Rügen small train
| Rügen small train | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
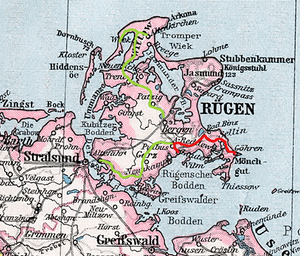
Route network of the Rügen Kleinbahn,
disused routes in green, traveled routes in red | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gauge : | 750 mm ( narrow gauge ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Top speed: | 30 km / h | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Altefähr – Putbus – Göhren | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route number (DB) : | 6982, 6775 (partly) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Course book section (DB) : | 199, 123k / 123h (1967); 125 (1944) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route length: | 59.4 km | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bergen – Altenkirchen | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Course book range : | 123k (1967); 125a (1944) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route length: | 59.4 km | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buhrkow – Bug (1918–1926) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Rügen Kleinbahn (RüKB) operated an extensive narrow-gauge railway network with a gauge of 750 millimeters on the island of Rügen in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania between 1895 and 1945 . After several changes of ownership and closure of parts of the route, the Rasender Roland ( line number : RB 32 ) called part of Putbus via Binz , Sellin and Baabe to Göhren is still used today , since 2008 by the railway construction and operating company Pressnitztalbahn (PRESS) from Jöhstadt ( business Rügensche Bäderbahn (RüBB)). Steam locomotives and wagons, some of which are almost 100 years old, run on this 24.1 km long route .
history


The oldest route section still in operation was opened in 1895 from Putbus to Binz. By 1899, the operator Rügensche Kleinbahn-Aktiengesellschaft (RüKB) expanded the network to 97.3 kilometers. The previous line was extended from Binz to Göhren and a new section was built from Altefähr station , across from Stralsund , to Putbus. Initially there was a separate quay in Altefähr. The main shareholder was Prince Wilhelm Malte zu Putbus , who had his own saloon car for the route. In addition to the topography, the winding route was due to the need for scattered agricultural goods that wanted loading points as close as possible to sell their products. They had to make the land available for the route free of charge.
A second route led from Bergen via the Wittower ferry to Altenkirchen near Cape Arkona . The purpose was to connect the chalk port of Wiek in addition to the connections of the estate operations.
The regular - gauge Lauterbach – Putbus – Bergen line has existed between Putbus and Bergen since 1889 , on the southernmost part of which a three- rail track has enabled narrow-gauge trains from Putbus to Lauterbach Mole to continue.
There were several plans to extend the route, but ultimately only the branch on the bow was realized for military reasons. Already approved route projects such as the route extension to Cape Arkona and from Trent to Schaprode were ultimately not implemented. A connection from Bubkevitz to Garz, approved in 1907, was also not built, although the connection of the two lines on Rügen promised enormous operational advantages.
The lines were built by the Rügen Kleinbahn-Aktiengesellschaft RüKB, in which the construction company Lenz & Co. owned a significant share of the share capital. Lenz & Co. initially took over the management. From April 1, 1910, the Kleinbahn was transferred to the Provincial Association of the Province of Pomerania. In 1935 the RüKB transported 311,776 people and 175,984 tons of goods. In 1940 the newly founded Pomeranian State Railways took over the Rügensche Kleinbahn-Aktiengesellschaft as a public corporation . After 1945, the lines, like all private small railways in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, were subordinated to the Demmin State Railway Authority. On April 1, 1949, the lines were taken over by the Deutsche Reichsbahn .
In the 1960s, the routes in freight traffic lost their importance, as more and more transports were transferred to road traffic. The reconstruction of the facilities that were neglected in the war and post-war years and due to the changed traffic conditions was no longer justifiable. The traffic between Putbus and Altefähr was stopped in December 1967. The northern route Fährhof – Altenkirchen followed on September 10, 1968, and traffic on the Bergen – Wittower ferry also ended on January 19, 1970. The branch to the Bug peninsula was finally closed in 1955. The routes were dismantled. Today some of its routes are used as cycling and hiking trails.
When the track was rebuilt from 1977 to 1979, the Putbus – Göhren line was equipped with superstructure K and mostly the S 33 rail shape. During renewed renovations at the beginning of the 1990s, rails of the shape S 49 were installed and the gravel bedding was replaced by more stable ballast bedding.
