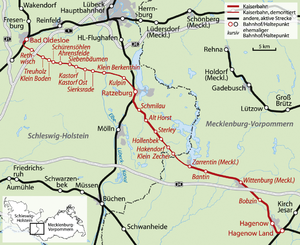
Railway line Hagenow Land – Bad Oldesloe
| Hagenow Land – Bad Oldesloe | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Route number (DB) : | 6928 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Course book section (DB) : | 172 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route length: | 78.3 km | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gauge : | 1435 mm ( standard gauge ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Hagenow Land – Bad Oldesloe railway (also known as the Kaiserbahn or Kaiserstrecke ) was a railway line in the states of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania and Schleswig-Holstein . It connected the places Hagenow , Ratzeburg and Bad Oldesloe with each other and with the continuation via Bad Segeberg and Neumünster formed the shortest rail connection between Berlin and Kiel , whereby the difference to the two other routes is about 55 kilometers each. Today, only the short section between the train stations Hagenow Land and Hagenow Stadt (only called Hagenow until 2010 ) is regularly served by passenger traffic; section Hollenbek -Ratzeburg is for trolley rides the experience Ratzeburg used. The Hagenow – Zarrentin section is still served occasionally. The other sections have been closed and dismantled. The name Kaiserbahn owes the route Kaiser Wilhelm II. , Who often used.
history
prehistory
Even before the line was built, there were two connections between Berlin and Kiel: the southern route led via Büchen on the Berlin – Hamburg railway line , the northern via Schwerin-Bad Kleinen and Bad Kleinen-Lübeck . However, both paths deviated greatly from the straight line . At the request of the emperor, a new route was designed that runs in the area "in between" and bypasses the Hamburg and Lübeck railway junctions . Wilhelm II is said to have given the rough route with a ruler , like Tsar Nicholas I on the St. Petersburg – Moscow railway line . The state contract to build the railway was finally signed on December 5, 1889.
The desired course leads the single-track route through several cuttings and many fields. To compensate for the latter, numerous bridges were built that had no further connection to other roads and were used exclusively for agricultural purposes. Some of these bridges still exist today.
There were crossing and passing tracks in the stations. Most of the underpasses were nevertheless prepared for the later installation of a second track and made accordingly wide.
State and Reichsbahn time
The railway was opened in three sections. The operation was the responsibility of the Prussian State Railway , although the eastern part was in the then independent Mecklenburg:
- September 1, 1894: Hagenow Land - Wittenburg
- May 1, 1896: Wittenburg - Zarrentin
- August 15, 1897: Zarrentin - Ratzeburg - Bad Oldesloe
With the opening of the last section, through traffic on the entire route was started. The Kaiser took part personally and was able to use the route 25 kilometers shorter than the two alternative routes from day one. In the following years, Wilhelm II used the route with his court train regularly for trips to Kiel, both to the Imperial War Port , to the Kiel Week and as the starting point for his annual trips to the north, which is why it was soon popularly referred to as the "Kaiserbahn". Nevertheless, the monarch sometimes preferred to use the northern route via Lübeck; the danger of an attack was higher on the new route because of the bridge over the Elbe-Lübeck Canal .
On April 1, 1899, the branch line from Hollenbek to Mölln was opened.
At the beginning of the 20th century there was an express train, and in the 1930s there were two express trains between Berlin and Kiel and back over the southeast part of the route between Hagenow and Ratzeburg. From Ratzeburg to Kiel, however, these trains ran via Lübeck and thus via the route of the private Lübeck-Büchener railway . In addition, the route was particularly important for local passenger and freight traffic. Up to 1945 up to 60 trains a day ran on the section between Hollenbek and Schmilau alone .
With the end of the Second World War , the decline of the railway began. In 1945 an ammunition train was hit by US bombers in Hollenbek station . The exploding ammunition tore a hole up to 12 meters deep, 150 × 25 meters. Rail fragments and the boiler of the locomotive flew up to a kilometer and into the village center. The disruption to rail traffic was nevertheless resolved after a few weeks.
