Little Odenwald
| Little Odenwald | |
|---|---|
| Highest peak | Königstuhl ( 570.3 m above sea level ) |
| location | Districts of Rhine-Neckar and Neckar-Odenwald and city of Heidelberg , Baden-Württemberg ; Germany |
| Coordinates | 49 ° 24 ' N , 8 ° 44' E |
Location of the Kleiner Odenwald in the Karlsruhe district of Baden-Württemberg
|

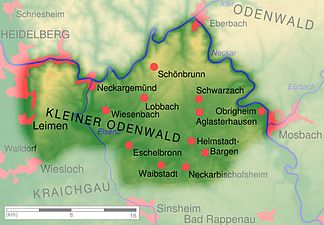
The Kleine Odenwald is up to 570.3 m above sea level. NHN high southern part of the low mountain range Odenwald and part of the natural area Sandstone-Odenwald in north-western Baden-Württemberg . Located east- southeast of Heidelberg or south of the Neckar , which separates the Kleiner Odenwald from the rest of the Odenwald, the sandstone that predominates in the northern Odenwald continues in its landscape .
geography
location
The Kleine Odenwald is located in the districts of Rhine-Neckar and Neckar-Odenwald and in the area of the urban city of Heidelberg . Viewed clockwise, it is viewed in the north by the Neckar, including Neckargemünd and Eberbach , in the east also by this river, for example with Obrigheim , in the south by Reichartshausen , Waibstadt and Eschelbronn and in the west by Wiesloch , Leimen and again on the Neckar Heidelberg limited. His communities include: Lobbach , Bammental , Gaiberg , Wiesenbach , Aglasterhausen , Schwarzach , Neunkirchen and Schönbrunn . The most important bodies of water in the landscape are Elsenz , Schwarzbach and Lobbach .
The building land lies a little east of the Kleiner Odenwald , south of the Kraichgau and west of the Upper Rhine Plain . In its southeast part is part of the well region .
Natural allocation and structure
The Kleine Odenwald belongs to the main natural unit group Odenwald, Spessart and Südrhön (No. 14) to the main unit Sandstone-Odenwald (144) and is divided into the sub-units Western Little Odenwald (144.1) and Eastern Little Odenwald (144.2). To the north, the landscape of both subunits leads over through the Odenwald-Neckar Valley (144.3) to the Central Sandstone Forest (144.6). In the south, the main unit group Gäuplatten in Neckar and Tauberland (No. 12) is followed by the main unit Kraichgau (125). Directly to the west is the western small Odenwald in the main unit group Northern Upper Rhine Lowland (22) and in the main unit Bergstrasse (226) the sub-unit Gaisbergfuß (226.1).
The western Kleine Odenwald lies roughly between Heidelberg in the northwest, Neckargemünd in the northeast, Mückenloch in the east, Wiesenbach and Bammental in the southeast, Gauangelloch and Maisbach in the south, Wiesloch and Nußloch in the south-southwest and Leimen and Rohrbach in the west. Within the landscape are Kohlhof , Waldhilsbach , Gaiberg and Lingental .
The eastern Kleine Odenwald lies roughly between Neckarhäuserhof in the northwest, Ersheim and Pleutersbach in the north, Neckarwimmersbach and Rockenau in the northeast, Guttenbach and Neunkirchen in the east, Michelbach and Reichartshausen in the south, Waldwimmersbach in the southwest and Mückenloch in the west. Within the landscape are Moosbrunn , Allemühl , Schwanheim , Leidenharterhof , Haag and Schönbrunn .
The two sub-units, the Western Kleiner Odenwald and the Eastern Kleiner Odenwald , do not come into direct contact, because they are separated from each other in the area around the village of Mückenloch by a northern part of the Kraichgau, which does not come into contact with the Odenwald-Neckar valley via the sub-units.
Natural park and geopark
The Kleine Odenwald is part of the Neckartal-Odenwald Nature Park . The municipalities assigned to the Neckar-Odenwald district and parts of the Rhein-Neckar district are part of the Bergstrasse-Odenwald Geo-Nature Park of UNESCO , the aim of which is, in particular, geotouristic upgrading and sustainable networking.
mountains
The mountains, elevations and their foothills in the Kleiner Odenwald include - sorted by height in meters (m) above sea level (NHN):
- Königstuhl (570.3 m), southeast of the old town of Heidelberg
- Hebert (518.8 m), south of Eberbach- Neckarwimmersbach
- Auerhahnenkopf (487.8 m), south of Heidelberg- Schlierbach
- Hirschhornberg (461.6 m), northwest of Ober Schönbrunn ; with the lower Neckarberg valley slope
- Piston (410.3 m), north-northeast of Schönbrunn- Moosbrunn ; with valley slope Oberer Neckarberg
- Gaisberg (375.7 m), south of the old town of Heidelberg
- Neckarberge (367.9 m), south of Mückenloch- Neckarhäuserhof
- Upper city forest (363.0 m), east of Neckargemünd
- Lower city forest (325.8 m), southwest of Neckargemünd
- Hirschberg (just over 300 m), northeast of Nussloch
- Neckarriedkopf (297.8 m), southwest of Neckargemünd in the Lower City Forest
- Hollmut (285.1 m), south of Neckargemünd
- Salzberg (259.3 m), west-southwest of Lobbach- Lobenfeld
- Bammertsberg (250.3 m), north of Bammental
geology
In the Odenwald north of the Neckar there are layers of red sandstone , which, in addition to where the stone appears naturally in the landscape, also shapes the regional architecture. South of the Neckar, the foothills of the Buntsandstein continue to a width of around 40 km in the so-called Little Odenwald . There are no longer any rugged cliffs here, but the historical buildings in the villages, made of regional stone, still show the characteristic shade of red. In the south the rock gradually changes into shell limestone ; there begins a new natural spatial unit, the Kraichgau .
Catholic church in Waibstadt made of typical red sandstone
Local well in Aglasterhausen made of red sandstone
Church in Breitenbronn
history
The castles of the Kleiner Odenwald such as the Minneburg or Schwarzach Castle were probably built in the high Middle Ages by followers of the Staufer , and the Lobenfeld monastery was also founded on Hohenstaufen estate. Many of the small villages in the Little Odenwald go back to Burgweiler or mill settlements of the castles. In most places, the regional lower nobility exercised the local rule. After the end of the Staufer, from the 13th century onwards, the region came mainly to the Electoral Palatinate , whose possessions there were summarized in the Stüber Zent within the Heidelberg Oberamt, whose central court met in Reichartshausen .
Traffic and walking
The Kleine Odenwald is practically enclosed by federal highways 37 and 292 . It is touched or crossed by the Schwarzbachtalbahn and Elsenztalbahn . The European long-distance hiking trail E1 runs through it in a north-south direction .
literature
- Working group of teachers of the Kleiner Odenwald (ed.): Der Kleine Odenwald , Heidelberg 1960
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Map services of the Federal Agency for Nature Conservation ( information )
- ↑ Josef Schmithüsen : Geographical land survey: The natural space units on sheet 161 Karlsruhe. Federal Institute for Regional Studies, Bad Godesberg 1952. → Online map (PDF; 5.1 MB)