On January 1, 1996, the operation of the line was transferred from what was now Deutsche Bahn AG to the newly founded Rügensche Kleinbahn GmbH & Co., which at that time belonged to the Karsdorf railway company KEG. After the insolvency of the Karsdorfer Eisenbahngesellschaft, its managing director Bernhard van Engelen sold RüKB, which he personally owned, to Ludger Guttwein's railway operating company (EBG) in March 2004. A dispute over the purchase price and the continuation of operations led to the contract being canceled in May 2004. In November 2004, RüKB was finally sold to Hermann Schöntag.
Since the Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania transport company did not want to extend the transport contract for legal reasons and instead put the local transport services on the route out to tender in autumn 2007, the obligation of the RüKB ended on December 31, 2007. The proceedings went in favor of the Eisenbahn-Bau- und Betriebsgesellschaft Pressnitztalbahn mbH (PRESS), which will operate the Putbus – Göhren line for 20 years. The new contract stipulates that the new operating company will receive the infrastructure for operation on loan from the district of Vorpommern-Rügen .
Due to disputes between the Rügen district and the former operator regarding the repurchase of the vehicle fleet, there was a transitional operation between Binz and Göhren with vehicles rented from PRESS since March 18, 2008. On April 9, 2008, the PRESS received power of disposal over the repurchased vehicles. Since April 26, 2008, there is again a two-hour service with two trains between Putbus and Göhren. On June 1, 2008, she took over the employees and the railway infrastructure from RüKB. Since June 7, 2008, the RüBB has been using a third train between Binz and Göhren, so that there is an hourly service.
A new workshop is planned in Putbus.
Route descriptions
Altefähr – Putbus – Göhren route
| Route section | Opening date |
|---|---|
| Putbus – Binz | July 22, 1895 |
| Binz – Sellin West | March 20, 1896 |
| Sellin West – Sellin East | May 23, 1896 |
| Sellin Ost – Göhren | October 13, 1899 |
| Altefähr – Putbus | 4th July 1896 |
| Putbus – Lauterbach pier | May 28, 1999 |
- Drive from Göhren to Putbus LB
Goehren-Sellin East
Sellin Ost – Garftitz
Garftitz – Serams
Serams-Putbus LB
The abbreviation "LB" after the station names Putbus and Binz stands for "Landesbahn".
Bergen – Altenkirchen route
| Route section | Opening date |
|---|---|
| Bergen – Wittower ferry | December 21, 1896 |
| Fährhof – Altenkirchen | December 21, 1896 |
| Buhrkow junction-Starrvitz-Gramtitz | November 1, 1918 |
| Starrvitz-Gramtitz-Bug | December 16, 1918 |
This route mainly opened up the agricultural hinterland of the island of Rügen and was of no importance for excursion traffic on the island of Rügen. As a special feature, there was a railway ferry connection between the Wittower ferry and the ferry station, which also served road traffic. The ferry Wittow built in 1896 and the Jaspar von Maltzahn built in 1911 (from 1945 Bergen ) were used. The ferry was only used by the railroad for freight transport and for the transfer of locomotives and wagons; no wagons were transferred for passenger trains.
The ferry connection between Wittower Fähre and Fährhof remained the property of the Deutsche Reichsbahn until 1975 and was only then transferred to the White Fleet . It was not until the 1990s that the old railway ferries were decommissioned and replaced by new buildings.
vehicles
Initially two-axle steam locomotives of the Lenz type n and type m were used on the railway , later also three-axle locomotives of the type o and four-axle locomotives of the type nn and type Mh . A Prussian T 36 also came to Rügen.
