Strychnine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
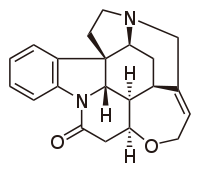
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Strychnine | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
(-) - strychnine |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 21 H 22 N 2 O 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless, bitter-tasting crystals |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 334.42 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.36 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
268 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
270 ° C (6.7 h Pa ) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
poor in water (143 mg l −1) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Strychnine [ ʃtʁɪçˈniːn ] is a very poisonous alkaloid . It belongs to the Strychnos alkaloids within the group of indole alkaloids . Even in small doses, strychnine causes muscles to become rigid. Strychnine was used in very low doses as an analeptic and is on the doping list. It was also used as a rat poison in the past .
history
Strychnine was first isolated in 1818 by the French pharmacists Pierre Joseph Pelletier and Joseph Bienaimé Caventou . The elucidation of the complex structure of strychnine succeeded Sir Robert Robinson in 1946 . In 1954 Robert Burns Woodward finally succeeded in the chemical synthesis of strychnine. Sir Robert Robinson and Robert Burns Woodward were honored for these achievements with the Nobel Prize (1947 and 1965). Since then, some chemists have achieved an enantioselective synthesis.
properties
Strychnine forms colorless, extremely bitter-tasting prism-shaped crystals that are hardly soluble in water, but readily soluble in alcohols - such as ethanol - or in chloroform .
Mode of action
Strychnine is a competitive antagonist at the glycine receptor . This means that in the nervous system , especially in the spinal cord, it displaces the inhibitory neurotransmitter glycine at the glycine receptor . Along with GABA, glycine is one of the most important inhibitory neurotransmitters. The receptor in question for glycine is a chloride channel in the spinal cord . Strychnine influences this receptor and thus prevents the inhibiting effect of glycine. This leads to overexcitation of the spinal cord nerves, which cause the symptoms of strychnine poisoning. Strychnine works in a similar way to other toxins that disrupt this channel, such as tetanospasmin .
poisoning
An amount of 30 to 120 mg of strychnine can be fatal to an adult human. Strychnine is quickly absorbed through the mucous membranes. Subcutaneous or intravenous amounts of 15 mg or more can be fatal. In the event of poisoning, an emergency doctor should be called immediately. Emergency treatment includes the use of benzodiazepines (such as diazepam ) as standard .
Symptoms of poisoning are:
- Shortness of breath
- Trembling / twitching of muscles
- severe convulsions
In contrast to the depiction in detective novels, strychnine is poorly suited for murder through (oral) poisoning, since it can still be tasted in a dilution of 1: 130,000. Nevertheless, isolated murders attributable to strychnine poisoning have been documented. The serial killer Thomas Neill Cream killed some of his victims in the USA and England with the help of strychnine.
Antidote, first aid for poisoning
If strychnine is swallowed, activated charcoal can be used to prevent further absorption of the poison into the body, and laxatives can be used to excrete the poison . In the event of skin or eye contact, the affected area should be cleaned with water or polyethylene glycol . Physostigmine is used as an antidote to strychnine and vice versa. Strychnine intoxications are often treated with drugs from the benzodiazepine group ( Valium , Diazepam ), which increase the inhibitory effect of the GABA receptors and thus counteract the toxicological effect of strychnine.
Occurrence
Strychnine is found in the seeds of the common peanut nut ( Strychnos nux-vomica ) and the Ignatius peanut ( Ignatia amara ).
synthesis
The classic total synthesis of strychnine goes back to Woodward (1954). Since then, the compound has always been an interesting target for organic chemists.
use
doping
Because of its analeptic (stimulating) effect, strychnine was added to the doping list after 1945 . During the marathon at the 1904 Olympic Games , Thomas Hicks took brandy strychnine.
At the 2016 Summer Olympics , the Kyrgyz weightlifter Issat Artykow was disqualified for consuming strychnine and had to return his bronze medal.
Strychnine as an intoxicant
In doses of 0.5 to 5 mg, strychnine leads to strong arousal with euphoria and an intensified perception of colors. Since around 1920, strychnine has been added to heroin used for smoking, mainly in Asia ; this displaced heroin has also appeared in Europe (the Netherlands and Italy) since 1973/1974. The strychnine serves here to compensate for the respiratory depression caused by the heroin , and thus enables higher doses.
Strychnine as a drug
In Ayurvedic medicine strychnine plays a significant role and is loss of appetite, fever, for example, anemia , lumbago and stimulate peristalsis applied. It was often used as an aphrodisiac in the past . It was popularly used for a variety of diseases such as gastrointestinal and cardiovascular problems as well as 'nervousness', depression and migraines. Adolf Hitler is said to have taken strychnine daily from 1936 to 1943 for flatulence. The strychnine-containing seeds of the peanut nut and the Ignatius bean are used in homeopathy under the names Nux vomica and Ignatius for the treatment of menstrual pain, headache, depressive mood, rheumatic pain and asthma, among other things. With sufficient homeopathic potentiation, these homeopathic preparations contain no or only very small amounts of strychnine and therefore have no typical effects or side effects.