Today, a wooden structure in a tree, similar to a wagon, reminds of this catastrophe at Hollenbek station. The Ratzeburg Adventure Railway operates the "Baumaggon-Hotel" there.
Separate companionway
The western section of the route

Immediately after the German surrender and the associated division into the British and Soviet zones of occupation , the Zarrentin – Hollenbek section was shut down and dismantled in 1952. In 1949 it was downgraded to the branch line .
In 1950, however, the Hollenbek – Klein Zecher section was reactivated on the western side; In addition to the new terminus, the Hakendorf, Sterley and Alt Horst stops were also opened. Used came railcars . In 1959 the section between Hollenbek and Mölln was closed, and on September 30, 1962, passenger traffic on the entire west German section between Klein Zecher and Bad Oldesloe finally ended.
On September 1, 1971, freight traffic between Hollenbek and Klein Zecher as well as between Ratzeburg and Bad Oldesloe was stopped, and the superstructure on these sections was removed a year later . On the remaining 13 kilometers to Ratzeburg, however, there was sparse freight traffic, with which mainly sugar beet was transported to Uelzen in Lower Saxony . This section of the route was able to hold up until December 14, 1994, but was then also discontinued due to unprofitable.
The eastern section of the route
Passenger and freight traffic on the Hagenow Land – Zarrentin section was initially continued until April 30, 1969. The line was then closed until September 27, 1975 in order to renovate the superstructure. After that, passenger traffic was sparse, but continued until the turn of the millennium. Regular freight traffic between Zarrentin and Wittenburg was only operated until December 31, 1994.
On May 28, 2000, the local rail passenger transport (SPNV) in the section Hagenow Land-Zarrentin was finally stopped. However, the infrastructure of the route will still be preserved for occasional freight traffic. After a great protest of the population, the reactivation of passenger traffic on the section Hagenow Land to Hagenow Stadt was successful from December 15, 2002.
The railway line Hagenow Land-Zarrentin was provided by the local in Zarrentin railway infrastructure companies Planning Association Transport industrial area Valluhn / Gallin (TGG) from the DB Netz acquired in September 2004 at the industrial park MEGA park on the Federal Highway 24 in rail freight to reach. This initially commissioned Mecklenburg Bahn GmbH , which was transferred to Ostseeland Verkehr GmbH in 2005 , with the maintenance of the route from kilometer 0.766. When the latter returned the approval, Torsten Meincke Eisenbahn GmbH (TME) was commissioned with operational management from July 1, 2007 , which has since also provided the personnel for the signal boxes in Hagenow Stadt, Wittenburg and Zarrentin.
Between 2008 and 2010, the West Mecklenburg Railway Company (WEMEG) ran two pairs of trains under the Schaalsee-Express brand between Hagenow Land and Zarrentin on the first Sunday of each month . The trips were carried out with two Uerdingen rail buses .
In autumn 2009, the tracks on the Hagenow Land – Hagenow Stadt section of the line used by local rail transport were renewed and the maximum line speed increased from 60 to 80 km / h. Since the subsequent section to Zarrentin is rarely used by freight trains, it cannot be operated at a cost-covering level.
Therefore, the owner planning association TGG intends to tender the Hagenow Land – Zarrentin line for takeover by third parties or to shut it down.
business
In the meantime, there is only sparse passenger and freight traffic on two short sections. On the western section between Hollenbek and Ratzeburg, the Ratzeburg Adventure Railway has been operating seasonal operations with a hand-lever trolley since 1998 . In addition to maintaining the route, it also serves as a plea for restarting operations and for traffic with regional trains.
Regular local rail transport, on the other hand, has been taking place on the approximately three and a half kilometers long section between Hagenow Land and Hagenow Stadt since the route was reactivated in 2002. The Hagenow city station is currently served by the ODEG line RB14 every two hours (with compressors).
