Detroit Institute of Arts
The Detroit Institute of Arts (DIA) in Detroit , Michigan , is one of the premier art museums in the United States . It was founded in 1885 . The collection includes more than 65,000 exhibits, starting with the art of ancient Egypt to contemporary art. One focus is the art and cultural history of the USA since the 18th century. The Detroit Industry fresco in the center of the museum is considered one of Diego Rivera's most important works . After the City of Detroit filed for bankruptcy, the future of the Detroit Institute of Arts was also in question. A sale of the collection was averted and the museum was permanently secured by a new sponsorship.
history
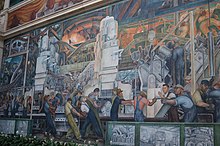
The Detroit Institute of Arts was founded in 1885. It was first located on Jefferson Avenue. As the collection grew steadily and the space in the first museum building was no longer sufficient, it was moved to a larger building on Woodward Avenue, which had been designed by Paul Cret . William Valentiner , an art historian from Berlin who was director of the museum from 1924 to 1945 , had a major influence on the development of the collection . Thanks to his good contacts in Europe and the support of numerous patrons, he was able to expand the collection considerably and secure important works for it. During his tenure, Diego Rivera was commissioned to paint the inner courtyard. He also acquired a self-portrait by Vincent van Gogh, the painter's first work for an American museum.
Two new wings were erected in the 1960s and 1970s. 1999 began the renovation and expansion of the Detroit Institute of Arts, which was completed in 2007. In 2000, the Detroit Institute of Arts established the General Motors Center for African American Art to bolster this area of the collection.
In December 2010, the Detroit Institute of Arts auctioned the Culbertson Guidon to finance the expansion of the collection. The stander , 69 × 83 cm in size, was led by General Custer's cavalry unit in the Battle of Little Bighorn against the Lakota and Cheyenne, which they lost on June 25, 1876 . The auction was carried out by Sotheby’s . The estimated price of two to five million dollars was barely reached with proceeds of 1.9 million (with an additional charge of 2.2 million) dollars. The flag was purchased in 1890 for $ 54, but had not been in line with the collection's orientation for a long time and was not exhibited.
In August 2012, citizens of the three counties of the metropolitan area voted that owners of land with a market value of $ 200,000 and more should pay an additional $ 20 annually for the next ten years. The income from this tax should benefit the museum. Citizens of Wayne County, Michigan , Oakland County, and Macomb Counties , which so far have 80% of visitors, will receive free admission to the museum in return.
After the city of Detroit filed for bankruptcy in July 2013 , state-appointed administrator Kevyn Orr had the DIA collection valued by Christie's auction house . According to the estimate, at best the collection could add $ 900 million to lower Detroit's $ 20 billion debt. However, this approach met with great national and international criticism. Still, Orr pursued the preparations. In January 2014, nine foundations, including the Ford Foundation , agreed to raise $ 330 million to save the museum. These are to be increased to 500 million by further private sponsors. The museum is to be converted into a non-profit organization and thus protected from access by the insolvency administrator. In return, the foundations secure part of the city's underfunded pension fund, as Alberto Ibargüen of the Knight Foundation announced.
During 2014, the total raised by foundations, donors, and state funds increased to $ 816 million. A vast majority of the city’s public service pensioners waived 4.5% of their entitlements. Thanks to these services, the museum was able to be separated from the bankruptcy estate and transferred to an independent foundation. As of November 7, 2014, buildings and collections are no longer subject to foreclosure. Due to the efforts of the foundations and other donors, the plan to build up a foundation fund of the DAI had to be postponed. The plans provide for USD 400 million in the medium term, but there was no specific schedule at the time of the outsourcing from the city budget.
building
The building was constructed in the neoclassical style with white marble between 1923 and 1927. The south wing was added in 1966 and the north wing in 1971. Its architect was Gunnar Birkerts . The building is 658,000 square meters and includes more than 100 galleries in which the works of art are presented. The building also has two lecture halls with seating for 1150 and 380 people, and an art library. The museum has its own laboratory for the restoration work.
Across from the Detroit Institute of Arts is the Detroit Public Library , also made of white marble and built in a neoclassical style.
collection
The collection includes American , European, Modern and Contemporary Art . The museum also has a graphic collection . Also, African , Asian , Native American , Oceanic and Islamic Art and antiques belonging to the collection of the DIA. The central work of the collection is Diego Rivera's mural Detroit Industry , which adorns the central courtyard. It extends over 434 square meters and is considered one of his most significant mural projects. William Randolph Hearst's weapons collection is displayed in the central entrance hall .

