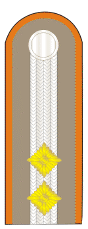
Ensign

The Oberfähnrich is a military rank of the Bundeswehr and former German armed forces .
armed forces
| Ensign | |
|---|---|
 
|
|
| Rank group | NCOs with portepee |
| NATO rank code | OF-D |
| Rank Army / Air Force | Ensign |
| Marine rank | Senior ensign at sea |
| Abbreviation (in lists) | OFähnr (OFR) |
| Grade | A 8Z according to BBesO |
The rank of Oberfähnrich is determined by the Federal President with the order of the Federal President on the rank designations and the uniform of the soldiers on the basis of the Soldiers Act .
Authority to command and positions
In the Federal Armed Forces, the Oberfähnrich is a sergeant grade , which, according to the Central Service Regulations (ZDv) A-1420/24 "Ranks and Rank Groups", belongs to the rank group of NCOs with portepee . Because they belong to the rank group of NCOs with portepee, senior middlemen can issue orders within the limits set there to soldiers of the rank groups of teams and NCOs without portepee on the basis of Section 4 ("Superiors relationship based on rank") of the Superiors Ordinance.
Senior middlemen are officer candidates and are usually in their studies while they hold this rank . Officer candidates in the career paths of officers in the military service usually complete a two-year training course at a technical college leading to a state-certified technician , state-certified business economist or state-certified educator . Some senior middlemen are at an officers' school for officer training . In the "ordinary" troops, these senior middlemen are usually only used in the context of troop internships . Oberfähnriche are then used, for example, as platoon leaders , company troop leaders , deputy platoon leaders and in staffs . On the basis of the listed and similar positions , senior middlemen can issue orders to all officially or professionally subordinate soldiers in the cases listed in the Supervisor Ordinance.
Appointment and remuneration
The decisive legal basis for the appointment as senior ensign is made by the Soldiers' Career Ordinance (SLV) and in addition the Central Service Regulations (ZDv) 20/7. A prerequisite for appointment to the rank of senior midshipman is belonging to one of the officers' careers . To rank Oberfähnrich to regular soldiers and ordered reservists are appointed. Reserve officer candidates do not have to go through the rank of senior ensign and therefore mostly skip it. The employment with the rank Oberfähnrich is possible if the applicant has usable knowledge in the application. After a change from sergeant major to a career as an officer in the military technical service , the previous rank is transferred to the rank of senior ensign. Most of the senior midshipmen had previously served in the rank of ensign . Officer candidates can be promoted to senior midshipman in most careers 30 months (24 months in the careers of officers in the military service) after starting this career. Any service time in a previous career can be taken into account (but often only partially and to a limited extent). When a sergeant major changes to the career path of officers in the technical military service, the appointment as senior ensign does not take place before he has had one year of service in the rank of sergeant major.
Upper cadets after the Bundesbesoldungsgesetz order (BBesO) with A8M A ( with duty allowance ) remunerated .
Rank badge
The insignia for upper cadets shows the service uniform and society suit a head angle with the tip pointing upwards as a shoulder badge with silver shoulder flap edging in type of piping of the shoulder straps of the officers. The background to this is that, as a special privilege, senior middlemen are allowed to wear the officer's uniforms. The rank badges in the other types of suits are the same as the rank badges for sergeant major : a corner of the head with the point upwards and a surrounding closed braid as a shoulder badge . To distinguish them from the rank badges of the sergeant major, upper middlemen wear these rank badges, like other officer candidates , a silver-colored cord made of woven metal as a pull-over loop on all epaulets.
history
The rank of Oberfähnrich was created with the sixth order of the Federal President on the rank designations and the uniform of soldiers from May 5, 1966.
Equivalent, subordinate and superior ranks
Only army and air force uniform bearers hold the rank of senior ensign . Officer candidates of the same rank wearing naval uniforms hold the rank of senior midshipman at sea . Soldiers who do cadets are to lead the ranking same ranks Sergeant (for Army and Air Force Uniform) or hauptbootsmann (for Navy Uniform). The privileges that senior middlemen already wear officers 'uniforms and, as a rule, already have access to the officers' mess, do not result in any formal differences in rank from the sergeant major. In the armed forces of NATO , the Sergeant Major is equivalent to all ranks with the NATO rank code OR-7, while the Oberfähnrich is designated in a separate category with the NATO rank code OF-D (Officer-designate, officer candidate).