In modern medicine, radioactively labeled strychnine is used as a tracer to detect glycine receptors .
Analytics
The reliable qualitative and quantitative detection of strychnine is possible with chromatographic methods. The thin layer chromatography is however rarely used and is usually only in the presence of relatively high concentrations as a qualitative test. Sufficient sample preparation steps are essential if complex test material is available . The methods most frequently used today are the GC / MS coupling or the coupling of HPLC with mass spectrometry . The latter methods are also suitable for doping controls and for use in forensics .
See also
- Peanuts ( strychnos )
- Brucine , a highly poisonous alkaloid also found in the nugget
- Bicuculline of the heart flowers and picrotoxin of the pseudo myrtle are also neurotoxins that prevent the effect of inhibitory neurotransmitters.
Web links
- Strychnine . In: Merck's Warenlexikon . 3rd ed. 1884 ff., P. 559 f.
- Strychnine . In: Meyers Konversations-Lexikon . 4th edition. Volume 15, Verlag des Bibliographisches Institut, Leipzig / Vienna 1885–1892, p. 399.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Entry on strychnine. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 22, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on strychnine in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Entry on Strychnine in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ a b R. B. Woodward, Michael P. Cava, WD Ollis, A. Hunger, HU Daeniker, K. Schenker: THE TOTAL SYNTHESIS OF STRYCHNINE. In: Journal of the American Chemical Society. 76, 1954, p. 4749, doi: 10.1021 / ja01647a088 .
- ↑ Umer Chaudhry: Hypoxia-Induced Spreading Depression Episodes in Acute Medullary Rat brainstem sections . Göttingen 2011, DNB 1042344914 , p. 15–16 , urn : nbn: de: gbv: 7-webdoc-2907-7 (dissertation, University of Göttingen).
- ^ Stanley I. Heimberger, A. Ian Scott: Biosynthesis of strychnine . In: Chemical Communications . No. 6 , January 1, 1973, doi : 10.1039 / c39730000217 .
- ↑ Entry on physostigmine in Flexikon , a wiki from DocCheck , accessed on November 25, 2015.
- ↑ M. Cloetta: Textbook of toxicology for study and practice. Springer-Verlag, 2013, ISBN 978-3-642-90813-2 , p. 293 ( limited preview in the Google book search).
- ↑ Behrends, Jan C .: Dual Series Physiology . 2., revised. Ed. Thieme, Stuttgart 2012, ISBN 978-3-13-138412-6 .
- ↑ New Total Syntheses of Strychnine . In: Angewandte Chemie . tape 106 , no. 11 , 1994, pp. 1204–1209 , doi : 10.1002 / anie.19941061106 .
- ↑ Kathryn Harkup: The cocktail of poison and brandy that led to Olympic gold. In: The Guardian . July 21, 2016, accessed February 20, 2020 .
- ↑ Weightlifting: Bronze winner Artykow convicted of doping. In: spiegel.de . August 18, 2016, accessed August 18, 2016.
- ↑ Thomas Geschwinde: Drugs: Market forms and modes of action. 5th edition, Springer Verlag, 2007, ISBN 978-3-540-43542-6 , p. 545.
- ↑ Gabrielle Drunecky: Strychnine in Heroin ( Memento from June 25, 2004 in the Internet Archive ). Information & Documentation Unit, Vienna, 2002.
- ↑ Thomas Geschwinde: Drugs: Market forms and modes of action. 5th edition, Springer Verlag, 2007, ISBN 978-3-540-43542-6 , p. 308.
- ^ A b c Rudolf Hansel: Hager's handbook of pharmaceutical practice. Volume 6: Drugs PZ. 5th edition. Springer, 1994, ISBN 3-540-52639-0 , pp. 835-837.
- ^ Volkmar Sigusch: Practical Sexual Medicine. Deutscher Ärzteverlag, 2005, ISBN 3-7691-0503-6 , p. 70.
- ^ Ernst Günther Schenck : Patient Hitler. Droste Verlag, 1989, pp. 199-201.
- ↑ Markus Wiesenauer, Suzann Kirschner-Brouns: Homeopathy - The great manual. Gräfe and Unzer Verlag, 2007, ISBN 978-3-8338-0034-4 , p. 391.
- ^ Y. Li, H. Zhang, J. Hu, F. Xue, Y. Li, C. Sun: A GC-EI-MS-MS method for simultaneous determination of seven adulterants in slimming functional foods. In: Journal of Chromatographic Science . 50 (10), 2012, pp. 928-933. PMID 22732254
- ↑ SS Kataev, EA Krylova: Quantitative determination of strychnine in blood and urine by gas chromatography with mass-selective detector. In: Sud Med Ekspert. 53 (6), Nov-Dec 2010, pp. 35-38. PMID 21404532
- ↑ SW Ng, CK Ching, AY Chan, TW Mak: Simultaneous detection of 22 toxic plant alkaloids (aconitum alkaloids, solanaceous tropane alkaloids, sophora alkaloids, strychnos alkaloids and colchicine) in human urine and herbal samples using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. In: J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 942-943, Dec 30, 2013, pp. 63-69. PMID 24216273







