection as the Mäder sand pit in 1976 . It offers the endangered sea buckthorn and a small population of pond frogs a home and serves as a resting place for migrating water birds.
A white poplar , a common oak and a white willow in the municipal area of Mäders are designated as natural monuments and are therefore under special protection.
3D model of the municipality
The Kairos - Institute for Impact Research and Development , Bregenz has developed a new tool for the representation of spatial planning . Mäder is a pilot project: According to national data from laser scans via aircraft, a 3D model of the landscape on a scale of 1: 1000 was 3D printed, which also shows all the houses in three dimensions. A multi-colored zoning plan or a historical aerial photo can be projected onto the white model from above . Even cartography laypeople should gain a good impression.
history
In the Middle Ages, Mäder belonged to the Reichshof Kriessern and was first mentioned in 1294 as “in the Mederen”. In 1513 the area came to Austria. The Habsburgs ruled the places in Vorarlberg alternately from Tyrol and Upper Austria (Freiburg im Breisgau).
From 1805 to 1814 the place belonged to Bavaria, then again to Austria. Until 1806 Mäder was incorporated into the Rankweil-Sulz court in the Feldkirch reign. Mäder was repeatedly hit by floods from the Rhine : So it came in the Rhine Valley on June 15, July 2 and August 28, 1817 to floods. On August 28, in particular, numerous dam breaches were recorded. On the Vorarlberg side, the Rhine broke through the dams at Ruggell, Bangs, Meiningen, between Koblach and Mäder, at Brugg and in Gaißau and caused great damage on both sides of the valley. In 1824 the mayor Johann Josef Ender rode to Vienna and managed to get the state to take over the measures to regulate the Rhine and build the dams.
Mäder has belonged to the Austrian state of Vorarlberg since it was founded in 1861. In 1892, the international regulation of the Rhine was adopted by a state treaty and implemented in the following years. After World War II, 1945 to 1955, the place was part of the French occupation zone in Austria.
Population development
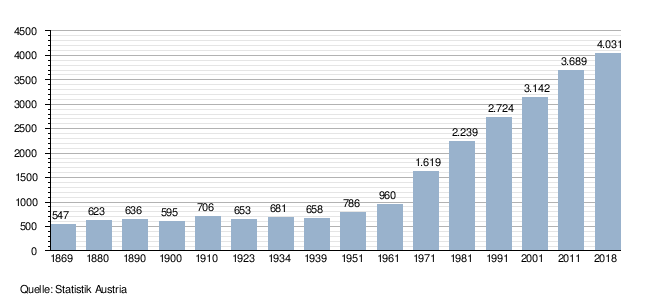
The proportion of foreigners at the end of 2002 was 11.5%.
The population is growing rapidly, as both the migration balance and the birth balance are positive.
Culture and sights
- Parish church Mäder hl. Bartholomew
- Mäder municipal office
- JJEnder-Saal: This hall, built in 1994 according to plans by Baumschlager-Eberle , is named after the Mäderer headmaster Johann Josef Ender, who achieved the takeover of the Rheinwuhrung by the state in 1824.
Economy and Infrastructure
In 2003 there were 43 commercial enterprises with 386 employees and 33 apprentices on site. There were 1,059 employees subject to wage tax. Agriculture plays an important role. The proportion of agricultural land in the total area is 56.6%.
energy
Mäder is one of the 24 municipalities in Austria (as of 2019) that were awarded the highest award of the e5 municipal energy project. The e5 community project aims to promote the implementation of a modern energy and climate policy at community level.
Mäder does not have a train station, but is well served by the Landbus Unterland and the local amkumma bus. There is a road connection across the Rhine to Switzerland, which is mainly chosen by commuters and holidaymakers.
There are (as of January 2003) 462 pupils on site and there is a new middle school with an ecological focus, an elementary school and two kindergartens.
politics
The municipal council of Mader has 24 members. After the municipal council and mayoral elections in 2015 , this consists of 18 mandataries from the ÖVP girls and non-party members and 7 members from the FPÖ and non-party members.
Mayor of the community is Rainer Siegele from the ÖVP. He was confirmed in office in the direct mayor election 2015 with 75.89 percent of the votes.
Personalities
Honorary citizen
- Albert Gisinger (1919–2003), former mayor
- Adolf Vallaster (* 1940), dialect author
Sons and daughters of the church
- Ewald Stadler (* 1961), politician
- Julian Erhart (* 1992), soccer player
- Martin Gisinger (* 1955), soccer player
Web links
- Mäder municipality
- 80412 - Mäder. Community data, Statistics Austria .
Individual evidence
- ^ J. Georg Friebe: Landscape history and landscape change in the Vorarlberg Rhine Valley . In: R. Alge (Hrsg.): Nature monograph Gsieg - Obere Mähder (= Vorarlberger Naturschau - research and discovery ). No. 6 . Dornbirn 1999, p. 29–34 ( PDF file; 262 kB [accessed July 30, 2017]).
- ^ Markus Staudinger: Update of the Vorarlberg biotope inventory, Mäder municipality. Arge Vegetation Ecology and Landscape Planning, August 2008, p. 9 , accessed on July 30, 2017 .
- ^ Markus Staudinger: Update of the Vorarlberg biotope inventory, Mäder municipality. Arge Vegetation Ecology and Landscape Planning, August 2008, p. 13 , accessed on July 30, 2017 .
- ^ Markus Staudinger: Update of the Vorarlberg biotope inventory, Mäder municipality. Arge Vegetation Ecology and Landscape Planning, August 2008, p. 18 , accessed on July 30, 2017 .
- ↑ Zoning plans conquer the third dimension orf.at, August 15, 2020, accessed August 15, 2020.
- ^ Wolfgang Scheffknecht: Rhine floods. In: Vorarlberg Chronicle. State of Vorarlberg, 2005, accessed on May 2, 2019 .
- ^ Statistics Austria, A look at the community of Mäder, population development. Retrieved March 30, 2019 .
- ↑ e5 communities in Austria as of March 2019