Wirmighausen
|
Wirmighausen
Diemelsee municipality
Coordinates: 51 ° 20 ′ 48 ″ N , 8 ° 49 ′ 34 ″ E
|
|
|---|---|
| Height : | 407 (300-500) m above sea level NHN |
| Area : | 14.45 km² [LAGIS] |
| Residents : | 374 (April 5, 2019) |
| Population density : | 26 inhabitants / km² |
| Incorporation : | December 31, 1971 |
| Postal code : | 34519 |
| Area code : | 05633 |
|
Location of Wirmighausen in Northern Hesse
|
|
Wirmighausen is a district of the Diemelsee community in the Waldeck-Frankenberg district in North Hesse . The place has over 900 years of local history .
geography
location
Wirmighausen is located on the eastern border of the Diemelsee Nature Park and is traversed by the Rhene tributary, the Wirme . The district borders on Adorf in the north, Vasbeck in the northeast, Gembeck (municipality of Twist valley ) in the east, Flechtdorf in the south and Benkhausen in the west . The place is between Dortmund and Kassel south of Paderborn , roughly in the middle of a triangle with the corner points Korbach , Brilon and Marsberg . The area assigned to the place is 1,445 hectares .
Natural structure
In terms of natural space , the location is assigned to the region “332 Ostsauerländer Gebirgsrand” and within it the Vorupländer Hügelland (332.61).
history
Prehistory and early history
The earliest human presence in the Wirmighauser region is documented by litter finds from the Neolithic period. Corresponding finds from this and subsequent periods are in the holdings of the Wolfgang Bonhage Museum in Korbach . Litter finds Finds of Celtic settlement in the region are dated from the 5th century. The Latène period was followed by Germanic colonization . The areas of Germanic tribes have shifted several times in the region. Initially there are Cheruscans and Chatten in the region . Sugambrer and Marser are later found in the region. Roman settlement around Wirmighausen is not known; the next evidence of Romans can be found in today's area of East Westphalia-Lippe . For the period from around 100 to around 500, little is known about regional history.
middle Ages
Wirmighausen was in the border areas of the Saxon and Franconian areas. From around 690 Wirmighausen was under the influence of the Angrivarians (also known as Angrevarier, Angarier, Engern, Latin: Angrivarii, Angarii). The missionary work of the chat follow, also sat in the range of Wirmighausen the Christianization one. Wirmighausen was initially in the sphere of influence of the Eresburg (in today's Marsberg ) and was evangelized from there. Wirmighausen was later located in the early medieval Gau Nithersi, which was later also known as Itergowe, Pago Itherga and Grafschaft Itter.
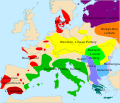
Borders of the Franconian Empire from 843 after the Treaty of Verdun
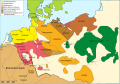
Area of the Angrivarians around 1000
1101, the town was first mentioned as Count Erpo von Padberg the monastery Boke gave an estate in Wirmighausen. The known documentary evidence can be found in the following overview:
- Winemarinchus, in (1101/1102) [Regesta historiae Westfaliae 1, No. 1303, Schwersmann, Benedictine monastery Flechtdorf, p. 327 with note 696]
- Wynnemarinkusen (1194) [Cop. 14th century regests of the archbishops of Cologne 2, p. 299, no. 1488]
- Winemarinchusen, in (1194) [cop. 14th century regests of the Archbishops of Cologne 2, pp. 297–298, no. 1482]
- Wynemarinchusen (1219) [Westphalian document book 4.1, pp. 53–54, no. 78]
- Winemarchusen (1248) [Schwersmann, Benedictine monastery Flechtdorf, p. 327 with note 701]
- Winemarinchusen, in (1263) [Schwersmann, Benedictine monastery Flechtdorf, p. 328 with note 703]
- Wynemarenchůsen (1326) [Documents Bredelar Monastery, pp. 146–147, no. 225]
- Weinmichusen, tho (1394) [Copy 1537 HStAM inventory 133 f No. Flechtdorf 7/40: 1394 May 13]
- Wermchusen (1457–1480) [Schwersmann, Benedictine monastery Flechtdorf, p. 329 with note 713]
- Wermerinckhusen (1482) [Copy of documents from the Propstei Marsberg, p. 205, no. 401]
- Wermickhusen (1537) [HStAM inventory 127 No. 3]
- Wirminghausen (1733) [HStAD inventory P 23 No. 56]
In the years 1155–1170 Abbot Uffo of the Flechtdorf Monastery had goods in the village. In 1194 the place was mentioned with the name Wymarinchusen , when the Flechtdorf monastery acquired further ownership there and this led to disputes with the Padberg residents . In 1293 Count Otto I von Waldeck pledged his tithe rights to the Lords of Padberg. In 1344 Herrmann von Adorf sold an estate to the Flechtdorf monastery. In 1526 the von Scarpenberg brothers donated their estate to the Bredelar monastery . From 1537 to 1578 most of the village was owned by the Flechtdorf Monastery, a few belonged to the Bredelar Monastery. Lieutenants of the Flechtdorf monastery in the village were the lords of Ditmerkhusen, the Gogrebe and the lords of Eppe. Around 1600 the place was then called Wirmighausen. In the period from 1816 to 1866 Wirmighausen belonged to the upper office of the Twiste.
