March (river)
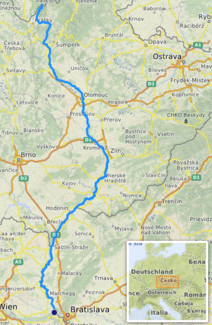
The March ( Morava in Czech and Slovak , Latin Marus ) is a left tributary of the Danube in Central Europe. It drains about three quarters of the Moravia named after it and is its main river.
In its lower course , it is accompanied on both sides by a flood dam . It is the border river between the Czech Republic and Slovakia (about 50 km) and between Austria and Slovakia (91 km). Because of the many meanders in the river, the straight line of these routes is only 37 or 50 km.
geography
The March rises in the Glatzer Schneegebirge at an altitude of 1194 m near the Quarklöchern (two limestone caves) on the southern slope of the Glatzer Schneeberg on the border between Poland and the Czech Republic, about one kilometer northwest of the border triangle Poland- Bohemia - Moravia and initially runs 13 km on the Territory of the Bohemian region of Pardubice until it reaches the Moravian region of Olomouc south of the municipality of Dolní Morava . After 358 km it flows into the Danube at the Thebener Pforte opposite Hainburg an der Donau (Austria) near Devín (Slovakia). The mean discharge at the Angern gauge is 108 m³ / s. The diverse ramifications of the March river limits its navigability to the lower course.
The main tributaries are the Bečva on the left and the Thaya on the right . To the right (west) of the lower reaches of the March is the Marchfeld in Lower Austria .
The only larger cities on the March are Olomouc and indirectly Bratislava , smaller cities and towns are Kroměříž , Uherské Hradiště , Hodonín , Hohenau , Dürnkrut , Angern an der March and Marchegg . There are currently only three bridges across the section where the March forms the border between Austria and Slovakia:
- Hohenau - Moravský Svätý Ján (road bridge)
- Hof Castle - Devínska Nová Ves ( Bicycle Bridge of Freedom , for pedestrians and cyclists, since August 9, 2012)
- Marchegg - Devínska Nová Ves (railway bridge connecting Vienna - Bratislava over the Eastern Railway (Marchegger Ast) )
There is a ferry between Angern an der March and Záhorská Ves , which should be replaced by a road bridge. Construction was initially scheduled to start in 2010, but as the financing was not secured at that time, construction was postponed. In 2013, the city of Bratislava announced that construction would start in 2015. In a referendum on September 21, 2014 about the planned March Bridge in Angern, almost three quarters of Angern voters spoke out against the construction of the road bridge (turnout 65%). Planning for this location was then canceled by the state of Lower Austria.
Bicycle bridges were planned in Marchegg and Dürnkrut, but failed in the referendum on February 19, 2017.
Surname


The name is of very ancient origin and is derived from the Indo-European term * mori (= body of water ). The March has nothing to do with the term “mark” ( border ), although it is a border river.
The body of water was first documented in 892 as "Maraha".
history
Even in antiquity, the lower March (in the southern area up to the mouth of the Danube) was important as a river that was difficult to cross. Only on the southern bank of the Danube were the Roman border fortifications , above all Carnuntum .
Since the beginning of the 7th century at the latest, Slavs, coming from the Danube, have been moving north along the March and colonizing the surrounding area. Since then, the March has been the center of the country named after it, Moravia ( Morava ). It is unclear whether the kingdom of Samo extended along the March around 623. In the 9th century the lower reaches of the March with the settlement complexes Morava ( Mikulčice ) and Veligrad ( Staré Město u Uherského Hradiště ) is the center of the Moravian Empire . In 1063, a Moravian diocese was founded on the Upper March in Olomouc .
The Austro-Slovak section of the March is one of the oldest state borders in Austria and Lower Austria, eastern border since the 11th century. From 1526 (accession of the Habsburgs to Hungary ) to 1918 (dissolution of Austria-Hungary ) the March was the internal border in this section of the Habsburg Monarchy , and until 1806 it was also the external border of the Holy Roman Empire .
In addition to an existing stone bridge from 1771, it was possible to cross the March from Vienna to Bratislava via a railway bridge two kilometers away from 1848. It was from here that railway construction began throughout Slovakia. In 1918–1939 and 1945–1992 Czechoslovakia bordered Austria here, and 1939–1945 the Nazi satellite state Slovakia bordered with the German Empire . 1945–1989 the March was part of the Iron Curtain here ; Refugees to Austria risked being shot by Czechoslovak border guards. The stone bridge was blown up by Czechoslovak communists in 1947.
After the fall of the Iron Curtain in 1989, numerous temporary arrangements were set up as walkways across the March during the initial euphoria. The ferry between Angern and Záhorská Ves also started operating in the late 1990s.
