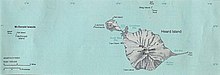
Heard and McDonald Islands
|
|||
| Basic data | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Country: | Australia | ||
| Administration: | Australian Antarctic Division of the Department of the Environment and Heritage | ||
| Research station: | ANARE, Atlas Cove (1947–1955) | ||
| Residents: | uninhabited | ||
| Geographical location: | 53 ° 6 ′ S , 73 ° 32 ′ E | ||
| Time zone | UTC + 5 | ||
| Surface: | 372 km² | ||
| highest elevation: | Mawson Peak ( 2745 m ) | ||
| Discovery: | Heard: November 25, 1853 by John Heard McDonald Islands: January 4, 1854 by William McDonald |
||
| Internet TLD | .Hm | ||
Heard and the McDonald Islands ( English Heard Island and McDonald Islands ) are an Australian outlying area in the southern Indian Ocean . The area has the official name Territory of Heard Island and McDonald Islands (abbreviation: HIMI , German: Territorium Heard and McDonald Islands ).
The island region originally claimed by the United Kingdom was given to Australia in 1947 . The islands are managed by the Australian Antarctic Division in the Department of Sustainability, Environment, Water, Population and Communities in Canberra .
geography
The territory is 1668 km north of East Antarctica , 3843 km southwest of Western Australia and 4205 km southeast of South Africa . The closest land is the Kerguelen , 445 km to the northwest.
It consists of the island of Heard with the secondary island of Shag and the McDonald Islands 43 km west of it, a few small skerries and the sea area around the islands. The area, including the territorial waters, has a total area of about 6600 km², of which only about 370 km² are land areas. Heard Island has an area of 368 km², the McDonald Islands are only about 2.5 km².
On the island of Heard there is the active volcano Big Ben , the highest point of which, Mawson Peak , is also the highest point in Australia at 2745 m (if you don't include Mount McClintock in the Antarctic area claimed by Australia). It is 517 m higher than Mount Kosciuszko on mainland Australia.
Heard and McDonald Islands are made up of volcanic rock and limestone . You are on the Kerguelen Plateau , an underwater mountain range that rises 3700 m above the sea floor. Apart from the Kerguelen , the islands are the only places where the Kerguelen Plateau protrudes above the surface of the water.
environment
The archipelago is a nature reserve where seals and birds live. Heard is home to one of seven king penguin breeding grounds .
There are no alien species on the islands, a case that is almost unique in the world. Australia allows a maximum of 400 visitors per year and a maximum of 60 at a time. In 1997, the archipelago was UNESCO for World Heritage and 2002 by Australia to a marine reserve , to Heard Iceland and McDonald Islands Marine Reserve declared.
geology
Heard Island has an east-west extension of 40 km and a north-south extension of 26 km. The topography is dominated by Mawson Peak. The Big Ben has a diameter of 21 km, the mountain has been climbed several times.
Until 1992, Big Ben was the only active volcano in Australia. Since that year, after a period of rest estimated at 35,000 to 100,000 years, there has been a chain of eruptions on the neighboring island of McDonald, the area of which has since more than doubled due to the magma flows.
Heard Island is both karstic and volcanic. About 70% of the island's surface is covered with ice. There are fourteen glaciers on Big Ben that are up to 7 km long and 10 km² in size. The individual glaciers (listed clockwise from north) are: Downes , Ealey , Compton , Brown , Stephenson , Winston , Fiftyone , Deacock , Gotley , Lied , Abbotsmith , Allison , Schmidt and Baudissin . The development of the glaciers is considered an indicator of global warming; In 1947 they reached the sea, today they end several hundred meters inland.
history

Drawing by HW Elliott based on a presentation by Capt. HC Chester, undated (before 1900)

Drawing by HW Elliott based on Capt. HC Chester, undated (before 1900)
discovery
The American captain John Heard , en route with his ship Oriental , sighted the island on November 25, 1853 during a voyage from Boston to Melbourne . He officially reported the discovery on December 24th. A little later, on January 4, 1854, Captain William McDonald discovered McDonald Island near Heard Island on board the ship Samarang . Isolated reports of earlier discoveries are dubious.
The first landing on Heard took place in March 1855 by crew members of the ship Corinthian under Captain Erasmus Darwin Rogers. Between 1855 and 1880, some American sealers spent a year or more on the island. In 1880 the seal population was almost completely wiped out and the seal hunters left the island.
exploration
In 1874 scientists from the HMS Challenger collected geological and botanical material. Between 1900 and 1929 there were some unsuccessful attempts at whaling. In 1902 Erich von Drygalski , head of the First German Antarctic Expedition , visited the island with the ship Gauß and for the first time compiled comprehensive scientific material on the island's geology , flora and fauna .
In 1929 the French geologist Edgar Aubert de la Rüe was doing some studies when he came to the island with a whaler. That same year, Sir Douglas Mawson , head of the British Australian and New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE), visited Heard Island for a week while en route to Antarctica . A shelter was built to serve as a shelter for shipwrecked people. Remnants of the hut still stand today.
The first of the Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions (ANARE) built a station at Atlas Cove on the western end of the island in December 1947. A total of between 10 and 15 employees were on the permanently manned station, which was closed again in 1955.
Research teams from the United States were also stationed at Atlas Cove for a year, where they built their own cabins. Other huts were built in 1970–1971 by French and Australian researchers. The last ANARE expedition stayed a year and used a base at Spit Bay.
Others
Although the islands are uninhabited, they have their own top-level domain with .hm .
Web links
- Heard Island & McDonald Islands. Official website. Australian Government - Department of the Environment and Energy - Australian Antarctic Division (English).
- The South Atlantic & Subantarctic Islands ( Memento from October 26, 2012 in the Internet Archive ).
- CIA World Factbook: Heard Island and McDonald Islands (English).
- Entry on the website of the UNESCO World Heritage Center ( English and French ).
Individual evidence
- ↑ Heard and the McDonald Islands. (PDF; 1.3 MB) In: Country directory for official use in the Federal Republic of Germany. Federal Foreign Office , April 30, 2019, p. 46 , accessed on June 13, 2019 .
- ↑ Heard and McDonald Islands. Outstanding Universal Value - Brief Synthesis. In: World Heritage List . UNESCO , accessed on May 15, 2017 .
- ↑ McDonald Islands. In: Volcano World. Oregon State University , accessed May 15, 2017 .
- ^ Patrick G. Quilty: Origin and evolution of the sub-Antarctic islands: the foundation . In: Papers and Proceedings of the Royal Society of Tasmania . tape 141 , no. 1 . Royal Society of Tasmania, 2007, ISSN 0080-4703 , Heard Island and the McDonald Islands, p. 53–54 (English, online as eprint from the University of Tasmania [PDF; 1,3 MB ]). online] as [[Eprint]] of the [[University of Tasmania] ( memento of the original from March 5, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link has been inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Global Volcanism Program, 2002. Report on McDonald Islands (Australia) . In: Richard Wunderman (Ed.): Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network . tape 27 , no. 12 . Smithsonian Institution , December 2002, doi : 10.5479 / si.GVP.BGVN200212-234011 (English).
- ^ Glaciology. In: Heard Island & McDonald Islands. Official website. Australian Government - Department of the Environment and Energy - Australian Antarctic Division , accessed November 4, 2016.
- ↑ Australian research expeditions. In: Heard Island & McDonald Islands. Official website. Australian Government - Department of the Environment and Energy - Australian Antarctic Division , accessed November 4, 2016.