Quaranja virus
| Quaranja virus | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Cygnet River Virus |
||||||||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Taxonomic characteristics | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||||||||
| Quaranja virus | ||||||||||||||||||
| Left | ||||||||||||||||||
|
Quaranjavirus (obsolete Quarjavirus ) is a genus of enveloped RNA - virus in the virus family Orthomyxoviridae . The genome is single-stranded segmented RNA of negative polarity . There are generally six genome segments. The type species is the Quaranfil virus ( scientifically Quaranfil quaranjavirus ), as well as u. a. the kind Johnston Atoll Virus ( scientifically Johnston Atoll quaranjavirus ). Other proposed members are the Cygnet River Virus , Lake Chad Virus , Wellfleet Bay Virus and Tyulek Virus. Quaranja viruses mainly affect arthropods and birds . However,in March 2015, Quaranfil quaranjavirus was found to be the only member of the genus that has been shown to (also) infect humans. The Quaranfil and Johnston Atoll viruses aretransmitted between vertebratesby ticks and are similar to members of the genus Thogotovirus from the same virus family.
Research history
The Quaranfil virus was first isolated from humans in Egypt in 1953. The Johnston Atoll Virus and Lake Chad Virus were first isolated from birds in 1964 and 1969, respectively. Based on the appearance of the virus particles ( virions ) under the electron microscope, HG Zeller and colleagues suggested in 1989 that they should be classified as arenaviruses .
However, this was not accepted by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). In 2009, Rachel Presti and colleagues proposed, based on sequence data and the structure of the virus particles, that the three virus species should be classified as a new genus of orthomyxoviruses originally named Quarjavirus . As a result, other candidates were proposed as members of the genre. In 2012 the genus was officially proposed to ICTV in 2012 under the name Quaranjavirus and formally confirmed by this body in 2013.
etymology
The Quaranfil virus is named after Quaranfil ( Arabic قَرَنْفيل, in German "Carnation"), a village near Cairo ( Egypt ), from where the virus was isolated for the first time. The Johnston Atoll Virus is named after the Johnston Atoll in the Pacific , also from where the virus was first isolated. The generic name combines the word parts "Quaran" with the initials "ja" for Johnston Atoll.
construction
The virus particles ( virions ) of Quaranja virus are enveloped and spherical (spherical), egg-shaped (ovoid) or variable in shape and have a diameter in the range of 80-120 nm . The virion contains about ten ribosome-like granules , a feature known from the arenaviruses .
The single stranded RNA genome is linear and segmented (multipartite), generally with six segments from 0.9 to 2.4 kb and a total size of about 11.5 kb. The Wellfleet Bay virus has a seventh segment of 519 nucleotides . The genome codes for six or - in the case of the Wellfleet Bay virus - seven proteins . The PA, PB1 and PB2 subunits of the trimeric RNA polymerase - enzyme to be coded, as in other orthomyxoviruses by the three largest segments (1-3). Segment 5 codes for envelope glycoprotein (GP). Segments 4 and 6 code proteins with an unknown function, provisionally assigned to the viral nucleoprotein or the matrix protein . Wellfleet Bay Virus segment 7 encodes an additional protein of unknown function.
The Quaranjavirus glycoprotein has no resemblance to the influenza virus -Glykoproteinen ( hemagglutinin and neuraminidase ) to, instead, it has some similarities with the gp64 glycoprotein of baculoviruses to infect the insects, as well as the glycoprotein of Thogotoviren , one of tick transmitted genus Orthomyxoviruses.
Propagation cycle
The replication cycle of the Quaranfil virus takes about 24 to 36 hours, which is comparable to the Thogotoviruses, but slower than the Influenza viruses.
Host spectrum and diseases caused
Quaranja viruses infect both arthropods and vertebrates . The most common arthropod hosts are soft-bodied species of leather ticks (family Argasidae) (). Most members of the Quaranjaviridae cannot infect mosquitoes in the laboratory . In 2015, however, several new members of the genus were proposed based on RNA sequences from mosquitoes, flies , as well as other insects and the spider Neoscona (true orb web spiders or Araneidae ).
