Flag of Germany
 | |
| Schwarz-Rot-Gold | |
| Use | Civil and state flag, civil and state ensign |
|---|---|
| Proportion | 3:5 |
| Adopted | 23 May 1949 |
| Design | A horizontal tricolour of black, red and gold. |
 | |
| Use | State flag and ensign, war flag |
| Proportion | 3:5 |
| Adopted | 7 June 1950 |
 | |
| Use | Naval ensign |
| Proportion | 3:5 |
| Adopted | 25 May 1956 |
The flag of Germany is a tricolour consisting of three equal horizontal bands displaying the national colours of Germany: black, red and gold.
The black-red-gold tricolour first appeared in the early 19th century and achieved prominence during the 1848 revolution. The short-lived Frankfurt Parliament of 1848–50 proposed the tricolour as a flag for a united and democratic German state. With the formation of the Weimar Republic after World War I, the tricolour was adopted as the national flag of Germany. Following World War II, the tricolour was designated as the flag of both West and East Germany. Both flags were identical until 1959, when socialist symbols were added to the East German flag. Since reunification on 3 October 1990, the black-red-gold tricolour has remained the flag of Germany.
The flag of Germany has not always used black, red and gold as its colours. After the Austro–Prussian War in 1866, the Prussian-dominated North German Confederation adopted a tricolour of black-white-red as its flag. This flag later became the flag of the German Empire, formed following the unification of Germany in 1871, and was used until 1918. Black, white and red were reintroduced as the German national colours with the establishment of Nazi Germany in 1933.
The colour schemes of black-red-gold and black-white-red have played an important role in the history of Germany and have had various meanings. The colours of the modern flag are associated with the republican democracy formed after World War II and represent German unity and freedom: not only the freedom of Germany, but also the personal freedom of the German people.[1]
Flag variants
Civil flag
The German national flag or Bundesflagge (federal flag), containing only the black-red-gold tricolour, was introduced as part of the (West) German constitution in 1949.[2] Following the creation of separate government and military flags in later years, the plain tricolour is now used as the German civil flag and civil ensign. This flag is also used by non-federal authorities to show their connection to the federal government – for example, the authorities of the German states use the German national flag together with their own flag.
Government flag
The government flag of Germany is officially known as the Dienstflagge der Bundesbehörden (state flag of the federal authorities) or Bundesdienstflagge for short. Introduced in 1950, the government flag is the civil flag defaced with a badge known as the Bundesschild (federal badge or shield), which overlaps with up to one fifth of the black and gold bands.[3] The Bundesschild is a variant of the coat of arms of Germany, where the main differences are the illustration of the eagle and the shape of the shield: the Bundesschild is rounded, the standard coat of arms is not. The government flag may only be used by federal government authorities and its use by others is an offence, punishable with a fine.[4] Public use of flags similar to the Bundesdienstflagge (e.g. using the actual coat of arms instead of the Bundesschild) is tolerated and such flags are sometimes seen at international sporting events.


Vertical flags
In addition to the normal horizontal format, many public buildings in Germany use vertical flags. Most town halls fly their town flag together with the national flag in this way – many town flags in Germany exist only in vertical form. The proportions of these vertical flags are not specified. In 1996, a layout for the vertical version of the government flag was established: the Bundesschild is displayed in the centre of the flag, overlapping with up to one fifth of the black and yellow bands.[5] When hung like a banner or draped, the black band should be on the left, as illustrated. When flown from a vertical flagpole, the black band must face the mast.[6]
Military flags
Since the German armed forces (Bundeswehr) are a federal authority, the Bundesdienstflagge is also used as the German war flag on land. In 1956, the Dienstflagge der Seestreitkräfte der Bundeswehr (Flag of the German Navy) was introduced: the government flag ending in a swallowtail.[7] This naval flag is also used as a navy jack.
Design