In the sergeant's careers , the main sergeant according to No. 127 f. ZDv 20/7 classified between the lower-ranking Oberfeldwebel or Oberbootsmann and the higher-ranking staff sergeant or staff boatman (first rank designation for Army and Air Force uniform wearers; second rank designation for naval uniforms). For the purposes of the presidential order on rank designation and uniform of soldiers applies to the classification of the top cadets same, even if top cadets after in the category provided for officers transport order is usually above the rank Ensign led then in the rank lieutenant transported .
|
|
||
| Lower rank | Higher rank | |
|
Oberfeldwebel Oberbootsmann |
Hauptfeldwebel Hauptbootsmann Oberfähnrich Oberfähnrich zur See |
Sergeant-in- Chief Officer in command |
|
Rank group : Teams-NCOs-NCO-NCOs-Lieutenant-Captains-Staff officers-Generals |
||
Other forces
According to the NATO rank code , the following ranks of other armed forces are comparable with the German rank Oberfähnrich:
-
 France → French aspirant
France → French aspirant
-
 Italy → Italian Allievo Ufficiale II
Italy → Italian Allievo Ufficiale II
-
 Austria → Ensign
Austria → Ensign
-
 Russia → Russian Курсант / cadet
Russia → Russian Курсант / cadet
-
 United Kingdom → English Officer designate
United Kingdom → English Officer designate
National Peoples Army
The senior ensign was the third highest rank in the rank group of ensigns in the National People's Army . The ensign careers formed an independent career group that was located between the NCOs and the officers. So it was not about officer candidates, as the name suggests if you know the ranks of the Bundeswehr and Wehrmacht. Officer candidates were referred to as officer students in the National People's Army and had different ranks .
The soldiers of the group of ensigns of the National People's Army were instead mainly recruited from senior, highly qualified NCOs with portepee or applicants with a higher school or university degree, who were appointed ensigns directly after completing a two-year training course . This training was carried out within the armed forces , for example for the NVA air forces at the MTS of the LSK / LV . Previously serving as a non-commissioned officer was desirable, but rather rare towards the end of the 1980s.
| Rank | ||
| lower: Ensign |
Ensign |
higher: Ensign in staff |
Reichswehr, Wehrmacht and Waffen-SS
Fahnenjunker-Oberfeldwebel
SS-Standartenoberjunker
In 1920, the Reichswehr first introduced the ranks for officer candidates (OA), Oberfähnrich (Army) and Oberfähnrich zur See (Navy), which were on an equal footing with the Sergeant Major and Chief Boatswain .
In the German Wehrmacht ( Army and Air Force ), NCOs who wanted to pursue an officer career were given the designation Fahnenjunker (short: Fhj in Lists Fj ) in front of their rank:
- Fahnenjunker NCO (Fhj-Uffz, Fj-U),
- Fahnenjunker-Unterfeldwebel (Fhj-UFw, Fj-UF),
- Fahnenjunker Sergeant (Fhj-Fw, Fj-F),
- Fahnenjunker-Oberfeldwebel (Fhj-OFw, Fj-OF) and
- Fahnenjunker staff sergeant (Fhj-StFw, Fj-SF).
Equivalent to the Fahnenjunker-Oberfeldwebel were Oberfähnrich zur See and SS-Standartenoberjunker (Waffeb-SS). In the army and air force , promotions to the rank of Fahnenjunker-Oberfeldwebel were suspended from 1940 to 1943 (promotions to senior ensign at sea until 1944). I.
Remarks
- ↑ Left: Rank badge on the epaulette of the jacket of the service suit for army uniform wearers of the Army Aviation Troops . Right: Rank badge on the shoulder flap of the jacket of the service suit for Air Force uniform wearers.
- ↑ Army and air force uniform wearers of this rank group are unofficially summarized as sergeant ranks. Non-commissioned officers with portepee who hold appropriate ranks for naval uniform bearers are also unofficially referred to as boatmen .
- ↑ According to the Soldier Career Ordinance, for example, potential officer candidates for the medical service who, in addition to other requirements , have successfully passed the first section of a preliminary medical examination .
- ↑ The promotion to senior ensign takes place for the officer candidates in the career paths of the officers of the troop service when recruited with the lowest rank as a rule after 30 months of service.
- ↑ ZDv 20/7 on the basis of Section 44 of the Soldiers ' Career Ordinance ( TitelErg = Ordinance on the Careers of Soldiers (Soldiers' Career Ordinance - SLV) . March 19, 2002, Section 44 ( online [accessed on March 25, 2014] Neugefasst by Bek August 19, 2011 I 1813. Last amended by Art. 2 Paragraph 5 G of April 8, 2013 I 730). )
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Hartmut Bagger , Command Staff of the Armed Forces I 3, Federal Ministry of Defense (Ed.): ZDv 37/10. Suit regulations for soldiers in the Bundeswehr . July 1996. Reprint from October 2008. Bonn July 16, 2008, 4 labels, p. 539 ( digital version (PDF; 3.5 MB) - reprint October 2008 replaces first edition from July 1996). Digitized version ( memento of the original from September 19, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ The Federal Minister of Defense (ed.): ZDv 14/5. Soldiers Act . DSK AV110100174, change status July 17, 2008. Bonn August 21, 1978, rank designations in the Bundeswehr, p. B 185 (not to be confused with the Law on the Legal Status of Soldiers (Soldiers Law) ).