A focus of the collection is on American painting, sculpture and the applied arts since the 18th century. These holdings are among the most important in the United States. Artists represented include John James Audubon , George Bellows , George Caleb Bingham , Alexander Calder , Mary Cassatt , Frederic Edwin Church , Thomas Cole , John Singleton Copley , Leon Dabo , Thomas Wilmer Dewing , Thomas Eakins , Childe Hassam , Robert Henri , Winslow Homer , George Inness , Georgia O'Keeffe , Charles Willson Peale , Rembrandt Peale , Frederic Remington , Augustus Saint-Gaudens , John Singer Sargent , John French Sloan , Marylyn Dintenfass , Gilbert Stuart , Yves Tanguy , Henry Ossawa Tanner , Louis Comfort Tiffany , Andy Warhol , William T. Williams , Andrew Wyeth , and James McNeill Whistler .
The collection of European art includes works from the 15th century to the counter-wall. Among other things, the Detroit Institute of Arts owns a Madonna and Child by Giovanni Bellini , the wedding dance by Pieter Brueghel the Elder and St. Jerome in his study by Jan van Eyck . The museum also has works by Benozzo Gozzoli , Albrecht Dürer , Lucas Cranach the Elder and Hans Holbein the Younger . Representatives of the Baroque include Gerard ter Borch , Diego Velázquez , Peter Paul Rubens , and Rembrandt van Rijn . Representatives of French art at the end of the 18th and 19th centuries include Jean-Baptiste Carpeaux and François Rude . French modernism is represented by Claude Monet , Odilon Redon , Eugène Boudin , Edgar Degas , Paul Cézanne , Eugène Delacroix and Auguste Rodin , among others . A cast of the Thinker von Rodins is placed in front of the main portal of the museum building. A Self-Portrait by Vincent van Gogh and The Window by Henri Matisse were acquired in 1922 and were the first works by these two artists in American museums. Works by German expressionists such as Heinrich Campendonk , Franz Marc , Karl Schmidt-Rottluff , Max Beckmann , Karl Hofer , Emil Nolde , Lovis Corinth , Ernst Barlach , Wilhelm Lehmbruck , Erich Heckel , Ernst Ludwig Kirchner , Paula Modersohn-Becker , and Max Pechstein were acquired early from the Detroit Institute of Arts. Other expressionists such as Oskar Kokoschka , Wassily Kandinsky , Chaim Soutine and Edvard Munch are also represented in the collection.
The collection of antiquities includes a dragon relief from the Ishtar Gate in Babylon and an Egyptian relief of a grieving woman. A collection of various puppets of hand puppets , shadow puppets and marionettes is also on display.
To collection also includes the Gothic Chapel , a Gothic chapel in 1927 Herbéviller in France in the museum translocated was.
Lucas Cranach the Elder , St. Christopher , 1518-20
Pieter Brueghel the Elder , The Wedding Dance , 1566
Edgar Degas , violinist and young woman , 1870–72
Paul Cézanne , Bathers , 1879
Vincent van Gogh , self-portrait , 1887
Auguste Rodin , The Thinker , 1880–82
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Information on the history of the museum at dia.org, accessed on January 17, 2014. ( Memento of the original from June 27, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Lisa Zeitz, "Culbertson Guidon" - From the last Indian uprising, on faz.net, July 14, 2010, accessed September 3, 2011.
- ↑ Detroit Free Press, Custer's last flag sells for less than expected at auction, on usatoday.com, December 20, 2010, accessed January 15, 2014.
- ↑ Citizens of Detroit Help Their Institute of Arts, on faz.net, August 16, 2012, accessed August 18, 2012.
- ↑ Dirk Hautkapp, Nine Foundations Want to Save Detroit's Museum, on derwesten.de, January 15, 2014, accessed on January 15, 2014.
- ↑ freep: How Detroit was Reborn , November 9, 2014
- ↑ New York Times: 'Grand Bargain' Saves the Detroit Institute of Arts , Nov. 7, 2014
Coordinates: 42 ° 21 '33.5 " N , 83 ° 3' 53.3" W.