Otherwise, the remaining section of the route northwest of Hagenow Stadt is occasionally used by block trains (bulk goods, wood). In autumn 2010, around 60 block trains also drove with the tubes for the Baltic Sea pipeline, which were reloaded onto trucks in Zarrentin and Wittenburg. Cement for the major construction site on the A 24 also came to Zarrentin by train in 2010.
The "Zarrentiner Eisenbahnverein - Posten 12" had its domicile in the Zarrentin station building, which ran a café and organized events there. However, the club has since disbanded.
Initiatives
Even today, the route would offer an alternative for traffic from Berlin to the ports of Schleswig-Holstein . In addition to the shorter connection, the Kaiserbahn would also provide relief for the Hamburg network. Above all, both the BUND and the IG Eisenbahn Ratzeburg – Zarrentin are trying to get them back into operation between Hagenow and Ratzeburg. A continuation to Bad Oldesloe is currently out of the question; This is justified by the fact that the route has already been dismantled .
The demand for a restart is related to the fact that part of the freight traffic would be shifted from road to rail and that a fast rail connection between Scandinavia and Berlin would exist after completion of a fixed Fehmarnbelt link . The state of Schleswig-Holstein guaranteed the line to be secured until 2007, and restarting it was even considered sensible for the period after 2010. The reactivation has not yet taken place (as of 2019).
Web links
- Route Hagenow Land - Zarrentin on the website of Torsten Meincke Eisenbahn GmbH
- Private website about the Kaiserbahn
- Passenger traffic on the Kaiserbahn and Hein Hollenbek - 1958
- Freight traffic on the Kaiserbahn and Hein Hollenbek - 1958
- List of operating points on eisenbahn-mv.de (formerly ralfs-eisenbahn.de)
- Website of the Ratzeburg Adventure Railway
- Website of the IG Eisenbahn Ratzeburg – Zarrentin ( Memento from June 30, 2010 in the Internet Archive )
- Website of the association Posten 12 - Zarrentiner Eisenbahnverein ( Memento from November 26, 2013 in the Internet Archive )
Individual evidence
- ^ Sven-Michael Veit: Borderline experiences (III) The emperor's new tracks. In: The daily newspaper . July 31, 2009 ( taz.de ).
- ↑ Funny hotel in the tree ( Memento from March 15, 2015 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Mecklenburg: Efforts to reactivate the line between Hagenow and Zarrentin. railfan.de, September 1, 2004, accessed on August 27, 2009 .
- ↑ Pinchas Unbelief: Visit to the "Kaiserbahn" . In: Bahn-Report . tape 33 , no. 196 , July 1, 2015, p. 32 .
- ↑ News in brief. WEMEG gives trips on the Schaalsee-Express. on lokrundschau.de, February 15, 2011, accessed on January 4, 2015 .
- ^ Hagenow Land - Hagenow Stadt railway tracks are being renewed. Schlotmann: The goal is shorter travel times. Ministry of Transport, Building and Regional Development, accessed August 26, 2009 .
- ↑ Resolution proposal: Initiation of the application procedure for the closure of the Hagenow Land - Zarrentin railway line. Amt Zarrentin , December 9, 2014, accessed January 4, 2015 .
- ↑ Mayk Pohle: The end of the Kaiserbahn is sealed. Schweriner Volkszeitung , December 11, 2014, accessed January 4, 2015 .
- ^ Railway report . 1/2011, p. 39.
- ^ Railway report . 5/2010, p. 34.
- ^ Future project Kaiserbahn ( Memento from March 17, 2005 in the Internet Archive ) NDR report by Kevin von Wissel and Marcel Gronau
- ↑ Debate on the preservation of the old Kaiserbahn ( Memento from September 27, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) In: Kieler Nachrichten. May 12, 2006.