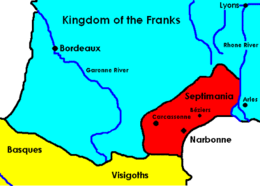
Septimania
Septimania is a historical territory in the south of France . It stretched along the Mediterranean coast from the mouth of the Rhone to the Pyrenees and essentially corresponds to the area of the former French region of Languedoc-Roussillon and belonged to the Visigoth Empire until 725 .
Delimitation and naming
By the administrative reforms under Diocletian (reigned 284-305.) And Constantine (reigned 306-337.) Originated in the southern part of Gaul the Diocesis XIV Septem Provinciarum (German: "Diocese XIV of seven provinces") with capital Vienna in the Rhone Valley . The seven provinces were
- Viennensis with the capital Vienna (Vienne)
- Aquitania I (Avaricum, Bourges )
- Aquitania II (Burdigala, Bordeaux )
- Novempopulana (Elusa, Eauze )
- Narbonensis I (Colonia Narbo Martius, Narbonne )
- Narbonensis II (Aquae Sextiae, Aix-en-Provence )
- Alpes Maritimae (Eburodunum, Embrun )
In a contract between the Visigothic king Amalrich († 531) and the Ostrogoth king Athalaric (516-534), which defines the boundaries of the Narbonensis , this area was already called Septimania . In the 9th century, bishops still used the term "brotherhood of the seven Gaulish provinces".
Other explanations for the name Septimania are also occasionally given:
- the Roman name for the lying in the center of the region city of Colonia Septimanarum Baeterrae ( Beziers ) made by veterans of the seventh legion had been settled
- the seven important bishoprics in the region: Elne , Agde , Narbonne , Lodève , Maguelone (today Mauguio , moved to Montpellier ), Nîmes and Uzès
history

From 418, Rome settled Visigoths throughout Aquitaine. These founded the Visigoth Empire in southwest Gaul , to which Septimania belonged; the capital was Tolosa ( Toulouse ), therefore one speaks of the Tolosan Empire . In 507, however, after a defeat by the Franks pushing south, they lost almost their entire Gallic imperial territory and therefore shifted their center of power to the Iberian Peninsula . North of the Pyrenees they only kept Septimania. This part of the empire enabled an important trade connection to the Ostrogoths, who settled in Italy. The name Septimania as Margraviate Gothien , which has also been in use since the middle of the 9th century - although not congruent - is derived from the Visigoths .
Between 719 and 725 the Moors invaded from Spain , but from 752 onwards they were allowed by Pippin III. and Charlemagne to be pushed back across the Pyrenees. The area came to the Franconian Empire as a duchy as early as 759 . At that time, only the area of the province of Narbonensis I was regarded as Septimania.
After conquering the areas south of the Pyrenees from 800, the Franks initially annexed this Spanish mark administratively to Septimania. In 865 the structure was again divided into two provinces; the capitals were Barcelona and Narbonne .
Since the end of the 11th century, the country was under the Duchy of Narbonne to the Counts of Toulouse. Together with their other possessions, it fell to the French crown as a result of the Albigensian Wars at the beginning of the 13th century.
Septimania and Languedoc-Roussillon
The French region of Languedoc-Roussillon ( Llenguadoc-Rosselló in Catalan , Lengadòc-Rosselhon in Occitan ) comprises the Aude , Gard , Hérault and Pyrénées-Orientales departments on the Mediterranean coast , as well as the geographically completely different department of Lozère , which belongs to the Massif Central .
After his election to the regional council in 2004, Georges Frêche ( PS ) campaigned for the renaming of Languedoc-Roussillon to "Septimania", and the regional assembly began to use the new name more and more frequently. However, it met with widespread opposition, especially among Catalans , who feared the loss of their Catalan identity in favor of a single Occitan identity for the entire region. They also argued that the territory of the former Septimania did not coincide with that of the Languedoc-Roussillon region. The opponents also used the phonetic similarity and polemicized with the term septicémie ( sepsis or blood poisoning ).
Due to the fierce opposition, Georges Frêche was finally forced to give up his intention in September 2005.
Margraves of Septimania
Septimania was ruled by dukes , mostly "of Septimania" and / or "Gothien" or "of Toulouse". The duke was one of the counts of the duchy.
- Beggo I († 816), son-in-law of Louis the Pious , from 811 Count of Paris ( Gerhardiner , Matfriede )
- Bernhard of Septimania (r. 828–832 and 835–844)
- Berengar of Toulouse (r. 832–835)
- William of Septimania (r. 848–850)
- Raimund (II.) Count of Rouergue († 961/965) Margrave of Septimania, 936 Duke of Aquitaine
literature
- John Insley: Septimania. In: Reallexikon der Germanischen Altertumskunde (RGA). 2nd Edition. Volume 28, Walter de Gruyter, Berlin / New York 2005, ISBN 3-11-018207-6 , pp. 185-194.