Manchuria
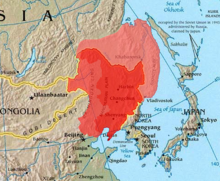
The Manchuria ( Chinese 滿洲 / 满洲 , Pinyin Mǎnzhōu - "land of the Manchus"), even Manjurei , is a historical landscape that in today's People's Republic of China , Russia and small parts in the Mongolia is located. It includes the provinces Heilongjiang , Jilin and Liaoning ( 東三省 / 東北 三省 / 东三省 / 东北 三省 , Dōngsānshěng / Dōngběi Sānshěng - " Three Provinces of the East / Northeast "), historically also Hulun Buir , Hinggan , Tongliao and Chifeng in the Inner Mongolia . The region is also called Northeast China ( 東北 / 东北 , Dōngběi , short for: 東北 地區 / 东北 地区 , Dōngběi Dìqū - " Northeast China Region ").
The area of today's Manchuria in the People's Republic of China is bordered in the northeast by Heilong Jiang (Amur) and Ussuri , in the north by Heilong Jiang and the Great Hinggan Mountains , in the southwest by the Great Wall of China and in the southeast by Yalu Jiang . It borders Russia ( Siberia ) in the north and east, Mongolia in the west and North Korea in the south with Manchuria.
history


The native inhabitants of Manchuria were mainly Koreans and Jurchen , the ancestors of the Manchu . The name of the region, which was naturalized in the 19th century, is derived from the latter. Furthermore, more recent theories (2012) assume that the original home of the Turkic peoples was in southwestern Manchuria.
The old traditional Chinese name is Guanwai ( 關 外 / 关 外 , Guānwài - "literally: outside the passport / border pass"). Probably from the 12th century, at the latest from the Yuan Dynasty , the province was an integral part of the Chinese Empire . In 1616 Nurhaci united the Manchu tribes and established the Manchu dynasty . After his death, his son Huang Taiji changed the name to Qing in 1636 (literally translated: "pure"), which from 1644 to 1912 became the name of the Chinese imperial dynasty led by the Manchu . Throughout Manchuria, Han and other Chinese tribes were banned from immigration until 1859 .
This was followed by a strong relaxation until 1930, in particular to counteract Russian expansion efforts in the sparsely populated region. This movement was called “chuang guandong” ( 闖關 東 / 闯关 东 , chuǎng Guāndōng - “literally: storm / push over the eastern pass”) in China . The influx meant that the Manchu are now only a minority in the region. The Manchurian language has now largely died out.
With the expansion of Russia to Siberia and Japan to Korea , Manchuria came into the interests of both great powers . In 1858, the Treaty of Aigun forced China to cede over half a million square kilometers of its Manchurian territory to Russia. Less than two years later, Russia broke the treaty and in 1860 was granted the entire Outer Manchuria on the basis of the Beijing Convention . Thereafter, the name Manchuria was limited to the part that remained with China, Inner Manchuria . The People's Republic of China later annexed western Manchuria to the autonomous Inner Mongolia .
From 1900 the Russian Empire tried to occupy the whole of Manchuria. This occupation led to tension between Russia and Japan and ended in 1904 in the Russo-Japanese War . The Japanese Empire won the dispute. Russia had to evacuate Inner Manchuria and return it to China. Regardless, the two powers maintained different territorial rights in Manchuria. Japan took over the South Manchurian Railway from Russia , which was protected by the Kwantung Army , and Russia kept the Chinese Eastern Railway , which was monitored by Russian troops.
The province, divided into different spheres of influence, experienced an epidemic of pulmonary plague in 1910/1911 , which spread along the railway routes. This fell victim to around 45,000 to 60,000 people in a population of around 12.5 million. The Chinese doctor Wu Lien-teh created the Manchurian Plague Prevention Service on behalf of the Chinese government in response to the epidemic . This became the nucleus of public health services during the Republic of China.
