Hybrid creatures
Hybrid beings or chimeras (according to Chimera , a hybrid creature in Greek mythology) are fictional living beings that are composed of parts of two or more living beings.
Even with the oldest sculptures, drawings and rock carvings of mankind, there were not only depictions of animals and humans, but also of anthropozoomorphic hybrid beings made up of combinations of humans and animals. This form of representation lasted into the Egyptian high culture , in which the gods were represented as humanoids with animal heads.
In archaeological parlance, in contrast to common parlance, “ monsters ” are hybrid beings with animal bodies and animal heads (e.g. griffins , manticore or dragons ), but mostly animal bodies with human heads such as the Sphinx (human head and lion body), centaurs (human upper body and horse body) or mermaids (female torso and fish lower body).
The opposite is formed by the term “ demon ”, which describes a theriocephalic (animal-headed) hybrid being with at least human legs. B. the goat demon.
New medical techniques make it possible to implant human cell nuclei in animal egg cells, which creates so-called cybrids .
Stone age
The oldest stone-age drawings probably depict demons, i.e. animal-headed hybrid beings. It is assumed that they depict the transformation of a shaman into an animal experienced in trance , intoxication or dream (see Shamanic Journey ) or that animal skulls or animal heads are mask-like when dancing Headgear were worn. It is also possible that the affiliation of the people marked with an animal's head to a clan named after the animal or a tribe associated with this animal as a totem is to be identified. In the case of people living in the Stone Age in Africa and North America, some tribes up to modern times had personal totems from individuals and totems from groups of men such as groups of hunters and warriors in addition to the tribal totems. Finally, it is also possible that a spirit or god or goddess is represented here. Hybrid creatures were probably drawn over the course of time for many of the reasons mentioned here.
In Ice Age art, depictions of animals are common, humans are rare, and hybrid creatures are even rarer. The oldest representation of a hybrid being is a person with a lion's head carved from a mammoth's tusk from the Hohlenstein-Stadel in the southern German Lone Valley , which belongs to the Aurignacian cultural stage (approx. 35,000 to 22,000 BC). See main article Leo Man . In the Lascaux cave there is a drawing of a human body with a phallus bearing a bird's head.
An ibex head, which clearly shows the pubic triangle and vulva , i.e. is shown with a woman's body, was found on a deer antler stick from Las Caldas in Asturias, Spain . The piece, however, only dates from around 14,000 BC. The cultural stage of the Magdalenian .
On a perforated rod, also from Magdalenian from Abri Mège in the French Dordogne department , three creatures with human legs and goat-like heads called "devils" were found among horses, birds and snakes.
Animal-headed hybrids were found among the cave paintings in the caves of Gabillou , Les Trois Frères , Fontanet, Altamira , Chauvet , Candamo , Pech-Merle , Los Casares , Les Combarelles and Hornos de la Pena .
In the former cave of Gabillou, the well-known figure of a man with a bison head, called the “magician”, “Le Sorcier”, was found.
Dog-headed people were strongly represented in the post-Iron Age art of rock art in the Sahara (e.g. in the Messak Mountains in Libya ). The cynocephalons attack strong animals such as rhinos, buffalo, elephants and hippos in the pictures.
In northwestern Saudi Arabia , goat-headed figures with human bodies were again found in the so-called Jubba rock art .
Strongly stylized human figures with T-shaped heads and M-shaped heads, reminiscent of the goat demon, were found in the western Turkish Latmos Mountains in the vicinity of the ancient city of Herakleia . The animal attributes are preserved for a long time. There are still depictions of Alexander the Great with ram's horns.
In the art of the Ice Age and the early post- Ice Age , only demons were found in Europe, Africa and the Middle East, i.e. hybrids with human bodies, but at least, if they have an animal upper body, with human legs. No creature with an animal body and human head has yet been found. Many of the animal-headed people, including the oldest, the lion-headed one from Hohlenstein-Stadel near Ulm , and the bison-headed “magician” from Trois-Frere, seem to be dancing. Some people believe to recognize the use of flutes . That is why most Stone Age researchers assume that these are not people adorned with animal skulls, but shamans who put themselves into a trance by means of dance in order to transform themselves into animals and thus come into contact with the world beyond. For this reason, the feet are sometimes depicted according to the species of the respective animal. In the Altamira cave, for example, there is a human-raised creature with a bird's head, human arms and a human phallus , but with the feet of a bear.
Egypt
The mythology of Egypt is rich in hybrid creatures .
