Rosemary heather
| Rosemary heather | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Rosemary heather ( Andromeda polifolia ), flowers |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name of the genus | ||||||||||||
| Andromeda | ||||||||||||
| L. | ||||||||||||
| Scientific name of the species | ||||||||||||
| Andromeda polifolia | ||||||||||||
| L. |
The rosemary heather ( Andromeda polifolia ), also called Polei-Gränke , lavender heather , Poleirosmarinheide and swamp rosemary , is one (or the only) plant species from the genus Andromeda within the heather family (Ericaceae). She was voted Flower of the Year 1991.
description
Vegetative characteristics
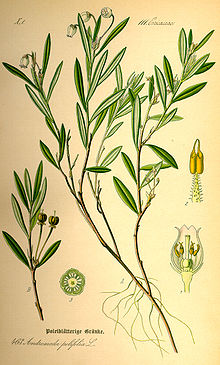
The rosemary heather is a woody, evergreen perennial plant , a dwarf shrub that reaches heights of 15 to 30 centimeters. It forms subterranean runners .
The alternate leaves arranged on the branches are divided into short petioles and leaf blades. The simple leathery leaf blade is lanceolate. The underside of the leaf is whitish. The leaf margin is rolled up. The leaves are thus similar to those of rosemary , from which this plant species also got the common name rosemary heather.
Generative characteristics
The rosemary heather forms two to five, rarely up to eight nodding flowers in an umbrella- shaped inflorescence . The egg-shaped and pink to white petals are fused with each other, as is typical of the family, spherical to bell-shaped.
The upright, five-fold capsule fruits , brown when ripe, contain many seeds.
The number of chromosomes is 2n = 48.
Ecology and phenology
The Rosmarienheide is an evergreen dwarf shrub . Vegetative reproduction occurs through underground runners . Their roots form a mycorrhiza of the Ericaceous type.
From an ecological point of view, it is a matter of "hanging bluebells with scattering device", i. H. the pollen trickles down on the visitors when it approaches. Pollinators are bees and other hymenoptera ; but also self-pollination takes place. Flowering period extends from May to July.
The capsule fruits jump open with five fruit flaps and act as wind spreaders. The seeds can spread like granular fliers. The Rosmarienheide is a winter lover . Fruit ripening is from August to October.
To germinate, it needs a cold stimulus (cold germ) and light (light germ).
toxicology
The rosemary heather is highly poisonous in all parts of the plant.
The main active ingredients are andromedotoxin , as well as several iridoid glycosides ; according to more recent information, however, no diterpenes should be present.
Poisoning has occurred in grazing animals, particularly sheep and goats .
In humans, poisoning has occurred from honey , which comes from the rosemary heather. Poisoning by such honey, which had been acquired in the Turkish Black Sea region, was treated in Austrian hospitals in 1981 and 1982. With symptomatic therapy, the patients recovered completely within 24 hours.
Occurrence
Andromeda polifolia is circumpolar in Eurasia and North America in the northern hemisphere .
The rosemary heather is widespread in Germany, Bavaria (especially the Bavarian Forest , Fichtelgebirge , Rhön ), Baden-Württemberg (especially Upper Swabia, Black Forest ), and in northern German moor areas. In other areas it is also rarely found, due to the rarity of the habitat .
In the Allgäu Alps, the rosemary heather in Wasenmoos near Unterkrumbach in Vorarlberg rises to an altitude of 1700 meters.
The rosemary heather is an inhabitant of the heather and rain bogs . It avoids lime and requires open locations. The family- typical mycorrhiza enables Andromeda polifolia to grow on soils that are very low in nitrogen, such as heaths and raised bogs. In Central Europe, the rosemary heather is an order character of the Sphagnetalia .
Systematics and distribution
Andromeda polifolia was first published in 1753 by Carl von Linné .
Depending on the author, Andromeda polifolia has subspecies:
- Andromeda polifolia L. subsp. polifolia ( Syn . : Andromeda polifolia var. concolor B. Boivin ): It is widespread in the northern hemisphere in Eurasia and North America .
- Andromeda polifolia subsp. pumila V.M. Vinogr. : It occurs in Lithuania and Russia.
- Andromeda polifolia var. Latifolia Aiton (Syn .: Andromeda canescens Small , Andromeda glaucophylla Link , Andromeda glaucophylla var. Iodandra Fernald , Andromeda polifolia subsp. Glaucophylla (Link) Hultén , Andromeda polifolia var. Glaucophylla (Link) DC. ): She is on widespread in the northern hemisphere in Eurasia and North America .