In the Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany – the German constitution – Article 22 states: "The federal flag shall be black, red and gold."[2] Following specifications set by the (West) German government in 1950, the flag displays three bars of equal width and has a width–length ratio of 3:5;[3] the tricolour used during the Weimar Republic had a ratio of 2:3.[8]
The exact colours used for the German flag were not officially defined at the time of the flag's adoption and have changed since then.[9] The federal cabinet introduced a corporate design for the German government on 2 June 1999, which currently uses the following colours:[10]
| Colour scheme | Black | Red | Gold | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAL | 9005 Jet black |
3020 Traffic red |
1021 Cadmium yellow | |||
| HKS | 0, 0, 0 | 5.0PB 3.0/12 | 6.0R 4.5/14 | |||
| CMYK | 0.0.0.100 | 0.100.100.0 | 0.12.100.5 | |||
| Pantone | Black | 485 | 7405* | |||
| HTML | #000000 | #FF0000 | #FFCC00 | |||
*The value given here is an alternative to the following more-complicated combination: Yellow (765 g), Red 032 (26 g), Black (11 g), Transp. White (198 g)
Gold or yellow?

Vexillology rarely distinguishes between gold and yellow; in heraldry, they are both or. For the German flag, such a distinction is made: the colour used in the flag is gold, not yellow.
When the black-red-gold tricolour was adopted by the Weimar Republic as its flag, it was attacked by conservatives, monarchists and the far right, who referred to the colours with spiteful nicknames such as Schwarz-Rot-Gelb (black-red-yellow), Schwarz-Rot-Senf (black-red-mustard) or even Schwarz-Rot-Scheiße (black-red-shit).[11] When the Nazis came to power in 1933, the black-white-red colours of pre-1918 Imperial Germany were swiftly reintroduced and their propaganda machine continued to discredit the Schwarz-Rot-Gold, using the same derogatory terms as previously used by the monarchists.[12]
On 16 November 1959, the Federal Court of Justice (Bundesgerichtshof) stated that the usage of "black-red-yellow" and the like had "through years of Nazi agitation, attained the significance of a malicious slander against the democratic symbols of the state" and is now an offence.[12] As summarised by heraldist Arnold Rabbow in 1968, "the German colours are black-red-yellow but they are called black-red-gold."[13]
Flag days

Following federal decree on 22 March 2005, the flag must be flown from public buildings on the following dates. Not all of these days are public holidays.
| Date | Name | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| 27 January | Commemoration Day for the Victims of National Socialism Tag des Gedenkens an die Opfer des Nationalsozialismus |
Anniversary of the liberation of Auschwitz concentration camp, observed by the United Nations as International Holocaust Remembrance Day (half-mast) |
| 1 May | International Workers' Day Tag der Arbeit |
n/a |
| 9 May | Europe day Europatag |
Anniversary of the Schuman Declaration, leading to the European Union (1950) |
| 23 May | Constitution Day | Anniversary of the German constitution (1949) |
| 17 June | n/a | Anniversary of the Uprising of 1953 in East Germany |
| 20 July | n/a | Anniversary of the July 20 plot, the failed assassination attempt on Adolf Hitler by Claus von Stauffenberg (1944) |
| 3 October | German Unity Day Tag der Deutschen Einheit |
Anniversary of German reunification (1990) |
| Two Sundays before the first Advent | National day of mourning Volkstrauertag |
In memory of all killed during wartime (half-mast) |
Election days for the Bundestag and the European Parliament are also flag days in some states, in addition to other state-specific flag days. The public display of flags to mark other events – such as the election of the president or the death of a prominent politician (whereupon flags would be at half-mast) – can be declared at the discretion of the Federal Ministry of the Interior.[14] When flags are required to be flown at half-mast, vertical flags are not lowered. A black mourning ribbon is instead attached, either atop the mast (if hung from a pole) or to each end of the flag's supporting cross-beams (if flown like a banner).[15]
History
Medieval period
 
