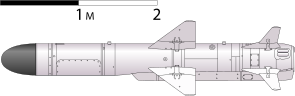
SS-N-25 Switchblade
| SS-N-25 Switchblade | |
|---|---|
| General Information | |
| Type | Anti-ship missile |
| Local name | 3M24, Ch-35, Uran, Uranus |
| NATO designation | SS-N-25 Switchblade, AS-20 Kayak |
| Country of origin |
|
| Manufacturer | Zvezda design office |
| development | 1984 |
| Commissioning | 1995 |
| Working time | in service |
| Unit price | 500,000 USD |
| Technical specifications | |
| length | 3.85 m (without booster) 4.40 m (with booster) |
| diameter | 420 mm |
| Combat weight | 520 kg (without booster) 620 kg (with booster) |
| span | 1330 mm |
| Drive First stage Second stage |
Turbojet solid fuel booster |
| speed | Mach 0.8-0.85 |
| Range | 120 km (3M24) 260 km (3M24U) |
| Furnishing | |
| steering | Inertial navigation platform plus GLONASS |
| Target location | active radar target search |
| Warhead | 145 kg highly explosive armor piercing with fire effect |
| Detonator | Impact and delay detonators |
| Weapon platforms | Ships, helicopters, planes, vehicles |
| Lists on the subject | |


SS-N-25 Switchblade is the NATO code for an anti-ship missile made in Russia . The GRAU index of the ship-based version is 3M24 , the designation of the air -based version is Ch-35 . The export variants are called uranium or Uranus .
development
At the beginning of the 1980s, the Soviet Union only had large and heavy anti-ship missiles in its inventory. Due to the successful use of the compact Exocet in the Falklands War, a decision was made in the Soviet Union to develop a small anti-ship missile. The aim was to develop a universally applicable, inexpensive and compact anti-ship guided weapon. It should be used from ships, airplanes, helicopters and trucks to combat small and medium-sized combat ships. The development contract was awarded in 1983. After testing the first drafts began in 1984 in the design office Zvezda with the development of the SS-N-25th The first test series with six guided missiles took place as early as 1986, of which the first three tests failed. The first successful test flight did not take place until January 1987. Another 14 test starts were carried out between 1988 and 1991. With the collapse of the Soviet Union , development was temporarily stopped and the project then stood still. In the meantime, the SS-N-25 was offered on the export market as the successor to the SS-N-2 Styx under the name Uran . In 1994, India expressed an interest in the SS-N-25. After India had paid part of the development costs, the first copies were delivered from 1996. At the same time, the Russian naval fleet ordered around a dozen copies for troop trials and tests. However, the tense financial situation of the armed forces in Russia prevented procurement for the time being. Only between 2009 and 2010 could around 100 copies be procured. The airborne version Ch-35 was ready for use in 2006. The SS-N-25 is to be regarded as the inexpensive counterpart of the French Exocet and the US-American R / UGM-84 Harpoon . In the west she got the nickname "Harpoonski". The airborne version of the Ch-35 is the first anti-ship missile from Russian production that can be used by tactical combat aircraft and helicopters.
technology
The SS-N-25 can be used by airplanes, helicopters, ships or vehicles. The missile can be installed on small missile speedboats as well as on larger corvettes , frigates and destroyers . The anti-ship missile is designed to combat and sink small and agile missile speedboats and ships with a displacement of up to 5,000 tons.
The ship-based 3M24 guided missiles are housed in watertight four-way launching canisters of the type KT-184 (3S24) on the ship's deck and are launched directly from these. The launch canisters have a fixed elevation of 30 °. It takes a maximum of 60 seconds to start up the system and prepare for the start. Before starting, the on-board computer of the missile must be given the approximate coordinates and the course of the target. These are determined by the respective launch platform using radar or ELINT . The start takes place with the help of a booster on the rear of the guided missile. After leaving the steel container at around 25 m / s, the eight stabilization and control surfaces unfold . The booster accelerates the missile to a speed of around 315 m / s and brings it to an altitude of 200 m. After starting, the 3M24 can curve 45 °, the 3M24U 130 °. The booster is thrown off after it has burned out and the TRDD-50AT - Turbojet ignites. Now the missile has covered a distance of around 5 km and now sinks to a cruising altitude of 10–15 m, depending on the sea . The Detal RWE radar altimeter ensures the necessary safety distance between the guided weapon and the sea surface. The cruise flight takes place at a speed of 270-280 m / s. The 3M24 is a fire-and-forget guided weapon and the flight to the target area takes place autonomously with the help of the digital on-board computer. This includes an inertial navigation system , an autopilot and the radar altimeter. The on-board ARGS-35 radar seeker is activated for the target approach . This has a weight of 47.5 kg. The radar search head has a detection range of around 20 km, the search sector in azimuth is +/- 45 ° and in elevation angle is + 10 / −20 °. The seeker automatically switches to the previously determined radar contact or to the largest radar target. If the target was detected by the radar, the missile sinks to a height of 3–5 m (depending on the sea state). The impact at the target takes place at wave height in the ship's hull. The warhead ignites with a time delay so that the explosion takes place inside the ship. If no target is hit, the missile falls into the sea after a certain flight time.
