Neumünster – Flensburg railway line
| Neumünster-Flensburg | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Neumünster – Flensburg and branches to Kiel and Husum
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route number (DB) : | 1040 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Course book section (DB) : | 134 (Kiel – Husum) 131 (Neumünster – Flensburg) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route length: | 101.542 km | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gauge : | 1435 mm ( standard gauge ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route class : | D4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Power system : | 15 kV 16.7 Hz ~ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Top speed: | 160 km / h | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dual track : | (continuous) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The railway line Flensburg-Neumünster is as part of the Jutland line , a major north-south rail link Schleswig-Holstein . Together with the route to Husum that branches off from this route in Jübek and the section of the route to Kiel that branches off in Rendsburg , it also serves as an important east-west axis between Kiel (on the east coast) and the march line on the west coast.
route
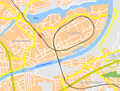
The route runs through agricultural plains. Noteworthy engineering structures are the Rendsburg high bridge and the Rendsburg loop . In Flensburg, the route has been circumnavigating the city in a large loop on the outskirts of the city at the time since 1927 in order to save trains traveling to Denmark from changing direction .
In addition to the starting points of the line, Neumünster - here connection to the Hamburg-Altona – Kiel line - and Flensburg (with cross-border traffic to Denmark ), the most important junctions are at Rendsburg station , where a line branches off to Kiel , and in Jübek near Schleswig . There a route branches off to Husum .
Operation and history
Emergence
The line was created subsequently - after the annexation of the Schleswig region by Prussia - by restructuring parts built for other purposes. The first thing to do was to open the 34-kilometer stretch of the Rendsburg-Neumünster Railway Company between Neumünster and Rendsburg-Glacis as the Jutland line, financed by interested parties in the region, on September 18, 1845. This was followed on January 1, 1847 by the connection of the port railway from Rendsburg-Glacis to Rendsburg-Obereider. These routes were integrated into the ownership of the Altona-Kieler Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft on January 1, 1864 .
On April 1, 1854 on the railway line Flensburg-Tonning later, first from outside the city Holzkrug, located in the city from October 4 from, English station called railhead operation added. This station at the southern end of the Flensburg Fjord in the old town of Flensburg was officially opened on October 25th by the Danish King Frederik VII , the namesake of the railway line.
The Flensburg – Husum – Tönninger Eisenbahn (FHTE) built the route from Flensburg via Eggebek right of the Treene to Oster-Ohrstedt and from Ohrstedt to Owschlag and Rendsburg to a length of around 40 kilometers. The route was led via Ohrstedt because the branch via Husum to Tönning was an essential reason for the railway construction by the English company Peto, Brassey and Betts for the transport of live cattle to England . This railway company built the port railway in Flensburg in 1854 as an extension of the route access to the English train station through the terminal station into the port area.
Restructuring
Schleswig was connected from Klosterkrug with a five-kilometer branch line on June 2, 1858, which Peto, Brassey and Betts built. After the Prussian-Danish War , the part of Schleswig went to Prussia and the route was restructured. The Schleswigsche Railway built with the company Peto, Brassey and Betts 1867-1869 from South Head station Klosterkrug over Schleswig-Friedrichsberg and Juebek left the Treene to Eggebek a 23 km long and thus 16.8 kilometers shorter distance and moved the Eggebek Station to 500 meters to the east. In addition, the Jübek – Sollbrück section of the Jübek – Husum line was created .
On March 26, 1898, the Prussian State Railways opened the Rendsburg port railway on what was then the Kaiser Wilhelm Canal . In preparation for the canal widening, the Rendsburg high bridge was built . It was tied in with a large loop in order to continue using the existing Rendsburg train station; it went into operation on December 1, 1913. In addition, the Osterrönfeld station ( old station ) , which was previously at the same level as the canal, now had to be relocated to the appropriate height following the southern fore bridge ( new station ).
In 1927, today's station was built in Flensburg , which replaced the two terminal stations on the fjord and, with a large loop around the urban settlements, allowed a connection with Denmark without changing locomotives, but also relocated the maintenance tasks on the railway vehicles to the closer urban area.
The scheduled electric train service began on March 17, 1996.
business
Long-distance transport
Until 2002 there was an interregional connection between Flensburg and Hanover. After this connection was discontinued, the state of Schleswig-Holstein ordered a replacement service from the private railway company Flex Verkehrs-AG after a short-term tender . This started operation with modern electric locomotives of the ES64U2 Taurus series from Siemens Dispolok and used passenger coaches. The interregional replacement service known as Flensburg-Express (FLEX) was listed in the timetable under the train type FLX .
After the insolvency of Flex Verkehrs-AG, the Nord-Ostsee-Bahn (NOB) operated this train service every two hours from Padborg (DK) to Hamburg Central Station with stops in Flensburg, Tarp , Schleswig, Rendsburg, Nortorf , Neumünster and Elmshorn until December 2005 . Since December 2005 this traffic has been operated again by the DB Regionalbahn Schleswig-Holstein as " Schleswig-Holstein-Express ". Since the timetable change in December 2010, trains have only run to Flensburg.