The most common vertebrate hosts are waterfowl that nest in colonies, including gannets , terns, and herons . The Cygnet River virus and the Wellfleet Bay virus are a frequently fatal disease in farmed and wild duck species have been associated with symptoms such as diarrhea ( diarrhea ) and lethargy . Most of the genus members tested can also infect mice under laboratory conditions ; they cause serious illnesses that are often fatal. The Quaranfil virus is the only member of the genus so far that has been shown to infect humans. The infection appears to be generally asymptomatic (with no symptoms of the disease) but has occasionally been associated with a mild fever.
Systematics
Internal system
As of March 2019, there are two species approved by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV):
- Genus Quaranjavirus
- Species: Johnston Atoll Virus ( Johnston Atoll quaranjavirus , JAV)
- Species: Quaranfil virus ( Quaranfil quaranjavirus , QRFV, type species)
Other suggested members of the family are the types or strains ( english strains ):
- Species: Cygnet River Virus ( Cygnet River virus , CyRV)
- Species: Lake Chad virus (aka Lake Chad virus , Lake Chad virus , LKCV)
- Species: Wellfleet Bay Virus ( Wellfleet Bay virus , WFBV)
- Tyulek virus ( Tyulek virus , alias Tjulok virus, TLKV, Russian Тюлёк вирус )
Over a dozen other species or strains most closely related to Johnston Atoll Virus have been identified using RNA data from a range of arthropods. The NCBI knows u. a. the following other candidates:
- Species: Jingshan Fly Virus 1 (JsFV-1)
- Species: Jiujie Fly Virus
- Species: Longchuang virus
- Species: Sanxia Water Strider Virus 3 (SxWSV-3)
- Species: Shayang Spider Virus 3 (SYSV-3)
- Species: Shuangao Insect Virus 4 (ShiV-4)
- Species: Wuhan Louse Fly Virus 3 (WhLFV-3)
- Species: Wuhan Louse Fly Virus 4 (WhLFV-4)
- Species: Wuhan Mosquito Virus 3 (WHMV-3)
- Species: Wuhan Mosquito Virus 4 (WHMV-4)
- Species: Wuhan Mosquito Virus 5 (WHMV-5)
- Species: Wuhan Mosquito Virus 6 (WHMV-6)
- Species: Wuhan Mosquito Virus 7 (WHMV-7)
- Species: Wuhan Mothfly Virus
- Species: Zambezi tick virus 1 (ZaTV-1)
External system
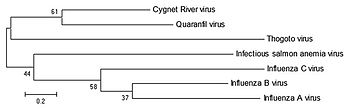
The following graphic shows the position of the genus Quaranjavirus within the Ortomyxoviridae :

Detailed descriptions
Some data are summarized in the following table:
| Species / line | RNA segments | Diameter (nm) | Vectors | Vertebrate hosts | distribution | reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cygnet River | Musk duck | Australia | ||||
| Johnston Atoll | 165-200 | Ornithodoros ticks | Chicken , mouse | Australasia, Pacific | ||
| Lake Chad | Mouse , yolk weaver (weaver birds) | Africa | ||||
| Quaranfil | ≥6 | 100 or 137–156 | Argas ticks | Mouse , human, sea birds | Africa, Asia | |
| Tyulek | 6th | Argas ticks | Asia | |||
| Wellfleet Bay | ≥7 | 90-110 | Eider | North America |
The type species is shown in bold .
Quaranfil virus and related species or lines
The Quaranfil virus was originally found in the villages of Quaranfil ( Arabic قَرَنْفيل, in German "carnation") and Sindbis (also Sindibis, Arabic سندبيس) Near Cairo ( Egypt ) in two children isolated with a slight fever. Antibodies to the virus were detected in around 8% of people sampled in the region , although no other cases of symptomatic illness were reported. The geographic range of the virus is wide, including Nigeria and South Africa in Africa; as well as Afghanistan , Iraq , Iran , Kuwait and Yemen in the Middle East / Asia . The virus has also been isolated from seabirds and leather ticks (soft-bodied ticks) such as Argas arboreus. The virus has been shown to be transmitted between vertebrates by ticks. In the laboratory, it also causes serious illness in mice.