- ↑ a b c Agreed English texts. STANAG 2116 . NATO standardization agreement (STANAG) . NATO codes for grades of military personnel. 5th edition. 1992 ( NATO Rank Codes - 1992 [accessed March 25, 2014] English).
- ↑ a b c d e f g The Federal President (Ed.): Order of the Federal President on the rank designations and the uniform of the soldiers . BPresUnifAnO. July 14, 1978 ( PDF - Order of the Federal President on the rank designations and uniforms of soldiers from July 14, 1978 ( Federal Law Gazette I p. 1067 ), last amended by Article 1 of the order of May 31, 1996 ( Federal Law Gazette I p. 746 ) has been changed).
- ^ Federal Minister of Defense ; Command Staff of the Armed Forces IV 1 (Ed.): Abbreviations for use in the Bundeswehr - German Abbreviations - ZDv 64/10 . Bonn January 19, 1979 ( PDF - as of September 17, 1999).
- ↑ a b Appendix I (to § 20, paragraph 2, sentence 1) Bundesbesoldungsgesetz orders of A and B . ( Online [accessed on March 25, 2014] Federal salary regulations (BBesO) only apply to professional and temporary soldiers and are an annex to the Federal Salary Act (BBesG)).
- ↑ The Federal Minister of Defense (ed.): Law on the legal status of soldiers (Soldiers Act - SG) . Bonn March 19, 1956, § 4 Paragraph 3 (2) - ( PDF [accessed on March 25, 2014] Revised by notice of May 30, 2005 I 1482. Last amended by Art. 1 G of April 8 2013 I 730).
- ↑ Federal Minister of Defense (Ed.): Ordinance on the regulation of the military superior relationship (Superior Ordinance - VorgV) . June 4, 1956, § 4 ( online [accessed on March 25, 2014] Last amended by Art. 1 No. 2 V of October 7, 1981 I 1129).
- ↑ The Federal Minister of Defense (ed.): ZDv 14/5. Soldiers Act . DSK AV110100174, amendment status July 17, 2008. Bonn August 21, 1978, The Superiors Ordinance, p. A 12 1 (not to be confused with the Ordinance on the Regulation of Military Superiors (Superiors Ordinance - VorgV) ).
- ↑ Federal Minister of Defense (Ed.): Ordinance on the regulation of the military superior relationship (Superior Ordinance - VorgV) . June 4, 1956 ( online [accessed on March 25, 2014] last amended by Art. 1 No. 2 V of October 7, 1981 I 1129).
- ^ Ordinance on the career paths of soldiers (Soldiers' Career Ordinance - SLV) . March 19, 2002 ( online [accessed on March 25, 2014] revised by notice of August 19, 2011 I 1813. Last amended by Art. 2 Par. 5 G of April 8, 2013 I 730).
- ↑ Note also: Annex (to § 3). Allocation of the career paths of the soldiers to the career groups of the men and women, the NCOs and the officers
- ↑ a b The Federal Minister of Defense ; Personnel, Social and Central Affairs Department (Ed.): ZDv 20/7. Provisions for the transport and for the recruitment, acceptance and admission of soldiers . Bonn March 27, 2002, Art. 635 ( PDF ( memento of October 26, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) [accessed on March 26, 2014] DSK AP210100187, reprint January 2008). Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ^ Federal President Heinrich Lübke et al .: Sixth order of the Federal President on the rank designations and the uniform of soldiers from May 5, 1966 . In: Federal Law Gazette Part 1 . tape 1966 , 20 of May 13, 1966. Bonn May 5, 1966, p. 325 ff . ( Online [PDF; accessed May 12, 2015]).
- ↑ a b The equivalent, higher and lower ranks are given in accordance with ZDv 14/5 B 185, cf. The Federal Minister of Defense (ed.): ZDv 14/5. Soldiers Act . DSK AV110100174, change status July 17, 2008. Bonn August 21, 1978, rank designations in the Bundeswehr, p. B 185 (Not to be confused with the Law on the Legal Status of Soldiers (Soldiers Act) . The order of the ranks shown in the info box does not necessarily correspond to one of the regular rank sequences provided for in the Soldiers' Career Ordinance , nor does it necessarily correspond to the rank hierarchy described in the Superiors Ordinance a managerial relationship ).