|
| Banners of the Holy Roman Emperor (left: 14th century, right: 15th–19th century) |
The Holy Roman Empire (10th century – 1806, known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512) did not have a national flag, but black and gold were used as colours of the Holy Roman Emperor and featured in the imperial banner: a black eagle on a golden background. After the late 13th or early 14th century, the claws and beak of the eagle were coloured red. From the early 15th century, a double-headed eagle was used.[16]
In 1804, Napoleon Bonaparte declared the First French Empire. In response to this, Holy Roman Emperor Francis II of the Habsburg dynasty declared his personal domain to be the Austrian Empire and became Francis I of Austria. Taking the colours of the banner of the Holy Roman Emperor, the flag of the Austrian Empire was black and gold. Francis II was the last Holy Roman Emperor, with Napoleon forcing the empire's dissolution in 1806. After this point, these colours continued to be used as the flag of Austria until 1918.

The colours red and white were also significant during this period. When the Holy Roman Empire took part in the Crusades, a war flag was flown alongside the black-gold imperial banner. This flag, known as the "Saint George Flag", was a white cross on a red background: the reverse of the St George's Cross used as the flag of England.[16] Red and white were also colours of the Hanseatic League (13th–17th century). Hanseatic trading ships were identifiable by their red-white pennants and most Hanseatic cities adopted red and white as their city colours (see Hanseatic flags). Red and white still feature as the colours of many former Hanseatic cities such as Hamburg or Gdańsk.
Napoleonic Wars

With the collapse of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806, many of its dukes and princes joined the Confederation of the Rhine, a Napoleonic client state. The confederation had no flag of its own; instead it used the blue-white-red flag of France and the Imperial Standard of its "protector", Napoleon.[17]
During the Napoleonic Wars, the German struggle against the occupying French forces were significantly symbolised by the colours of black, red and gold. This was largely attributed to the uniforms of the Lützow Free Corps, a volunteer unit of the Prussian Army. The uniforms for this unit were black with red facings and gold buttons. The colour choice here was a pragmatic one, even though it was also a popularisation of the former black-red-gold colours used by the Holy Roman Empire.[18] Members of the corps were required to supply their own clothing and, in order to present a uniform appearance, it was easiest to dye all clothes black. Gold-coloured buttons were widely available and pennons used by the lancers in the unit were red and black. At the time, the colours were symbolised as: Out of the darkness (black) of servitude through bloody (red) conflict to the (golden) light of freedom.[19] As the members of this unit came from all over Germany and were mostly university students and academics, the Lützow Free Corps and their colours gained considerable prominence among the German people.[18]
German Confederation
The 1815/6 Congress of Vienna led to the creation of the German Confederation, a loose union of all remaining German states after the Napoleonic Wars. The Confederation was created as a replacement for the now-extinct Holy Roman Empire, with Francis I of Austria – the last Holy Roman Emperor – as its president. The confederation did not have a flag of its own, although the black-red-gold tricolour is sometimes mistakenly attributed to it.[20]

Upon returning from the war, veterans of the Lützow Free Corps founded the Urburschenschaft fraternity in Jena in June 1815. The Jena Urburschenschaft eventually adopted a flag with three equal horizontal bands of red, black and red, with gold trim and a golden oak branch across the black band, following the colours of the uniforms of the Free Corps.[18] Since the students who served in the Lützow Free Corps came from various German states, the idea of a unified German state began to gain momentum within the Urburschenschaft and similar Burschenschaften that were subsequently formed throughout the Confederation. On 18 October 1817, the fourth anniversary of the Battle of Leipzig, hundreds of fraternity members and academics from across the Confederation states met in Wartburg in Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach (in modern Thuringia), calling for a free and unified German nation. The red-black-gold flag of the Jena Urburschenschaft featured prominently at this Wartburg festival and so the colours black, red and gold eventually became symbolic of this desire for a unified German state. Austria, in its determination to maintain the status quo,[21] enacted the Carlsbad Decrees of 1819 that banned all student organisations, officially putting an end to the Burschenschaften.
In May 1832, around 30,000 people demonstrated at the Hambach Festival for freedom, unity and civil rights. The colours black, red and gold had become a well established symbol for the liberal, democratic and republican movement within the German states since the Wartburg Festival and flags in these colours were flown en masse at the Hambach Festival. While contemporary illustrations showed prominent use of a gold-red-black tricolour (an upside-down version of the modern German flag), surviving flags from the event were in black-red-gold. Such an example is the Ur-Fahne, the flag flown from Hambach Castle during the festival: a black-red-gold tricolour where the red band contains the inscription Deutschlands Wiedergeburt (Germany's rebirth). This flag is now on permanent display at the castle.[22]
Revolution and the Frankfurt Parliament