In long-distance traffic , Intercity Express trains on the Aarhus - Hamburg - Berlin route used this route from December 2007 to December 2015, with stops in Flensburg , Schleswig , Rendsburg and Neumünster . On December 9, 2007, the ICE-TD from Aarhus to Berlin Ostbahnhof, the first scheduled ICE, rolled into Flensburg station. Today three to four direct pairs of intercity trains run daily from Hamburg to Denmark.
In addition, presented Intercity trains Friday direct from Flensburg to Munich and Cologne ago (also with stops in Schleswig, Rendsburg and Neumünster). IC trains ran from Berlin and Schwarzach - St. Veit to Flensburg on Sundays . On the Husum - Jübek side branch , there was only intercity traffic when the trains had to be rerouted to the march line along the west coast due to construction work.
A CityNightLine train on the Copenhagen - Munich route ran until 2014 on the route with stops in Flensburg and Neumünster.
Regional traffic
The DB Regionalbahn Schleswig-Holstein operates regional express trains every hour between Neumünster and Flensburg . It also runs the Husum - Kiel route with modern multiple units every hour. During the Kieler Woche in particular, the availability of trains on this route is significantly increased, so that sometimes locomotive-hauled trains are also used.
| line | Line designation | Line course |
|---|---|---|
| IC | - | Flensburg - Hamburg - Berlin / Cologne / Munich / Schwarzach-St. Vitus |
| RE | RE 7 | Flensburg - Hamburg |
| RE | - | Husum - Jübek - Schleswig - Rendsburg - Kiel |
Freight transport
The freight line is part of the main connection from Germany ( Maschen marshalling yard ) to Denmark and Sweden and should therefore be the first to be prepared for 835-meter-long trains. The signaling technology had to be adapted for this. So far, only 670 meters long trains have been possible on this route, the maximum limit in Germany was 740 meters. The first such train ran in November 2012. Electric locomotives of the 185 , Hector Rail 241 or DSB EG series are mostly used as locomotives .
Expansion plans
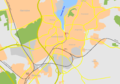
In August 2018, plans were announced to build the former Büdelsdorf station as a new stop.
The line is to be equipped with ETCS by 2025 . The largest possible sections should be equipped with ETCS Level 2 .
literature
- Erich Staisch (Ed.): The train to the north. 150 years of rail traffic in Schleswig-Holstein. From the Christian Bahn to electrification . Ernst Kabel, Hamburg 1994, ISBN 3-8225-0298-7 .
- Holger Kaufhold, Eckhard Klein, Detlef Schikorr: 150 years of the railway in Flensburg. From the Southern Schleswig Railway to the Deutsche Bahn AG (= Society for Flensburg City History. Series of publications . Volume 58 ). LOK Report-Verlag, Sigmaringen 2004, ISBN 3-935909-22-5 .
Web links
Individual evidence
- ^ Bent Hansen: Flensborg. Spedition Steckhan & Peters Logistik GmbH, Flensborg Weiche. In: bentsbane.dk. December 31, 2016, accessed May 31, 2020 (Danish).
- ^ A b Alev Doğan: Nah.SH is planning seven new train stations. In: kn-online.de. August 2, 2018, accessed August 5, 2018 .
- ↑ Route chronicle 1847. Archived from the original on June 17, 2008 ; Retrieved July 29, 2015 .
- ↑ a b Jochen Schulz, Alexander Horn: Description of the OPTION FAST-SLOW APPROACH KEEL RENDSBURG (-FOCKBEK) with potential analysis for new stations. (PDF) LVS Schleswig-Holstein, Landesweit Verkehrsservicegesellschaft mbH, November 27, 2008, p. 25 , archived from the original on November 15, 2012 ; accessed on December 30, 2015 .
- ↑ DB Netze - Infrastructure Register
- ↑ Railway Atlas Germany . 9th edition. Schweers + Wall, Aachen 2014, ISBN 978-3-89494-145-1 .
- ↑ Railway statistics BD Hamburg
- ↑ Holger Kaufhold, Eckhard Klein, Detlef Schikorr: 150 Years of the Railway in Flensburg - From the Southern Schleswig Railway to the Bahn AG. Berlin 2004, ISBN 3-935909-22-5 , p. 37
- ↑ Erich Preuss: Trains under power. The history of electric train operations in Germany, 1st edition Munich 1998, ISBN 3-932785-30-4 , pp. 173-174.
- ↑ Federal government allows longer freight trains
- ↑ 835 m long freight trains planned between Padborg (DK) and Maschen. Archived from the original on December 3, 2013 ; accessed on December 30, 2015 .
- ↑ Markus Lorenz: Successful maiden voyage: Deutsche Bahn lets XXL freight trains roll. In: shz.de. Retrieved July 13, 2017 .
- ↑ Michael Hoffmann: Operational tasks of the corridor Flensburg - Maschen (PD Hamburg) - ETCS -. (PDF) DB Netze, August 17, 2017, pp. 5, 23 , archived from the original ; Retrieved on January 7, 2020 (file 17.1. BAST ETCS Flb-Mas V_1.0.pdf in the ZIP archive).