Upper Hesse (region)
Upper Hesse is a landscape in central Hesse and was the name of various historical administrative units.
geography
Upper Hesse is located in the state of Hesse . It is limited in the south by Wetterau and the Rhine-Main area , in the east by the Vogelsberg and the Knüllgebirge , in the north by the Kellerwald and in the west by the Gladenbacher Bergland . The landscape is characterized by low mountain ranges. Today Upper Hesse includes the Lahn-Dill-Bergland and Hoher Vogelsberg nature parks and the urban regions around Marburg and Gießen .
history
Historically, the term Upper Hesse was used several times to denote the political subdivisions of the Hessian states.
Middle Ages and early modern times
In the Middle Ages, the "Upper Principality of Hessen" referred to the southern part of the Landgraviate of Hesse , which was separated from the "Lower Principality of Hessen" around Kassel and Gudensberg until 1450 by the County of Ziegenhain . The names Upper Hesse and Lower Hesse were later derived from this.
After the death of Landgrave Philip I , Hesse was divided among his four sons. The Landgraviate Hessen-Marburg was created in the area of Upper Hesse . After the childless death of Marburg Landgrave Ludwig IV in 1604, Hesse-Marburg was divided between the Landgraviate of Hesse-Kassel and the Landgraviate of Hesse-Darmstadt and was nevertheless fiercely contested for more than four decades between the two Landgraves.
Only with the Peace of Westphalia was stability achieved for about 150 years. Hessen-Darmstadt received the southern area of the former Landgraviate Hessen-Marburg with Giessen as its center. The so-called Hessian hinterland around Gladenbach, Biedenkopf and Battenberg also came to Hessen-Darmstadt. Hessen-Kassel received the northern part of Upper Hesse with Marburg .
1815-1945
Hessen-Kassel
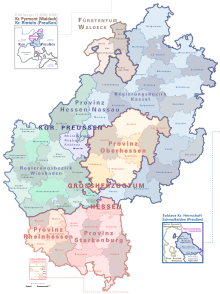
The Electorate of Hesse led in 1821 immediately after the change of government Elector Wilhelm I to Elector Wilhelm II. With the organizational edict Wilhelm II. Comprehensive reforms in the judiciary and administration through. The Hessian province of Upper Hesse was also created as one of four provinces . The provincial capital and largest city in the province was Marburg .
In the course of the March Revolution in 1848, the districts were replaced by districts and the provinces dissolved. Under Elector Friedrich Wilhelm this was reversed on September 15, 1851 and the administrative structure from 1821 was restored.
The Kurhessische province of Upper Hesse existed until 1868 and was then dissolved as a result of the annexation by Prussia . In the Kingdom of Prussia, the province of Upper Hesse became part of the administrative district of Kassel in the province of Hesse-Nassau .
Hessen-Darmstadt
The province of Upper Hesse (until 1816: Principality of Upper Hesse ) was a province of the Landgraviate of Hesse-Darmstadt and its successors, the Grand Duchy of Hesse and the People's State of Hesse . It existed from 1803 to 1937.
aftermath
Territorial whereabouts
Today's regional authorities in the area of the former province are the Hessian districts of Gießen , Vogelsberg and Wetterau , which almost exactly map the former Upper Hesse territory. At the regional level there has been the Gießen administrative district since 1981 , which resumed the tradition of Gießen as the seat of the state administration. In contrast to the former province , there is no area of the administrative district of the Wetterau , but it includes the former Kurhessische Marburg , the former Rhenish Wetzlar and the former Nassau Limburg .
Central Hesse
With the creation of Greater Hesse in the US occupation zone in 1945, the borders between the two Hessian states that emerged from the division in 1567 were abolished. For the area of the former Upper Hesse provinces - in relation to the newly constituted state of Hesse - the term Central Hesse was formed . The term "Regional Council Central Hesse" is also used colloquially for the Gießen Regional Council. The term "Upper Hesse" is still used today mainly in the historical context and to denote the landscape northeast of the Rhine-Main area .
Further use
The term is used continuously in the institutions Oberhessisches Museum and Oberhessischer Geschichtsverein , Propstei Oberhessen , Oberhessischer Gebirgsverein and Jägerervereinigung Oberhessen . The newspaper publisher Oberhessische Presse and the company Oberhessisches Backhaus Horst, founded in 1859 (company logo) also bear witness to the tradition and regionality. Furthermore, two slogans refer to the traditional name of the region: Schlammbeiser Pils. A beer for Gießen - handcrafted in Upper Hesse and Licher Hessenquell Landbier. Brewed according to a recipe from Upper Hesse . In the area of transport, the Verkehrsgesellschaft Oberhessen (OVG) carries on the traditional name. Some stations along the route of the Upper Hessian Railway , today Vogelsberg Railway , have the addition (Oberhess) : Alsfeld , Assenheim, Bleichenbach, Büdingen, Ehringsdorf, Grünberg , Langsdorf and Lich .
Web links
- Literature about Upper Hesse in the Hessian Bibliography
- Internet presence of today's "Upper Hesse region" - according to the EAFRD funding program, the eastern part of the Wetterau district
- Erwin Knauß: Upper Hesse - landscape or province? . Upper Hessian History Association Gießen e. V.