| Type / series | Company number | design type | Construction year | comment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RüKB | Pomeranian State Railways | German Reichsbahn | ||||
| Lenz type n | 1 n -6 n | 201, 202 | - | B n2t | 1895-1896 | Retired by 1942 |
| Lenz type m | 7 m -9 m | 203-205 | 99 4602, 4603 | B n2t | 1896, 1912 | |
| Type o | 11 o -12 o | 221, 222 | - | C n2t | 1902, 1910 | 1928 by Altmärkischer Kleinbahn ; retired around 1947 |
| Lenz type nn | 31 nn -35 nn | 241-245 | 99 4521-4525 | B'B n4vt | 1902-1911 | |
| Type M | 51 M -52 M | 257, 258 | 99 4631, 4632 | D n2t | 1913-1914 | |
| Type Mh | 53 M. | 259 | 99 4633 | D h2t | 1925 | |
| pr. T 36 | - | 265 | 99 4621 | C2 'n2t | 1901 | |
| Railcar | T 1 | 1082 | (1A) (A1) | 1936 | 1942 to Greifswald – Jarmener Kleinbahn | |
German Reichsbahn
Following the acquisition of the course by the German Reichsbahn locomotives were other paths added, some only for a short time, the series 99 451 , 99 453 , 99 464 , 99 465 and 99 480 , but above all the series 99 51-60 , the Saxon IV K, from the 1980s also new locomotives of the class 99 77-79 . The latter are still available today , in addition to type M and class 99 480 locomotives . Since 1965 there were also diesel locomotives, primarily for shunting tasks, initially two former Heeresfeldbahn Köf , one of which is still available.
The Görlitz weight brake was used in the Rügen narrow-gauge network from the start . In 1965 the switch to air brakes began . In contrast to many other narrow-gauge routes, the line couplings on the vehicles are arranged symmetrically. Since the original machines had no heating couplings, the passenger cars had to be equipped with ovens. The wagons that have been moved by Saxon routes since the 1960s have also been retrofitted with ovens. The balancing lever coupling is used from the start. There was never an operation with rolling vehicles .
The time after
At times in the 1990s, various privately owned steam locomotives were also on the route. The V 51 901 from the Deutsche Bundesbahn has also been running on Rügen since 1998 .
Rügen bath railway
The transitional traffic from March 21, 2008 took place with the diesel locomotive 199 008 of the IG Pressnitztalbahn and the steam locomotives 99 773 of the SDG and 99 787 of the Saxon-Upper Lusatian Railway Company (SOEG). Baggage and passenger coaches were rented from SDG and SOEG. After the operation with rental vehicles was terminated at the beginning of the winter timetable 2008/09, the vehicles were brought back to Saxony.
The former locomotive 7 of the Mansfeld mining railway has been in service as a new locomotive since October 2008 under the number 99 4011. The 99 1781 has been in use on Rügen since 2011. It was given to the DB Museum in Nuremberg in 1992 and was brought back to Saxony by the Preßnitz Valley Railway in 2006. In 2010 the press sold the locomotive to the Rügen district, which gave it to RüBB as a loan. At DLW Meiningen she got, among other things, new water boxes and a new coal box.
In October 2013, RüBB celebrated its fifth anniversary. There was a photo weekend between October 11th and 13th. The SDG 99 608 was transferred to Rügen as a guest locomotive. It was the eighteenth IV K deployed on Rügen. On October 14, the machine hauled the first train from Putbus to Göhren and back. That was the first trip of an IV K with a scheduled passenger train on Rügen since 1969.
The locomotives 99 1783 and 99 1594, which were previously privately owned, have been owned by PRESS since July 10, 2014. These stood on a siding in Putbus for a long time and are now to be optically refurbished. The second fan weekend for railway fans took place from October 10 to 12, 2014. 99 4511 was transferred as a guest locomotive . In addition, suitable passenger cars were brought to the island, the 53Mh was again painted black and red and signposted with its DR number 99 4633.
On October 31, 2014, the 99 1594 was sold to the IG Preßnitztalbahn eV and brought from the island on December 2, 2014. The Aquarius C was sold by PRESS to Club 760 in December 2016 . She was transported to Austria. The exterior of the 99 1783 was refurbished and exhibited in the Pomeranian Kleinbahnmuseum in Putbus. At the beginning of February 2015 she was transported from the island to Glauchau . Since then it has been exhibited in Glauchau next to 99 1594 on a narrow-gauge transport car. In the early summer of 2020, the 99 1783 came back to Rügen from processing and has been used in scheduled service ever since.