In 1915, Japan made twenty-one demands on China, including a claim for greater influence in Manchuria. These demands, and the acceptance by Yuan Shikai , sparked violent protests in China and supported the May Fourth Movement . From 1917 Manchuria was an autonomous province and only united with the Republic of China in 1928 under the Chinese warlord Zhang Xueliang . In the Soviet-Chinese border war in 1929, the Republic of China tried to push back the spread of Soviet power in Manchuria. This conflict ended in Chinese defeat and left a power vacuum in Manchuria.
In the course of the Manchurian Crisis , the Kwantung Army occupied Manchuria in 1931 without consulting the Japanese government and established the Manchurian Empire ( Manchukuo ) as a puppet state . The head of state became Puyi , the last emperor of China . The League of Nations protested against this process unsuccessfully . In 1935, the Soviet Union concluded an agreement with the Manchurian Empire on the sale of the East China Railway, along with other trade agreements, in which at least a de facto recognition of Manchukuos was to be seen.
To the horror of the national Chinese as well as the Chinese communists, the Japanese-Soviet relations culminated in a peace and friendship treaty after the Nomonhan incident, in which the Soviet Union promised, among other things, to respect the territorial integrity and inviolability of Manchukuo, while Japan did the same for them Mongolian People's Republic , the puppet state of the Soviet Union, did.
With its concept of the " Greater East Asian Prosperity Sphere ", the Japanese government lured millions of Chinese and tens of thousands of Mongolians to Manchukuo. Indeed, the economic indicators were staggering. For example, Japan quickly expanded the Manchurian railway network to 12,000 kilometers, which was more than half of the Chinese railway network. Manchuria thus developed into the most modern industrial region with the highest standard of living in China. As a result, the population in Manchuria rose from around 17 million (1917) to around 40 million by the end of the 1930s. In 1939 nine out of ten residents were Han (35.7 million), followed by Koreans (three percent) and Mongols (two and a half percent).
On August 8, 1945, two days after the atomic bombing of Hiroshima , at a time when the Japanese government was already conducting armistice talks, the Soviet Union declared war on Japan and occupied Manchuria as part of what is now known as Operation August Storm . In the months that followed, the Soviet occupiers dismantled all armaments and industrial facilities that Japan had built in Manchuria. Thousands of trains with machines, equipment and dismantled factory buildings rolled in the direction of Siberia. Before they withdrew, the Soviets also unscrewed all the rails. The value of the Manchurian looted property exceeded two billion dollars - a huge sum at the time. Manchuria was returned to China in May 1946.
The clashes over the areas annexed by the Red Army in the Soviet-Chinese border war in 1929 led to further military conflicts in the 1960s, such as the incident on the Ussuri . The territorial dispute was only resolved after the collapse of the Soviet Union . In the “Supplementary Agreement on the Eastern Part of the Sino-Russian Border between the People's Republic of China and the Russian Federation” of October 14, 2004, Russia undertook to return some of the areas it occupied in 1929, such as Abagaitu Zhouzhu , Heixiazi Dao and Qagan Shuangwa , to China . The return and the establishment of the 4300-kilometer border between the two states was ratified on July 23, 2008.
Shamanism
Manchurian shamans continue to exercise their office in some villages in northeast China's provinces . The Chinese emperors of the Manchu dynasty had already codified Manchurian shaman rituals. The sacrificial rituals show similarities with those of the Altaic Turkic peoples and the Tungus . In addition to medicine, Manchurian shamans are primarily concerned with the preservation of the clan cult.
Major cities
- Changchun ( 長春 / 长春 )
- Dalian ( 大連 / 大连 )
- Fushun ( 撫順 / 抚顺 )
- Harbin ( 哈爾濱 / 哈尔滨 )
- Jilin ( 吉林 )
- Qiqihar ( 齊齊哈爾 / 齐齐哈尔 )
- Shenyang ( 瀋陽 / 沈 阳 ; formerly Mukden)
Important rivers
- Hēilóng Jiāng ( 黑龍江 / 黑龙江 ; Russian Amur)
- Songhua Jiang ( 松花江 )
traffic
The Trans-Manchurian Railway , a branch of the Trans-Siberian Railway, runs through Manchuria .