Diseases
The rosemary heather is attacked by the two naked basidia Exobasidium karstenii and Exobasidium sundstroemii . In the former, the leaves are wider than normal and are purple to black-red on top. When infected with Exobasidium sundstroemii , the leaves are hardly enlarged, but red-purple-green spotty. The rosemary heather wrinkled scab ( Rhytisma andromedae ) forms black spots 2 to 10 millimeters wide on the upper side of the leaf.
Common names
For the rosemary heath, the names Gränke, small border, small grantze ( Silesia ), small post (Mark), small Prost (Mark), small rosemary (Silesia, Mecklenburg , Carinthia ), wild rosemary are or were, in some cases only regional (Silesia, Mecklenburg, Carinthia), small rosemary heather, peat heather and peat rosemary commonly used.
Naming
Most of the names of this plant species refer to the similarity with other plant species, including the scientific epithet polifolia for "poleiblättrig", which compares with Polei-germander Teucrium polium .
Hermann Löns dedicated his poem "Lost" to the rosemary heather.
- photos
swell
- Dorothy M. Fabijan: Andromeda L .: Andromeda polifolia , p. 503 - same text online as printed work , In: Flora of North America Editorial Committee (Ed.): Flora of North America North of Mexico , Volume 8 - Paeoniaceae to Ericaceae , Oxford University Press, New York and Oxford, 2009, ISBN 978-0-19-534026-6 . (Sections systematics and description)
- Ruprecht Düll , Herfried Kutzelnigg : Pocket dictionary of the plants of Germany and neighboring countries , 7th edition, Quelle & Meyer-Verlag, 2011, ISBN 978-3-494-01424-1 Ruprecht Düll , Herfried Kutzelnigg : Pocket dictionary of the plants of Germany and neighboring countries. The most common Central European species in portrait . 7th, corrected and enlarged edition. Quelle & Meyer, Wiebelsheim 2011, ISBN 978-3-494-01424-1 .
- Lutz Roth , Max Daunderer , Kurt Kormann : Poison Plants - Plant Poisons. Poisonous plants from AZ. Emergency assistance. Occurrence. Effect. Therapy. Allergic and phototoxic reactions . 4th edition. Nikol, Hamburg 2000, ISBN 3-933203-31-7 (reprint from 1994).
Individual evidence
- ^ Andromeda polifolia L., Polei-Gränke. In: FloraWeb.de.
- ↑ a b Erich Oberdorfer : Plant-sociological excursion flora for Germany and neighboring areas. 8th edition. Stuttgart, Verlag Eugen Ulmer, 2001. Page 731. ISBN 3-8001-3131-5
- ↑ Erhard Dörr, Wolfgang Lippert : Flora of the Allgäu and its surroundings. Volume 2, IHW, Eching 2004, ISBN 3-930167-61-1 .
- ↑ a b B. Valdés, with contributions from E. von Raab-Straube, G. Parolly, 2009: Ericaceae. : Datasheet Andromeda polifolia In: Euro + Med Plantbase - the information resource for Euro-Mediterranean plant diversity. Berlin 2011.
- ↑ a b c Dorothy M. Fabijan: Andromeda L .: Andromeda polifolia , p. 503 - the same text online as the printed work , In: Flora of North America Editorial Committee (Ed.): Flora of North America North of Mexico , Volume 8 - Paeoniaceae to Ericaceae , Oxford University Press, New York and Oxford, 2009, ISBN 978-0-19-534026-6 .
- ↑ Svengunnar Ryman & Ingmar Holmåsen: Mushrooms . Bernhard Thalacker Verlag, Braunschweig 1992, p. 72. ISBN 3-8781-5043-1 .
- ↑ Svengunnar Ryman & Ingmar Holmåsen: Mushrooms . Bernhard Thalacker Verlag, Braunschweig 1992, p. 658. ISBN 3-8781-5043-1 .
- ^ Georg August Pritzel , Carl Jessen : The German folk names of plants. New contribution to the German linguistic treasure. Philipp Cohen, Hannover 1882, page 27, online.
Web links
- Rosemary heather . In: BiolFlor, the database of biological-ecological characteristics of the flora of Germany.
- Andromeda polifolia L. In: Info Flora , the national data and information center for Swiss flora . Retrieved January 14, 2016.
- Distribution in the northern hemisphere according to Eric Hultén
- Thomas Meyer: Data sheet with identification key and photos at Flora-de: Flora von Deutschland (old name of the website: Flowers in Swabia ).
- Nature Conservation Foundation: Flower of the Year 1991 PDF, 417 kB.
- Information on toxicity at giftpflanze.com .