Ebnat-Kappel
| Ebnat-Kappel | |
|---|---|
| State : |
|
| Canton : |
|
| Constituency : | Toggenburg |
| BFS no. : | 3352 |
| Postal code : | 9642 |
| UN / LOCODE : | CH EKP |
| Coordinates : | 726 982 / 236442 |
| Height : | 630 m above sea level M. |
| Height range : | 617–1949 m above sea level M. |
| Area : | 43.55 km² |
| Residents: | 5031 (December 31, 2018) |
| Population density : | 116 inhabitants per km² |
| Website: | www.ebnat-kappel.ch |
|
Ebnat-Kappel |
|
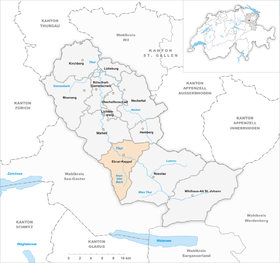
| Location of the municipality | |
Ebnat-Kappel is a municipality in the canton of St. Gallen in Switzerland. The municipality of Ebnat-Kappel is located in the Toggenburg constituency . The hamlets of Brandholz , Wintersberg and Bendel belong to it .
geography
The highest mountain Ebnat-Kappels and at the same time the highest Nagelfluhberg in Europe is the Speer at 1950 m above sea level. M.
The neighboring communities of Ebnat-Kappel are Nesslau , Hemberg , Wattwil , Gommiswald , Kaltbrunn , Schänis and Amden .
history
Until 1762 Ebnat was called Ober-Wattwil , then Ebnet . Kappel was in 1218 as a chapel , probably mentioned because of a chapel located there. On July 26, 1854, a village fire almost completely destroyed the village of Kappel. In 1847 Johann Gerhard Oncken founded the first Swiss Baptist congregation in Ebnat-Kappel .
In 1965 the municipalities of Ebnat and Kappel merged to form the municipality of Ebnat-Kappel . At the same time the two coats of arms were merged into one coat of arms. It was thus the first merger coat of arms in the canton of St. Gallen. In 2007 the hyphen between Ebnat and Kappel was deleted by the local council. Large parts of the population do not approve of the decision. In their eyes, this line symbolizes a connection between the two districts. It is argued that when they are left out, what was once merged will be separated again. In addition, the municipality is still written in official documents as Ebnat-Kappel . Since 2012, the hyphenated spelling has been common again. But even without a hyphen, Ebnat Kappel appears on the municipality's website.
→ see also section history in article Ebnat SG
→ see also section history in article Kappel SG
climate
| Ebnat-Kappel, 1981-2010 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate diagram | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Average monthly temperatures and precipitation for Ebnat-Kappel, 1981–2010
Source:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Parish partnership
There is a community partnership with the German Aalen-Ebnat .
population
| Population development | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| year | 1824 | 1850 | 1900 | 1950 | 1980 | 2000 | 2010 |
| Residents | 3721 | 4630 | 5019 | 4660 | 4950 | 5007 | 4916 |
| until 1950: Ebnat and Kappel together | |||||||
traffic
Due to an existing bypass classified as a car road, Ebnat-Kappel is spared traffic. The main road 16 leads through the village.
The railway line from Wattwil to Nesslau of the Südostbahn runs through the municipality of Ebnat-Kappel, the trains stop at a central station. In addition, the double community is developed by the Lichtensteig – Wattwil – Ebnat-Kappel bus company (BLWE).
Sightseeing and tourism
- Reformed church in the center of Ebnat, built in 1762 by Hans Ulrich Grubenmann . Hall church with front tower.
- Steinfels House , built in 1667 under Hans Jakob Bösch. Gothic-style structure with baroque detail design.
- Ackerhaus , built in Füberg in 1752 and rebuilt in Ebnat in 1951 for Albert Edelmann (1886–1963), who founded the local history museum there .
- Typical Toggenburg wooden houses have been preserved in Eich (nos. 16, 18 and 19).
- House Felsenstein in Kappel (No. 15) from 1624; Cross-ridge building with late Gothic window groups and groin-vaulted rooms.
- Near the train station there are willow figures depicting a chapel and a unicorn (flags from Kappel and Ebnat )
The 60 kilometer long Thurweg , a hiking trail along the Thur from Wil to Wildhaus, runs through the municipality .
In May 2014, the Sinnepark was opened south of the village .
Ski areas
Dance floor
South above the village at about 880 m above sea level. M. begins the ski lift Tanzboden , which leads near the dance floor . Night skiing is also possible there thanks to headlights.
| Tanzboden ski area | ||||
| lift | Persons / h | length | Height difference | Height of mountain station |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
1000 | 1350 m | 300 m | 1200 m |
Girls
Another ski area was the Girlen in the southwest of the village. The lifts were built in 1965. 1971 Girlen was the FIS homologated and approved for FIS competitions. Then European Cup races were held there, followed by a giant slalom race as part of the Alpine Ski World Cup on January 2, 1977 , with Heini Hemmi winning . The second and final event in the World Cup was on January 4, 1981 . A giant slalom took place there, won by Christian Orlainsky . This giant slalom was with the downhill in Val d'Isere on December 7, 1980 of the combined score , the Andreas Wenzel won, Pirmin Zurbriggen took there his first World Cup points. In 1997 the operation was stopped, in 1999 the Girlen lifts were dismantled and sold to South America.
Personalities
- Wendelin Looser (1720–1790), house organ builder
- Joseph Looser (1749–1822), house organ builder
- Johann Melchior Grob (1754–1832), house organ builder
- August Scheler (1819–1890), linguist
- Babeli Giezendanner (1831–1905), painter
- August Bösch (1857–1911), sculptor
- Albert Edelmann (1886–1963), teacher, painter and promoter of local folk and cultural assets
- Guido Looser (1892–1937), writer
- Toni Brunner (* 1974), politician
photos
Aerial photo of Walter Mittelholzer's brush factory from 1925
Aerial photo of the gymnastics equipment factory Alder-Fierz & Gebr. Eisenhut by Walter Mittelholzer , approx. 1918–1937
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Permanent and non-permanent resident population by year, canton, district, municipality, population type and gender (permanent resident population). In: bfs. admin.ch . Federal Statistical Office (FSO), August 31, 2019, accessed on December 22, 2019 .
- ↑ Ebnat-Kappel again with hyphen
- ↑ Climate table. (PDF) In: meteoschweiz.admin.ch. meteoschweiz, accessed on April 9, 2018 .
- ↑ a b Information from an old ski atlas ( online )
- ↑ Speer Ski Club: About Us , accessed on November 30, 2015
- ↑ St. Galler Tagblatt: Girlen Races In the beginning there were four disciplines , February 9, 2015, accessed on November 30, 2015
- ↑ FIS: Database with all World Cup races in Ebnat-Kappel ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , accessed November 30, 2015
- ↑ beat glogger: Hot time: climate change and natural disasters in Switzerland , page 109. vdf university Verlag AG, 1998. ISBN 978-3-7281-2613-9
- ↑ St. Galler Tagblatt: At that time: Poor tax increased from 15 to 25 Rp. ( Memento from March 4, 2016 in the Internet Archive ), November 12, 2008