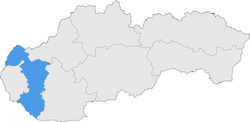
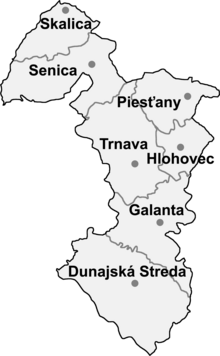
Trnavský kraj
| Trnavský kraj | |||
|
|||
| Parent state | Slovakia | ||
| Type of administrative unit | Kraj | ||
| Administrative division | 7 okresy | ||
| surface | 4,158 km² | ||
| Residents | 564,917 (December 31, 2019) | ||
| Population density | 135.86 inhabitants / km² | ||
| Language (s) | Slovak , Hungarian , Czech | ||
| Religion (s) | Roman Catholic | ||
| Nationality (s) | Slovaks , Hungarians , Czechs | ||
| Administrative seat / capital | Trnava | ||
| Code number / character | 02 | ||
| Telephone code | +421 | ||
| Time zone | UTC +1 | ||
| Code according to ISO 3166-2 | SK-TA | ||
The Trnavský kraj ( Tyrnauer Landschaftsverband ) is an administrative area in western Slovakia .
Districts
The Kraj consists of the following 7 districts ( okresy ):
geography


The area has an area of 4,158 km² and 564,917 inhabitants (as of December 31, 2019), is narrow and elongated and is considered a connecting region between Bratislava and the rest of Slovakia. It borders the Czech Republic and Austria in the northwest and Hungary in the south. The northern third (districts Senica and Skalica) is separated from the rest by the Little Carpathians and is mainly formed by the Záhorie lowland with its two subdivisions - the hilly Chvojnická pahorkatina and the flat Borská nížina . Parts of the Myjavská pahorkatina and the White Carpathians also encroach on the Kraj area. South of the Little Carpathians is the large Danube lowland , divided into the Danube hill country in the north and the Danube plain in the south, including part of the large Schüttinsel . The Inowetz extends along the Hlohovec-Piešťany line . Larger rivers are the March in the northwest, the Waag in the east, the Little Danube and the Danube in the south, dammed here in the Gabčíkovo hydropower plant . The highest point is the Záruby mountain ( 767 m nm ), which is also the highest point of the Little Carpathians; the lowest point is on the Little Danube near the municipality of Okoč ( 110 m nm ).
There are four protected landscape areas in the Kraj area: Biele Karpaty (White Carpathians), Dunajské luhy (Danube meadows), Malé Karpaty (Little Carpathians) and Záhorie (Marchauen).
From the point of view of the administrative structure, the Trnavský kraj borders on the Trenčiansky kraj in the north, the Nitriansky kraj in the east, the Hungarian Győr-Moson-Sopron county in the south, the Bratislavský kraj in the west and Lower Austria and the Jihomoravský kraj in the north-west.
Historical administrative units
In the Kingdom of Hungary , the area in the south around the city of Trnava and, to a lesser extent, in the north part of Pressburg County ; smaller parts in the south belonged to Moson County and Raab County . The rest belonged to Neutra County .
Development after the collapse of Austria-Hungary in 1918:
- 1918 / 1919–1922: as above, but Moson county was incorporated into Bratislava county ( Bratislavská župa ) and Raab county into Komorn ( Komárňanská župa ) county , Czechoslovakia
- 1923–1928: Bratislavská župa (Bratislava County), Czechoslovakia
- 1928–1939: Slovenská krajina / zem (Slovak Land), Czechoslovakia
- 1940–1945: Bratislavská župa (Bratislava County), Nitrianska župa (Neutra County) and Trenčianska župa ( Trenčian County), First Slovak Republic
- 1945–1948: Slovenská krajina (Slovak Land), Czechoslovakia
- 1949–1960: Bratislavský kraj (Bratislava landscape association, majority) and Nitriansky kraj (Neutra landscape association, smaller parts) - they are not to be confused with today's, Czechoslovakia
- 1960–1990: Západoslovenský kraj (West Slovak Regional Association), Czechoslovakia
- since 1996: today's Trnavský kraj
population
Trnavský kraj is the least populous of all Kraje, but not the smallest in terms of area. The population density is 134 / km² and the proportion of the urban population is around 50% (as of 2008). The capital and the largest city is Trnava (Tyrnau) with 65,033 inhabitants, other cities are Piešťany , Hlohovec (Freistadtl), Galanta (Gallandau) and Dunajská Streda . The regional association consists of a total of 251 municipalities , 17 of which are cities.
According to the 2011 census, exactly 554,741 people lived in Trnavský kraj. The largest part was made up of the Slovaks (394,902 inh., 71.2%), followed by the Magyars (120,784 inh., 21.8%), Czechs (3,259 in., 0.6%) and Roma (3,048 inh. , 0.5%). Other ethnic groups together make up 0.5% (2,670 inh.) Of the population, while 30,778 inhabitants (5.4%) gave no information about the ethnic group.
In terms of denomination, the Roman Catholic Church is the most widespread denomination with 388,914 inhabitants (70.1%), followed by the Evangelical Church AB (20,441 inh., 3.7%) and the Reformed (Calvinist) Church (10,849 inh., 2%). Furthermore, the population committed to the Greek Catholic Church (1,350 inh., 0.2%), the Evangelical Methodist Church (1,165 inh., 0.2%) and the Jehovah's Witnesses (1,041 inh ., 0.2%) %); a total of 5,413 inhabitants (0.9%) professed a different denomination. 71,057 inhabitants (12.8%) had no denomination and for 54,705 inhabitants (9.9%) no denomination was determined.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ^ Kopa, Ľudovít et al .: The Encyclopaedia of Slovakia and the Slovaks . Encyclopedic Institute of the Slovak Academy of Sciences ( Memento of June 26, 2008 in the Internet Archive ), Bratislava 2006, ISBN 80-224-0925-1 .
- ^ Kováč, Dušan et al .: Kronika Slovenska 2 . Fortuna Print, Bratislava 1999, ISBN 80-88980-08-9 .
- ^ The area of Dunajská Streda and Galanta was part of Hungary from 1938–1945 through the First Vienna Arbitration .
- ↑ Statistical Office of the Slovak Republic ( Memento of the original dated February 26, 2011 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Results of the 2011 census (Slovak)