The legendary Ajia express train (see Shinkansen ) ran on the Dalian - Changchun section from 1934 to 1945 (during the Japanese occupation ).
See also
literature
- Thomas R. Gottschang, Diana Lary: Swallows and Settlers. The Great Migration from North China to Manchuria . Center for Chinese Studies, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor 2000, ISBN 0-89264-134-7 .
- Gustav Fochler-Hauke : Manchuria. A geographical-geopolitical study of the country (= writings on military geopolitics. Volume 3). Vowinckel, Heidelberg 1941.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Term "Dongsansheng (東三省 / 东三省)", Chinese / English: [1] on zdic.net, accessed on February 19, 2018 - online
- ^ Term "Dongbei (東北 / 东北)", Chinese: [2] on zdic.net, accessed on February 19, 2018 - Online
- ^ Ahn, Sung-Mo (June 2010). "The Emergence of Rice Agriculture in Korea: Archaeobotanical Perspectives". Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences . 2 (2): 89-98. doi: 10.1007 / s12520-010-0029-9 . ISSN 1866-9557.
- ↑ 한민족 . ( naver.com [accessed August 29, 2018]). 한민족 ( Memento from June 22, 2013 on WebCite )
- ^ Johanson, Lars. 2010. "The high and low spirits of Transeurasian language studies" in Johanson and Robbeets (2010), 7-20.
- ^ Wolfram Eberhard , Alide Eberhard: Geschichte Chinas. From the beginnings to the present (= Kröner's pocket edition . Volume 413). Kröner, Stuttgart 1971, DNB 456503854 , p. 32 f.
- ↑ ibid
- ^ Hermann Beyer-Thoma: Munich research on the history of Eastern and Southeastern Europe. Ars Una, 2002, p. 66.
- ↑ ibid
- ^ William C. Summers: The Great Manchurian Plague of 1910-1911. New Haven, 2012, p. 1; P. 63f, p. 105, p. 109
- ↑ Gerald Mund: East Asia in the Mirror of German Diplomacy. Franz Steiner Verlag, 2006, p. 46 f.
- ↑ Felix Patrikeeff: Russian Politics in Exile. The Northeast Asian. Balance of Power 1924-1931. Palgrave Macmillan UK, 2002, p. 52 f.
- ↑ Patrick J. Buchanan: Churchill, Hitler and the unnecessary war . Military history publisher Pour le Mérite, Selent 2009, p. 107.
- ^ Stefan Talmon: Collective non-recognition of illegal states. Basics and legal consequences. Mohr Siebeck, 2006, p. 121.
- ^ Stuart D. Goldman: Nomonhan, 1939. Naval Institute Press, 2012, 171.
- ^ Declaration Regarding Mongolia April 13, 1941. Avalon Project at Yale University, accessed July 1, 2017.
- ↑ Felix Patrikeeff: Russian Politics in Exile: The North East Asian balance of power, from 1924 to 1931. In: Manchurian Railways and the Opening of China: An International History, Basingstoke 2002, p. 16.
- ↑ Ulrike Jureit: Contested spaces. Spatial images, the will to order and the mobilization of violence. Wallstein, 2016, pp. 217-238.
- ↑ Ulrike Jureit: Contested spaces. Spatial images, the will to order and the mobilization of violence. Wallstein, 2016, pp. 217-238.
- ↑ Gottfried Schramm: Handbook of the history of Russia. From autocratic reforms to the Soviet state. Volumes 1856–1945. Hiersemann-Verlag, 1992, p. 992.
- ↑ The barbarians - insignificant and obnoxious. Der Spiegel from July 3, 1989, accessed on September 17, 2017
- ^ Long border between Russia and China Die Welt, July 23, 2008, accessed on September 17, 2017
- ↑ Mihály Hoppál : The Book of Shamans. Europe and Asia. Econ Ullstein List, Munich 2002, ISBN 3-550-07557-X . P. 80 ff.