In the Springtime of the Peoples during the Revolutions of 1848, revolutionaries took to the streets, many flying the tricolour. Liberals took power and, after prolonged deliberation, a national assembly was formulated. This Frankfurt Parliament declared the black-red-gold as the official colours of Germany and passed a law stating its civil ensign was the black-red-yellow tricolour.[23]
In 1850, the Frankfurt Parliament collapsed and the German Confederation was restored under Austrian presidency, who suppressed the actions of the failed Frankfurt Parliament, including the tricolour. Afterwards, the most pressing issue was whether or not to include Austria in any future German nation, as Austria's status as a multi-ethnic empire complicated the dream of a united Greater Germany – the grossdeutsch solution. Alternatively, there was the kleindeutsch (Lesser German) solution for a Germany that encompassed only German lands and excluded Austria. The Prussian–Austrian duality within the Confederation eventually led to the Austro–Prussian War in 1866. During the war, the southern states allied with Austria adopted the black-red-gold tricolour as its flag, and the 8th German Army Corps also wore black-red-gold armbands.[20] The Kingdom of Prussia and its predominately north German allies defeated Austria and made way for the realisation of the Lesser German solution a few years later.
Prussian-dominated Germany

 Flag of the North German Confederation (1866–71) and the German Empire (1871–1918).
Flag of the North German Confederation (1866–71) and the German Empire (1871–1918).Also used during the Weimar Republic by foreign services (1922–33)
Following the dissolution of the German Confederation, Prussia formed its unofficial successor, the North German Confederation, in 1867. This coalition consisted of Prussia – by far the largest member state – and 21 other north-German states.
The question regarding what flag should be adopted by the new confederation was first raised by the shipping sector and its desire to have an internationally recognisable identity. Virtually all international shipping that belonged to the confederation originated from either Prussia or the three former Hanseatic city-states of Bremen, Hamburg and Lübeck. Based on this, Adolf Soetbeer, secretary of the Hamburg Chamber of Commerce, suggested in the Bremer Handelsblatt on 22 September 1866 that any planned flag should combine the colours of Prussia (black and white) with the Hanseatic colours (red and white). In the following year, the constitution of the North German Confederation was enacted, where a horizontal black-white-red tricolour was declared to be both the civil and war ensign.[24]
King Frederick William IV of Prussia was satisfied with the colour choice: the red and white were also taken to represent the Margraviate of Brandenburg, the Imperial elector state that was a predecessor of the Kingdom of Prussia.[18] The absence of gold from the flag also made it clear that this German state did not include the "black and gold" monarchy of Austria. Following the Franco–Prussian War, the remaining southern German states allied with the North German Confederation, leading to the unification of Germany and the elevation of the Prussian monarch to Emperor of this new state in 1871. In its constitution, the German Empire retained black, white and red as its national colours,[25] with the tricolour previously used by the North German Confederation officially adopted as its flag in 1892.
The black-white-red tricolour remained the flag of Germany until the end of the German Empire in 1918, in the final days of World War I.
Weimar Republic


