Bergamo Airport
| Il Caravaggio International Airport Bergamo Orio al Serio |
||
|---|---|---|
|
|
||
| Characteristics | ||
| ICAO code | LIME | |
| IATA code | BGY | |
| Coordinates | ||
| Height above MSL | 238 m (781 ft ) | |
| Transport links | ||
| Distance from the city center | 5 km southeast of Bergamo , 45 km east of Milan |
|
| Street |
|
|
| Basic data | ||
| opening | 1939 | |
| operator | SACBO SpA | |
| Terminals | 1 | |
| Passengers | 13,857,257 (2019) | |
| Air freight | 118,964 t (2019) | |
| Flight movements |
95,377 (2019) | |
| Runways | ||
| 10/28 | 2937 m × 45 m asphalt | |
| 12/30 | 778 m × 18 m asphalt | |
The Bergamo ( Italian Aeroporto di Bergamo-Orio al Serio , even Il Caravaggio International Airport - Bergamo Orio al Serio , IATA code : BGY , ICAO : LIME ) is an international airport in northern Italy . It is located 45 km northeast of Milan and 5 km southeast of Bergamo in the Lombardy municipality of Orio al Serio . This airport is mainly used by low-cost and cargo airlines, which also refer to it as "Milan-Bergamo Airport" or "Milan-Orio al Serio".
Transport links
- Car: The airport is on the A4 motorway , the most important east-west traffic axis in northern Italy . Both the greater Milan area and western Veneto can be reached quickly. The most important car rental companies are represented at the airport .
- Bus : Autostradale, Terravision and Orioshuttle compete for the shuttle connection to Milan Central Station . Each of the companies offers around 60 one-hour trips a day. The price is a uniform 5 euros, 9 euros with a return ticket. (As of 2018) There are also regular bus connections to Bergamo city center and a bus connection to Bergamo train station. A direct rail connection to the airport is planned.
history
The airport was established as a military airfield near the Serio River in 1937 . In September 1943, the Wehrmacht Air Force took over the airfield and used it together with the Aeronautica Nazionale Repubblicana until the end of World War II . During this time there were other military airfields around Bergamo at Ponte San Pietro , Seriate and Zanica .
In the 1950s and 1960s, local entrepreneurs and local politicians demanded civilian use of the Orio al Serio airport, but this failed due to the negative attitude of the city of Milan and the operators of the Linate and Malpensa airports there . On July 16, 1970 the airport company Società per l'Aeroporto Civile di Bergamo - Orio al Serio (SACBO) was founded, which also achieved the start of commercial flight operations on March 21, 1972. Civil flight operations developed slowly at first, although the airport is relatively centrally located in the Po Valley and around 5 million people live in its direct catchment area. At the end of the 1980s, the SEA , the operator of the two Milan airports, got involved in SACBO, but without obtaining a majority stake. The originally envisaged project to bring all three airports in the greater Milan area under control and to use them synergistically also failed. In addition, the city of Brescia , east of Bergamo, said it needed its own commercial airport, the Brescia-Montichiari airport , although Verona and Bergamo airports are easy to reach from there.
In this environment, Bergamo Airport has been able to assert itself on the one hand against Brescia and on the other hand to find its own role in the greater Milan area, as Malpensa for the eastern parts of Milan and on the other hand, thanks to the commitment of freight and low-cost airlines such as DHL Aviation and Ryanair Lombardy is less favorable and Linate is subject to various restrictions. The above-average growth of Bergamo Airport was triggered in the summer of 2002 when Linate had to temporarily close due to the renovation of the runway there and flight operations were also relocated to Bergamo. On this occasion, Bergamo managed to better convey its potential.
The passenger and cargo terminals are currently south of the runway. In the north there is still a small military part with a repair unit for army aviation and an area for general aviation with an almost 800 m long runway. Bergamo Airport is to be expanded in this northern area.
Airlines and Destinations
From Bergamo Airport, destinations in Italy, Europe, the Mediterranean, the Red Sea and the Canary Islands are served in particular . In German-speaking countries, Berlin-Schönefeld , Bremen, Weeze, Hahn, Hamburg, Cologne, Frankfurt am Main and Nuremberg are served by Ryanair. The most important local airline is Ryanair , which has a base in Bergamo. There are also other low-cost airlines such as Wizz Air and Blue Air , regional airlines and providers of charter flights .
In the air freight industry, the airport is mostly served by air mail companies. It is mainly DHL Aviation and some of its subsidiaries that serve the airport. They serve European destinations, including Cologne / Bonn and Leipzig / Halle .