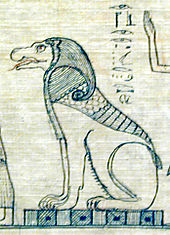
The best known is the sphinx with the body of a male lion and mostly with a human head. In addition, were Ram , - hawks - and Sperber heads in use.
Ammut or Ammit , a deity of Egyptian mythology , is made up of the largest and most dangerous animals in Egypt : the head of a crocodile , the front body of a lion and the rear part of a hippopotamus . She has the nickname "great eater", translated: "eater of the condemned dead", because in the course of the judgment of the dead she eats the hearts of the deceased when their souls are burdened with sin. The souls can then no longer exist.
Greece

In Greek mythology the Chímaira was a daughter of the monsters Echidna and Typhon , her siblings were the Hydra , the Kerberos and the Sphinx . She lived in Chimaira in Lycia , where she threatened people and animals.
Homer describes her in the Iliad as a fire-breathing hybrid creature with three heads: that of a lion , that of a goat on the neck , and the tail of a snake or a dragon . King Iobates gave Bellerophon , a grandson of Sisyphus , the order to kill the Chimera. For this purpose, a Greek deity ( Athena or Poseidon ) put a hybrid creature, the winged horse Pegasus , at his disposal: from the air he was able to kill the Chimera with his arrows. King Iobates was so happy about it that he gave the Bellerophon his daughter to wife.
Starting from the chimera, the term chimera was extended to other hybrid beings. Apart from that, Greek mythology brought the most well-known hybrid creatures into the consciousness of the West, such as the aggressive centaurs and harpies , dangerous manticores and the gentle winged horses Pegasus and Celeris .
Rome
Knowledge of the Greek hybrid beings was imparted to the Romans through the Greek colonies that had existed in Italy for centuries and the Etruscans . So were in the Roman mythology z. B. later equated the faunas with the Greek satyrs , the companions of Pan .
middle Ages
The Romanesque art of the High Middle Ages is full of hybrid creatures of all kinds - such as the tympana of the former abbey churches of Beaulieu-sur-Dordogne and Carennac . Combinations of lion and griffin (“ Leogryph ”) were particularly popular .
Asia
India
Japan
In Japanese popular belief, there is the nue with the head of a monkey, the body of a tanuki , the legs of a tiger and a snake as a tail.
List of hybrid beings
Mythical creatures of ancient oriental cultures:
Egyptian mythology , see list of Egyptian gods :
Medieval mythical creatures:
Other mythical creatures:
Mixed human beings in the traditional carnival
Tschäggättä (Swiss German for "[Bunt] Gescheckter") in the Lötschental
Hybrid beings in research
Experimental animals in whose bodies human genes , chromosomes , cells or entire organs have been built into their bodies for experimental purposes are also referred to as “hybrid beings”. The aim is to develop an animal model for a human disease and thus better research the disease. To obtain human embryonic stem cells , the entire nucleus of a human cell can also be inserted into the egg cell of an animal. This is then a cytoplasmic hybrid , or cybrid for short . In 2011 there will be no such tests in Germany. There are guidelines in the Embryo Protection Act . In 2011 it is not a criminal offense in Germany to manufacture cybrids and implant them in the womb of a person or an animal.
Hybrid creatures in film and art
The film Splice, released in 2009, shows a hybrid creature consisting of a human being with a mammal, an amphibian and a bird, with a spiked tip on its tail.
See also
literature
- Wolfgang Speyer : hybrid creatures. In: Real Lexicon for Antiquity and Christianity . Volume 24, Hiersemann, Stuttgart 2012, ISBN 978-3-7772-1222-7 , Sp. 864-925.
- Klaus Schmidt: You built the first temple. The enigmatic sanctuary of the Stone Age hunters. CH Beck 2006, p. 210 ff.
- Friedrich Schlette, Dieter Kaufmann (ed.): Religion and cult in prehistoric and early historical times. Berlin 1989.
Web links
- Henrike Frey-Anthes: hybrid creatures. In: Michaela Bauks, Klaus Koenen, Stefan Alkier (eds.): The scientific biblical lexicon in the Internet (WiBiLex), Stuttgart 2006 ff., Accessed on February 27, 2013.
- TimeForFantasy , detailed lexicon on hybrid creatures of all kinds
- www.mischwesen.net - Information site about medicine vs. ethics
Individual evidence
- ↑ Monika Seynsche : The human being in the animal - German Ethics Council comments on research on so-called hybrid beings , Deutschlandfunk Research aktuell dated September 27, 2011.
- ↑ Splice - the experiment [1]