The improved version 3M24U is equipped with the new Ts-074U on-board computer with a navigation system. In addition to the inertial navigation system, this includes a satellite navigation system . This has a multi-channel receiver for the satellite navigation systems GLONASS and GPS . Depending on availability, the steering system automatically selects one of the two satellite signals. Before the start, navigation waypoints can be programmed in the on-board computer so that the guided missile can fly a predetermined route . The new U-502U Fringe-K radar seeker head was also installed. After it has captured the target with active radar search, it switches to passive search mode. This is based on the electromagnetic emissions (radar, interference systems) that the target emits. If the seeker loses the target, the active radar seeker is reactivated immediately. The new radar search head has a detection range of around 50 km. The 3M24U version can also be used against weakly fortified land targets near the coast.
Variants and weapon platforms
Surface units (SS-N-25 Switchblade)
- 3M24: Standard version anti-ship missile, range 130 km.
- 3M24E uranium: export version of the 3M24 (from 1996).
- 3M24E1: Cruise missile based on the Ch-35U for combating land targets, range 250 km.
- 3M24U: Anti-ship missile based on the Ch-35U, range 250 km, presented in 2012. Use with the Klub-K system .
- 3M24UE Uranus: Export version of the 3M24U.
- 3M24EMW: Target display drone without a warhead.
Airborne (AS-20 Kayak)
- Ch-35: Standard version for use from airplanes, range 150 km.
- Ch-35W: Version with additional rocket booster for use from helicopters.
- Ch-35E uranium: export version of the Ch-35.
- Ch-35U: Improved Ch-35 from 2015 with a smaller 64M turbo engine, smaller air intake, larger fuel supply, Ts-074U steering unit with INS , GLONASS and GPS as well as active / passive radar seeker head U-502U Fringe-K . Range 260 km.
- Ch-35UL: Reduced version of the Ch-35U for use from the MiG-29K and Su-33 .
- Ch-35UE Uranus: Export version of the Ch-35U.
- Ch-35ULE: Export version of the Ch-35UL.
Land Based (SS-C-6 Sennight)
- 3K60 Bal : Version for coastal defense installed on your MAZ-7930 chassis. With eight 3M24 guided missiles, range 120 km, since 2008.
- Rubesch-ME: Version for coastal defense installed on your KamAZ-6350 chassis. With four 3M24 guided missiles, range 120 km, since 2019.
Versions outside of Russia
- Kumsong-3: Replicas of the 3M24 and 3M24U from North Korea .
- R-360 Neptune: Further development of the 3M24 from Ukroboronprom from the Ukraine . Range 280 km.
- VCM-01: Further development of the 3M24UE from Vietnam . Range 300 km.
status
The SS-N-25 guided missiles are one of the weapon systems of Soviet design that were only ready for series production in the 1990s. Due to an acute lack of money, the Russian armed forces were only able to procure the guided weapons to a limited extent, which is why they are mainly produced for export. The SS-N-25 is used by the following states:

-
 Algeria
Algeria
-
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
-
 India
India
-
 Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan
-
 Malaysia
Malaysia
-
 Myanmar
Myanmar
-
 North Korea
North Korea
-
 Russia
Russia
-
 Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan
-
 Ukraine
Ukraine
-
 Vietnam
Vietnam
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Kh-35. In: military-today.com. Military Today, accessed March 9, 2017 .
- ^ A b Duncan Lennox: Jane's Strategic Weapon Systems. Jane's Information Group , 2005, ISBN 0-7106-0880-2 .
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k ПРОТИВОКОРАБЕЛЬНЫЙ КОМПЛЕКС 3К24 «УРАН» («УРАН-Э») С РАКЕТОЙ Х-35 (3М24, 3М24Э). In: bastion-karpenko.ru. НЕВСКИЙ БАСТИОН, accessed June 23, 2020 (Russian).
- ↑ a b Russian / Soviet Sea-based Anti-Ship Missiles DTIG, Nov, 2005, accessed on August 12, 2015 (English)
- ↑ nr2.ru ( Memento from February 1, 2014 in the Internet Archive ), accessed on March 27, 2014 (Russian)
- ↑ a b c Х-35 / 3М24 - SS-N-25 SWITCHBLADE / AS-20 KAYAK. In: militaryrussia.ru. November 17, 2017, accessed June 23, 2020 (Russian).
- ↑ a b c d ТАКТИЧЕСКАЯ ПРОТИВОКОРАБЕЛЬНАЯ РАКЕТА Х-35УЭ КОМПЛЕКСА «УРАН». In: bastion-karpenko.ru. НЕВСКИЙ БАСТИОН, accessed June 23, 2020 (Russian).
- ↑ a b x-35 at airwar.ru , accessed April 1, 2014 (Russian)
- ^ Carlo Kopp: Soviet / Russian Cruise Missiles. In: ausairpower.net. April 2015, accessed on June 24, 2020 .
- ↑ rbase.new-factoria.ru , accessed April 1, 2014 (Russian)
- ↑ a b Piotr Butowski: Russia is preparing a precision guidance revolution for its fast jet, strike, and bomber forces . Jane's International Defense Review, August 2014, United Kingdom, 2014.
- ↑ Missilethreat: Kumsong-3 (Kh-35 Variant)
- ↑ Missiledefenseadvocacy: Kumsong-3
- ↑ Janes.com: Ukraine's Neptune anti-ship cruise missile ready for service
- ↑ Navyrecognition.com: Newest Ukrainian R-360 cruise missile of Neptun coastal system unveiled
- ↑ Navyrecognition.com: Vietnam unveils its new VCM-01 anti-ship cruise missile
- ↑ a b c d e f g SIPRI Arms Transfers Database. In: sipri.org. Stockholm International Peace Research Institute, accessed June 22, 2020 .