NGC 1535
|
Planetary nebula data from NGC 1535 |
|
|---|---|
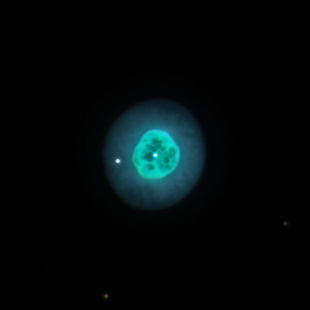
|
|
| NGC 1535 imaged with the 81 cm reflecting telescope of the Mount Lemmon Observatory | |
| AladinLite | |
| Constellation | Eridanus |
|
Position equinox : J2000.0 |
|
| Right ascension | 04h 14m 15.8s |
| declination | -12 ° 44 ′ 22 ″ |
| Appearance | |
| Apparent brightness (visual) | 9.6 likes |
| Apparent brightness (B-band) | 9.6 likes |
| Angular expansion | 0.85 ' |
| Central star | |
| designation |
HD 26847 (BD −13 ° 842, GSC 05318-00563, GCRV 2426) |
| Physical data | |
| Redshift | −0.000005 ± 0.000007 |
| Radial velocity | (−1 ± 2) km / s |
| distance | approx. 5500 ly |
| history | |
| discovery | Wilhelm Herschel |
| Date of discovery | February 1, 1785 |
| Catalog names | |
| NGC 1535 • PK 206-40.1 • PN G206.4-40.5 • GC 826 • H IV 26 • h 2618 • 2MASX J04141578-1244216 • IRAS 04119-1251 • CS = 12.2 | |
NGC 1535 is the name of the brightest planetary nebula in the constellation Eridanus . The distance from NGC 1535 is given as 5000 to 6000 light years, the true diameter a little more than one light year .
It was discovered on February 1, 1785 by the German-British astronomer Wilhelm Herschel .
Visual observation
The brightness of NGC 1535 is sufficient for observation in a small telescope from an aperture of around 70 mm, but there you will only find a faint, stellar object. In a larger telescope with an aperture of around 6 inches or more, NGC 1535 is already very noticeable. The 12-mag central star is a bit difficult to observe, even with a 10-inch aperture; successful observation requires correspondingly good seeing .
Web links
Commons : NGC 1535 - collection of images, videos, and audio files
Individual evidence
- ↑ NASA / IPAC EXTRAGALACTIC DATABASE
- ↑ a b SEDS: NGC 1535
- ↑ a b SIMBAD
- ↑ Stars and Space October 2005 p. 60
- ↑ Seligman