Cygnet River Virus and Wellfleet Bay Virus
The Cygnet River virus was isolated in 2010 from embryonated eggs (eggs with embryo , English embryonated eggs ) of the bluefin duck ( Cairina moschata ) from the Cygnet River ( Kingscote , Kangaroo Island , Australia). The virus was responsible for an outbreak of serious diseases in breeding ducks.
The Wellfleet Bay virus was of eider ducks ( Somateria mollissima insulated), on Jeremy Point , Wellfleet Bay ( Cape Cod , Massachusetts USA,), hibernate. The virus was linked to a serious disease outbreak in 2010, and it is believed that there were a number of similar outbreaks caused by the virus in 1998–2013.
The two lines are closely related and can be strains of the same virus species. They are also related to the Quaranfil virus .
Lake Chad virus
The Lake Chad virus ( Lake Chad virus ) was isolated from an infected weaver bird (yolk weaver, scientifically Ploceus vitellinus ) from Lake Chad in Nigeria in 1969 . The virus causes severe illness in mice under laboratory conditions. It is most closely related to the Quaranfil virus .
Johnston Atoll Virus
The Johnston Atoll Virus was first isolated in 1964 from leather ticks of the species Ornithodoros capensis , which attack the brown Noddise tern ( Anous stolidus ) from Sand Island in the Johnston Atoll in the Pacific . The range also includes Hawaii , Australia and New Zealand. It has been shown that the virus is transmitted between vertebrates by ticks. In the laboratory, it causes serious illness in mice and chicks.
Tyulek virus
The Tyulek virus (Tjulok virus, TLKV) was isolated from leather ticks of the species Argas vulgaris - ticks that attack birds on the Aksu River near the Kyrgyz village of Tyulek (also Tjulok, Russian Тюлёк ). The virus is closely related to the Quaranfil virus and the Johnston Atoll virus .
More candidates
13 RNA sequences with a sequence match of 34-40% to the Johnston Atoll Virus have been identified in insects and spiders in China. Suspected hosts include:
- Neoscona nautica ( true orb web spiders , scientifically Aranidae)
- Pepper fruit ., Scientific Atherigona orientalis ( True Flies ., Scientific Muscidae: Atherigoninae)
- the oriental latrine flies Chrysomya megacephala ( blowflies , calliphoridae) and Sarcophaga sp. ( Meat flies , scientific Sarcophagidae)
- Housefly , scientific Musca domestica
- Culex tritaeniorhynchus , C. quinquefasciatus and Anopheles sinensis ( mosquitoes , scientific Culicidae)
- the moth fly Psychoda alternata ( butterfly mosquitoes , scientific Psychodidae, English moth flies )
- Species of the louse flies , scientific Hippoboscidae and more generally the Hippoboscoidea
- other unidentified species of the families Tabanidae (horseflies), Gerridae (water striders) and Stratiomyidae (gun flies).
Individual evidence
- ↑ ICTV Master Species List 2018b.v2 . MSL # 34, March 2019
- ↑ a b ICTV: ICTV Taxonomy history: Akabane orthobunyavirus , EC 51, Berlin, Germany, July 2019; Email ratification March 2020 (MSL # 35)
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i McCauley JW, Hongo S, Kaverin NV, Kochs G, Lamb RA, et al .: Create 2 new species in the proposed new genus Quaranjavirus . International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses . 2012. Accessed September 12, 2019.
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p Presti RM, Zhao G, Beatty WL, Mihindukulasuriya KA, Travassos da Rosa AP: Quaranfil, Johnston Atoll, and Lake Chad viruses are novel members of the family Orthomyxoviridae . In: Journal of Virology . 83, No. 22, 2009, pp. 11599-606. doi : 10.1128 / JVI.00677-09 . PMID 19726499 . PMC 2772707 (free full text).
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Zeller HG, Karabatsos N, Calisher CH, Digoutte JP, Murphy FA, Shope RE: Electron microscopy and antigenic studies of uncharacterized viruses. I. Evidence suggesting the placement of viruses in families Arenaviridae , Paramyxoviridae , or Poxviridae . In: Archives of Virology . 108, No. 3-4, 1989, pp. 191-209. doi : 10.1007 / bf01310934 .