Traffic figures
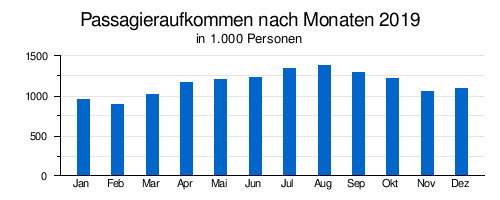

| year | Passenger volume | Air freight ( tons ) (with airmail ) |
Flight movements |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 13.857.257 | 118.964 | 95,377 |
| 2018 | 12,938,572 | 123.032 | 89,533 |
| 2017 | 12,336,137 | 125,948 | 86.113 |
| 2016 | 11,159,631 | 117,765 | 79,953 |
| 2015 | 10,404,625 | 121,045 | 76,078 |
| 2014 | 8,774,256 | 123.206 | 67,674 |
| 2013 | 8,964,376 | 116.112 | 71,742 |
| 2012 | 8,890,720 | 117.005 | 74,220 |
| 2011 | 8,419,948 | 112,556 | 71,514 |
| 2010 | 7,677,224 | 106,921 | 67,636 |
| 2009 | 7.160.008 | 100.354 | 65,314 |
| 2008 | 6,482,590 | 122,398 | 64,390 |
| 2007 | 5,741,734 | 134,449 | 61,364 |
| 2006 | 5,244,794 | 140.630 | 56,358 |
| 2005 | 4,356,143 | 136,339 | 51,635 |
| 2004 | 3,337,671 | 130,974 | 45,471 |
| 2003 | 2,844,379 | 128,687 | 48,362 |
| 2002 | 1,252,878 | 114,636 | 33,493 |
| 2001 | 1,061,397 | 96,253 | 36,586 |
| 2000 | 1,241,138 | 100,494 | 40,944 |
Incidents
- On April 9, 1975, was the start of a Fokker F28-1000 Fellowship of Itavia ( I-TIDA ) to a stall . The aircraft sank back onto the runway and stopped 200 m from the end of the runway. All 31 occupants survived the accident. The machine was totaled.
- On August 5, 2016 from shot Paris coming freight aircraft Boeing 737-400SF the ASL Airlines Hungary with the air vehicle registration HA-FAX over the runway addition, broke through a guardrail and came only on a country road to a halt. The two pilots were injured. At the time of the accident, the weather conditions at Bergamo Airport were poor and flight operations had to be suspended for around three hours. The Italian investigative authority ANSV found that the crew had not noticed that the machine had touched down only after about two thirds of the runway and that the runway was no longer sufficient to bring the aircraft to a standstill. At the time of the accident, the copilot had only had 86 flying hours on the Boeing 737 and had not questioned the captain's decision not to fly a go-around due to thunderstorms, but said in retrospect that this option could have prevented the accident from his point of view .
See also
Web links
- Website of the Aeroporto di Bergamo-Orio al Serio (Italian, English)
- Aeroporto di Bergamo-Orio al Serio (English)
- Details about the airport operator on trail.unioncamere.it
- History of the airport on sacbo.it
- History of the airport on bergamopost.it
- Aerial photo and history on ivao.it
- History of the airport on the website of the municipality of Orio al Serio
- Airport data on World Aero Data ( 2006 )
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f Statistiche. In: assaeroporti.com. Assaeroporti , accessed January 24, 2019 (Italian).
- ↑ https://autostradale.it/Images/Linee/Orari/141.pdf
- ↑ https://www.terravision.eu/tedesco/airport_transfer/bus-flughafen-bergamo-mailand-zentrum/preise-fahrplan-flughafen-bergamo-mailand-entrum/
- ↑ http://www.orioshuttle.com/_eng/pdf/OS_01_ENG.pdf
- ↑ Henry L. deZeng IV: Air Force Airfields 1935-45 Italy, Sicily and Sardinia , pp 23-24 , accessed on October 3, 2015
- ↑ ryanair.com , accessed September 14, 2016
- ^ Accident report I-TIDA, Aviation Safety Network (English) , accessed on February 23, 2016.
- ↑ Boeing 737 shoots over runway in Bergamo. aerotelegraph.com, August 5, 2016, accessed August 6, 2016 .
- ^ Accident report HA-FAX. aviation-safety.net, August 5, 2016, accessed on August 6, 2016 .
- ↑ DASHBOARD: Storms led 737 overrun captain to opt against go-around. In: FlightGlobal. August 9, 2018, accessed August 9, 2018 .