colonization
The settlement of the place began even before the first documentary mention. Around the year 800, Charlemagne is said to have moved north on an army road that led through what is now the district. The residents were forced to adopt the Christian faith. An early place name was Wennemaringhusen , possibly named after the founder Wennemar. Presumably the founder was a Saxon from the Engern tribe . The names of the places founded by Engern often end with -ingsen or -inghusen , and this ending is interpreted as "descendant of" .
Customs House
On a high plateau outside of the village there is a group of farmsteads called Zollhaus. Here the Counts of Waldeck had set up a customs post to the nearby Westphalia . Up until the 1920s there was still a large stable for up to 60 horses. Nearby, a castle is mentioned to protect the trade route , of which only the floor plan, a rampart and a moat can be seen today.
Incorporations
As part of the regional reform in Hesse , Wirmighausen and twelve other communities formed the new Diemelsee community on December 31, 1971. For Wirmighausen, as for each of the municipalities that were absorbed into the Diemelsee municipality, a local district with a local advisory board and local councilor was established.
church
Around 1200 the place belonged to the Archdiakonat Adorf . After its dissolution, Wirmighausen was assigned to the Archdeaconate Horhusen (today Niedermarsberg ). Only in the years 1457–1480 was a chapel built with the support of Flechtdorf Abbot Herrmann von Frowyn ; it was consecrated to St. Catherine . It was renovated around 1700 and demolished in 1907. Today's church was built next to the demolished chapel between 1906 and 1908.
Nature reserve on the Buchenlied near Wirmighausen
To the east of Wirmighausen is the nature reserve Auf der Buchenlied near Wirmighausen . It has a size of 19.26 hectares and was designated in 1990 because of its special diversity of plants. The area is also designated as an FFH area .
Sports
To the north of Wirmighausen on the street "Hinterm Gürenberg" is the Wirmetalhalle with around 700 seats and a sports field. Among other things, both host the annual cross-country run of the LG Diemelsee, in which the Hessian cross-country championships were integrated in 2016.
literature
- Fritz Peter: Wirmighausen . 2 volumes. Arolsen: Waldeckischer Geschichtsverein 2000 (= Waldeckische Ortssippenbücher 66)
- Literature on Wirmighausen in the Hessian Bibliography
- Search for Wirmighausen in the archive portal-D of the German Digital Library
Web links
- The district on the website of the Diemelsee municipality
- "Wirmighausen, Waldeck-Frankenberg district". Historical local dictionary for Hessen. (As of July 27, 2016). In: Landesgeschichtliches Informationssystem Hessen (LAGIS).
- The history of Wirmighausen
Individual evidence
- ↑ Status: April 5, 2019 in “Facts and Figures” on the Diemelsee municipality's website ( Memento from April 5, 2019 in the Internet Archive ).
- ↑ a b Sudeck, Waldeck-Frankenberg district. Historical local dictionary for Hessen. (As of October 16, 2018). In: Landesgeschichtliches Informationssystem Hessen (LAGIS).
- ↑ As of: 30.06.2016 in "Facts and Figures" on the website of the Diemelsee municipality ( Memento from August 12, 2016 in the Internet Archive ).
- ↑ State of Hesse: The natural areas of Hesse and their main units ( Memento from March 27, 2019 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ a b Alfred Emde: Adorf The story of a Waldeck village , 1st edition 1992, pages 15 ff. (Accessed on May 24, 2019).
- ^ "Customs house, Waldeck-Frankenberg district". Historical local dictionary for Hessen. In: Landesgeschichtliches Informationssystem Hessen (LAGIS).
- ^ The history of Wirmighausen ( Memento from October 11, 2007 in the Internet Archive )
- ^ Federal Statistical Office (ed.): Historical municipality directory for the Federal Republic of Germany. Name, border and key number changes in municipalities, counties and administrative districts from May 27, 1970 to December 31, 1982 . W. Kohlhammer, Stuttgart / Mainz 1983, ISBN 3-17-003263-1 , p. 408 f .
- ↑ Wolfgang Lübcke, Achim Frede: Nature reserves in Hessen. Volume 4: Waldeck-Frankenberg district with Kellerwald-Edersee National Park. Cognitio, Niedenstein , 2007, ISBN 978-3-932583-23-0 , pp. 119-121
- ↑ Announcement of the Hessian Cross-Country Championships 2016 ( Memento from February 27, 2016 in the Internet Archive ), accessed in February 2016.