RüKB locomotive 53 Mh , built at Vulcan, Stettin in 1925
AQUARIUS C , here in Saxony
| Company number | origin | Operational |
|---|---|---|
| 99 4632-8 | Lenz type M | yes (until 2026) |
| 99 4633-6 | Lenz type MH | yes (until 2019) |
| 99 4801-9 | KJI No. 20 and 21 | Yes |
| 99 4802-7 | KJI No. 20 and 21 | Yes |
| 99 1781-6 | DR series 99.77–79 | yes (until 2019) |
| 99 1782-4 | DR series 99.77–79 | yes (until 2023) |
| 99 1783-2 | DR series 99.77–79 | yes (until 2028) |
| 99 1784-0 | DR series 99.77–79 | no (HU Putbus) |
| 99 4011-5 | Mansfeld Mining Railway No. 7 | yes (until 2020) |
| 6003 | Army field railway locomotive HF 130 C. | yes (until 2018) |
| 251 901-5 | DB class V 51 | Yes |
business
The Göhren - Binz - Putbus route is served every two hours all year round. From May to September, after Christmas and at Easter, the trains between Göhren and Binz run every hour. The trains Binz - Putbus run from May to September to Lauterbach Mole. A pair of night trains runs between Göhren and Binz from June to August.
Others
In the film Hot Summer , film scenes from the last year of operation can be seen on the Altefähr – Putbus route.
literature
- Walter Bauchspies, Klaus Kieper, Klaus Jünemann: The big book of the Rügen small railways. Verlag Feld- und Schmalspurbahnen Karl Paskarb, Celle 2005, ISBN 3-938278-01-3 .
- Ludger Kenning, Achim Rickelt: Small train journey across the island of Rügen. Volume 1: The vehicles since 1950, Volume 2: Routes and stations. Kenning Verlag, Nordhorn 2014/2017, ISBN 978-3-944390-03-1 or ISBN 978-3-944390-04-8 .
- Klaus-Jürgen Kühne: Everything about the mad Roland. Transpress Verlag, Stuttgart 2011, ISBN 978-3-613-71404-5 .
- Detlef Radke: Attention, Kleinbahn has right of way! The history of the Putbus-Göhren narrow-gauge railway. 4th edition. Radke-Verlag, Schwerin 2009.
- Kai-Uwe Thiessenhusen, Axel von Blomberg: The Rasende Roland. Rhino-Verlag, Ilmenau 2017, ISBN 978-3-95560-057-0 .
Web links
Pictures on stillosed.de:
- Inspection of the disused Altefähr – Putbus section
- Inspection of the disused section Bergen (East) - Wittower ferry
Individual evidence
- ↑ Line profile on the website of Verkehrsgesellschaft Mecklenburg-Vorpommern mbH, accessed on February 1, 2020
- ↑ Measurement table sheet 1880–1919
- ↑ Lehmann / Meyer, “Rügen AZ”, Wähmann-Verlag, Schwerin, 1976, p. 43
- ↑ Lehmann / Meyer, “Rügen AZ”, Wähmann-Verlag, Schwerin, 1976, p. 43
- ↑ Cf. Railways in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, section "Train traffic as scheduled again at the 'Rasenden Roland'". (No longer available online.) March 23, 2008, archived from the original on December 31, 2010 ; Retrieved February 8, 2011 .
- ↑ railway magazine 6/2008
- ↑ Achim Rickelt: The history of the Rügen small railways. June 2008, accessed February 8, 2011 .
- ^ Verkehrsgesellschaft Mecklenburg-Vorpommern mbH: Services - 404015-2018. In: TED Tenders Electronic Daily. September 15, 2018. Retrieved November 15, 2018 .
- ↑ Pressnitztalbahn.de ( Memento from November 12, 2016 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Tobias Lampe: See file: “The locomotive 99 4011 sits down in Putbus on a passenger train to Göhren.” October 25, 2008, accessed on February 8, 2011 .
- ^ Achim Rickelt (RüBB employee) in the Bimmelbahnforum. (No longer available online.) July 15, 2014, archived from the original on July 18, 2014 ; accessed on July 15, 2014 .
- ^ RüBB fan weekend, my favorite locomotive ( Memento from June 21, 2015 in the Internet Archive ), Bimmelbahn forum
- ^ Preßnitztalbahn - Locomotives ( Memento from June 21, 2015 in the Internet Archive ), Preßnitztalbahn
- ↑ From the island to home? ( Memento from December 6, 2014 in the Internet Archive ), Bimmelbahn-Forum
- ↑ http://www.inselbahn.de/index.php?nav=1405962&lang=1&id=19155&action=portrait
Coordinates: 54 ° 23 ' N , 13 ° 37' E