At the end of December 2007, the border controls between Slovakia and Austria no longer exist due to the Schengen Agreement.
On September 25, 2011 the groundbreaking ceremony for the pedestrian and cycle path bridge over the March between Hof Castle and Devínska Nová Ves took place. The bridge, which aims to stimulate cycle tourism on both sides of the river, was opened to traffic on August 9, 2012. In September 2012 it was opened as a bicycle bridge for freedom . The Maria-Theresien-Brücke had been at this point since 1771, but was destroyed 100 years later by ice floes.
Protected areas

There are several protected areas along the March, including:
- Ramsar area Donau-March-Thaya-Auen (cross-border)
- Austria
- European protected areas March-Thaya-Auen (European bird sanctuary and FFH protected area)
- Landscape protection area Donau-March-Thaya-Auen
- Angerner nature reserve
- Dürnkruter Marchschlingen nature reserve
- Untere Marchauen nature reserve and WWF Marchegg nature reserve
- Slovakia
- Záhorie Protected Landscape Area (CHKO Záhorie)
- Czech Republic
- Národní přírodní rezervace Ranšpurk , near Lanžhot
- Ramena řeky Moravy , wetland between Litovel and Olomouc
- Národní přírodní rezervace Vrapač , near Litovel
With the National Park Strategy 2010 it was announced that a national park would be set up for the March-Thaya floodplains, which are still insufficiently protected at national level .
In addition to the specified protected areas, there are ongoing individual projects that aim to protect flora and fauna in sub-areas as well. Cross-border projects are also increasingly being carried out. For example, since 2007, an action for the protection of birds of prey (such as Imperial Eagle and Saker ), storks and owls ( owls under the name) CORO-SKAT (Conservation Of Raptors and Owls) run in. Organizations such as Birdlife Austria and Ochrana dravcov na Slovensku (Raptor Protection of Slovakia - RPS) work together.
Floods
The March floods annually, especially after the snow has melted. The higher water levels necessary for the flooding of the Marchauen usually only lead to roadblocks at the border crossings that are not suitable for flooding.
However, major flood events are recorded again and again. So that in 1997 caused great damage on the Slovak side. A younger one that surpassed the previous one and caused a lot of damage was that after the snow melt in spring 2006. Several dam breaks in Austria, as in Jedenspeigen, caused great damage on the private side as well as on the infrastructure, for example on the northern railway . It was a 100-year flood with a total damage amount of 72 million euros in Austria alone.
Main article: Thaya-March flood 2006
Flood protection in Austria
For this reason, there are long dams on both the left and right banks. On the Austrian side alone, there are 57 km of dams that were continuously built between 1936 and 1964. As a result of the straightening that took place, the March was deepened to two meters and the gradient was increased from 0.0153% to 0.021%.
Renewal of the dams was planned after the flood in 1997. The Angern – Mannersdorf – Stillfried and Waidendorf – Dürnkrut – Jedenspeigen sections should be repaired as a priority. The EIA was only submitted in 2004 . The dam heights should be aligned with those in Slovakia. The flood in 2006 overran these plans, as it revealed the actual poor condition of the dams. Except for two short sections, the dam had to be renovated along its entire length. The second phase was completed on schedule in 2007. The complete renovation should have been completed by 2012. Initial differences about responsibilities and the related financing issues were resolved in such a way that via donau was responsible for the renovation . Most of the renovation has now been carried out, but has not yet been completed. Remaining work should be carried out in 2015.
The WWF criticizes the state of Lower Austria for these flood protection measures. Due to an amendment to the Nature Conservation Act in 2007, the construction measures are excluded from a nature compatibility assessment, so that the nature conservation interests no longer have to be adequately taken into account in the eyes of the WWF.
There are differences of opinion regarding nature conservation procedures. While the state of Lower Austria wanted to repair it as soon as possible due to the massive damage, the environmental umbrella organization lodged a complaint with the European Union because, in its opinion, the EU bird protection directive was not taken into account. The state argued that it was a repair and that human protection had priority over nature conservation.
In February, the renewed dam system was opened on the Lower Austrian side with a length of 65 km. It should offer protection against a 100-year flood. Feeder dams with a length of 3 km were also included in this project, which cost 125 million euros. It took seven years to build.
International flood protection
As part of the CEframe (Central European Flood Risk Assessment and Management in Centrope ) project, the state of Lower Austria took over the management in 2010 in order to work with the states of Austria, the Czech Republic, Slovakia and Hungary to establish the basics for the common river basins, to which the March also belongs for future flood management.
literature
- General German real encyclopedia for the educated classes. Conversation lexicon; 10th edition 1853, FA Brockhaus Leipzig
- A. Stancik, H. Schiller, O.Behr et al .: Hydrology of the River Danube / Hydrologie der Donau. Joint research project of the Danube countries and the IHD , 272 p., Priroda Verlag, Bratislava 1988.