- ↑ a b c d e f Kessell A, Hyatt A, Lehmann D, Shan S, Crameri S et al .: Cygnet River virus, a novel orthomyxovirus from ducks, Australia . In: Emerging Infectious Diseases . 18, No. 12, 2012, pp. 2044-46. doi : 10.3201 / eid1812.120500 . PMID 23171630 . PMC 3557875 (free full text).
- ↑ a b c d e L'vov DK, Al'khovskiĭ SV, Shchelkanov MIu, Shchetinin AM, Deriabin PG, Aristova VA, Gitel'man AK, Samokhvalov EI, Botikov AG: Taxonomic status of the Tyulek virus (TLKV) (Orthomyxoviridae , Quaranjavirus, Quaranfil group) isolated from the ticks Argas vulgaris Filippova, 1961 ( Argasidae ) from the birds burrow nest biotopes in the Kyrgyzstan . In: Voprosy virusologii . 59, No. 2, 2014, pp. 28–32. PMID 25069282 .
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Allison AB, Ballard JR, Tesh RB, Brown JD, Ruder MG et al .: Cyclic avian mass mortality in the Northeastern United States is associated with a novel orthomyxovirus . In: Journal of Virology . 89, No. 2, 2015, pp. 1389-403. doi : 10.1128 / JVI.02019-14 . PMID 25392223 . PMC 4300652 (free full text).
- ↑ a b c d Li CX, Shi M, Tian JH, Lin XD, Kang YJ et al .: Unprecedented genomic diversity of RNA viruses in arthropods reveals the ancestry of negative-sense RNA viruses . In: eLife . 4, 2015. doi : 10.7554 / elife.05378 . PMID 25633976 . PMC 4384744 (free full text).
- ↑ ICTV Taxonomy History for Quaranjavirus . International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses . Retrieved March 16, 2015.
- ^ Adams MJ, King AM, Carstens EB: Ratification vote on taxonomic proposals to the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (2013) . In: Archives of Virology . 158, No. 9, 2013, pp. 2023-30. doi : 10.1007 / s00705-013-1688-5 . PMID 23580178 .
- ↑ a b ViralZone : Quaranja virus . Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics (SIB). Retrieved September 12, 2019.
- ↑ a b c Descriptions of Plant Viruses: Notes on Genus: Quaranjavirus . Rothamsted Research . Retrieved September 12, 2019.
- ↑ ICTV : Master Species List 2018b.v2 MSL # 34v from April 2019
- ↑ NCBI: Cygnet River virus (species)
- ↑ NCBI: Lake Chad virus (species)
- ↑ NCBI: Wellfleet Bay virus (species)
- ^ Vsevolod L. Popov, Robert B. Tesh, Scott C. Weaver. Nikos Vasilakis: Electron Microscopy in Discovery of Novel and Emerging Viruses from the Collection of the World Reference Center for Emerging Viruses and Arboviruses (WRCEVA) , in: Viruses 11 (5), 2019, p. 477, doi: 10.3390 / v11050477
- ↑ Tyulek Virus , on: Influenza News - An Encyclopedia of Forever Changing Viruses (Blog)
- ↑ NCBI: Quaranjaviridae (family)
- ↑ NCBI: Jingshan Fly Virus 1 (species)
- ↑ NCBI: Jiujie Fly Virus (species)
- ↑ NCBI: Longchuang virus (species)
- ↑ NCBI: Sanxia Water Strider Virus 3 (species)
- ↑ NCBI: Shayang Spider Virus 3 (species)
- ↑ NCBI: Shuangao Insect Virus 4 (species)
- ↑ NCBI: Wuhan Louse Fly Virus 3 (species)
- ↑ NCBI: Wuhan Louse Fly Virus 4 (species)
- ↑ NCBI: Wuhan Mosquito Virus 3 (species)
- ↑ NCBI: Wuhan Mosquito Virus 4 (species)
- ↑ NCBI: Wuhan Mosquito Virus 5 (species)
- ↑ NCBI: Wuhan Mosquito Virus 6 (species)
- ↑ NCBI: Wuhan Mosquito Virus 7 (species)
- ↑ NCBI: Wuhan Mothfly Virus (species)
- ↑ NCBI: Zambezi tick virus 1 (species)