- The lower course of the March around 1873 (recording sheets of the land survey )
Dürnkrut, Stillfried
Marchegg and Zwerndorf ,
See also
- List of rivers in Slovakia
- Morava (river) , namesake in Serbia
Individual evidence
- ↑ BMLFUW (Hrsg.): Area directory of the river areas: Danube area from the Enns to the Leitha. In: Contributions to Austria's Hydrography Issue 62, Vienna 2014, p. 148. PDF download , accessed on July 8, 2018.
- ↑ Federal Ministry for Agriculture, Forestry, Environment and Water Management (Ed.): Hydrographisches Jahrbuch von Österreich 2011. 119th Volume. Vienna 2013, p. OG 259, PDF (12.9 MB) on bmlrt.gv.at (Yearbook 2011)
- ↑ Bridge Angern comes in 2014 at the earliest Niederösterreichische Nachrichten, 21 September 2010
- ↑ Green light for the new March Bridge on ORF on February 19, 2013, accessed on February 19, 2013.
- ↑ Angern votes against the March Bridge , orf.at (September 21, 2014), accessed on June 26, 2017
- ↑ Marchegg und seine Brücke , Bezirksblätter.at (April 18, 2017), accessed on June 26, 2017
- ^ No to the bridges in Marchegg and Dürnkrut , Bezirksblätter.at (February 20, 2017), accessed on June 26, 2017
- ^ E. Schuster: The Etymology of Lower Austrian Place Names , Part 2, Association for Regional Studies of Lower Austria, 1990 Vienna, p. 592ff
- ↑ Bridge at the castle courtyard and Devínská Nová Ves ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. Retrieved September 26, 2011 by Karol Kattos
- ↑ The bridge to nowhere ( memento of the original from January 3, 2009 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. in the folder on May 7, 2008, accessed on March 28, 2010.
- ↑ Old borders - new bridges (PDF; 1.8 MB) from 1997, accessed on February 2, 2013.
- ↑ EU supports cyclist bridge with several million euros. ( Page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. on Radio Slovakia International on March 9, 2010, accessed on April 4, 2010
- ↑ LH Pröll signs work programs with Bratislava and Trnava ( Memento of the original from August 19, 2011 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link has been inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. to Das Land Niederösterreich from April 15, 2009, accessed on May 15, 2010
- ↑ The construction of the new pedestrian bridge has started on the Groissenbrunn site , accessed on June 14, 2011
- ↑ [1]
- ↑ Ranšpurk National Nature Reserve accessed on May 17, 2010 (Eng.)
- ↑ Ramena řeky Moravy National Nature Reserve accessed on May 17, 2010
- ↑ Vrapač National Nature Reserve accessed on May 17, 2010
- ↑ WWF on National Park Strategy : Time is ripe for Austria's 7th National Park - March-Thaya-Auen must be protected. In: OTS press service. WWF Austria, June 21, 2010, accessed June 21, 2010 (OTS0111).
- ↑ Conservation of Raptors and Owls - Slovakia-Austria ( Memento of the original from December 19, 2011 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , accessed November 5, 2011
- ↑ a b Flood protection on the March ( Memento of the original from December 3, 2013 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (PDF; 235 kB) Area of activity Lower Austria 2008/9, accessed on May 15, 2010.
- ↑ Ecological flood protection for March and Thaya ( Memento of the original from August 13, 2011 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. Retrieved from WWF Austria on May 15, 2010
- ↑ Management report of via donau - Österreichische Wasserstraßen-Gesellschaft mbH download ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Flood protection in Lower Austria: Auen im Zwangskorsett at WWF October 16, 2009, accessed on May 15, 2010.
- ↑ Flood structures: EU threatens to take legal action against ORF on June 25, 2012
- ↑ 68 kilometers of flood protection on ORF from February 17, 2013, accessed on February 17, 2013.
- ↑ CEframe - Central European Flood Risk Assessment and Management in CENTROPE on the website of the Lower Austrian state government from December 22, 2010, accessed on February 17, 2013.
- ↑ CEframe , accessed February 17, 2013.
Web links
- Water level and flow indicator on Czech territory (de)
- Water level and flow indicator on Austrian territory
- Water level and flow indicator on Slovak territory (de)
- Povodí Moravy - catchment area of the March (pdf) (2.37 MB)
- Border area cooperation on March and Tisza problems, findings and consequences (PDF; 143 kB) Presentation AZ Ost-Forum April 2002