 Flag of Weimar Germany (1919–33)
Flag of Weimar Germany (1919–33)Following the declaration of the German republic in 1918 and the ensuing revolutionary period, the so-called Weimar Republic was founded in August 1919. To form a continuity between the anti-autocratic movement of the 19th century and the new democratic republic, the old black-red-gold tricolour was designated as the national German flag in the Weimar Constitution in 1919.[26] As a civil ensign, the black-white-red-tricolour was retained, albeit with the new tricolour in the top left corner.
This change was not welcomed by many people in Germany, who saw this new flag as a symbol of humiliation following Germany's defeat in World War I. In the Reichswehr, the old colours continued to be used in various forms. Many conservatives wanted the old colours to return, while monarchists and the far right were far more vocal with their objections, referring to the new flag with various derogatory names (see Gold or yellow? above). As a compromise, the old black-white-red flag was reintroduced in 1922 to represent German diplomatic missions abroad.[8]
The symbols of Imperial Germany became symbols of conservative protest and were often used by nationalist organisations (e.g. Stahlhelm, Bund der Frontsoldaten). This included the Reichskriegsflagge (war flag of the Reich), which has been revived in the present for similar use. Many right-wing political parties during the Weimar period – such as the DNVP (see poster) and the Nazi Party – used the imperial colours, a practice that has continued today with the NPD.
On 24 February 1924, the organisation Reichsbanner Schwarz-Rot-Gold was founded in Magdeburg by the member parties of the Weimar Coalition (Centre, DDP, SPD) and the trade unions. This organisation was formed to protect the fragile democracy of the Weimar Republic, which was under constant pressure by both the far right and far left. Through this organisation, the black-red-gold flag became not only a symbol of German democracy, but also of resistance to political extremism. This was summarised by the organisation's first chairman, Otto Hörsing, who described their task as a "struggle against the swastika and the Soviet star".[27]
In the face of the increasingly violent conflicts between the communists and the national socialists, the growing polarisation of the German population and a multitude of other factors, the Weimar Republic collapsed in 1933 with the Nazi seizure of power (Machtergreifung) and the appointment of Adolf Hitler as German chancellor.
Nazi Germany

 Flag of the National Socialist German Workers Party (1920–45)
Flag of the National Socialist German Workers Party (1920–45)National flag of Germany (1933–45)

 Used jointly with the swastika flag (1933–35), then banned as "reactionary"
Used jointly with the swastika flag (1933–35), then banned as "reactionary"With the establishment of Nazi-ruled Germany on 5 March 1933, the black-red-gold flag was swiftly scrapped: a ruling on 12 March reintroduced the old black-white-red imperial tricolour and established the banner of the Nazi Party as the two national flags of Germany.[28] In 1935, one year after the death of Reich President Paul von Hindenburg and Hitler's self-elevation to the position of Führer, the dual flag arrangement ended with the exclusive use of the Nazi flag as the national flag of Germany,[29] while the old black-white-red flag was banned as "reactionary".[30]
The design of the Nazi flag was introduced by Hitler as the party flag in the summer of 1920: a flag with a red background, a white disk, and a black swastika in the middle. In addition to the flag forming a link to Imperial Germany via its colour choice, the national socialist flag had additional meaning, according to Hitler in Mein Kampf: white for nationalism, red for socialism, and the swastika to symbolise the superiority of the Aryan race and antisemitism. Albert Speer stated in his memoirs that "in only two other designs did he (Adolf Hitler) execute the same care as he did his Obersalzberg house: that of the Reich War Flag and his own standard of Chief of State".[31]
An off-centred disk version of the swastika flag was used as the civil ensign on German-registered civilian ships and was used as the jack on Kriegsmarine (the name of the German Navy, 1933–45) warships.[32] Nazi ensigns had a through and through image, so the "left-facing" and "right-facing" version were each present on one side. The Nazi flag on land was right-facing on both sides while the centred-disk flag was commonly used by civilians and the German armed forces aside from the navy. There is still debate as to whether the off-centred disk flag was the official national flag from 1935 to 1945.[33]
From 1933 to at least 1938, before any official swastika flag went into use, it had to take part in a ceremony where it touched the Blutfahne (blood flag), the swastika flag used by Nazi paramilitaries during the failed Beer Hall Putsch in 1923. This lengthy ceremony took place at every Nuremberg Rally. It is unknown whether this tradition was continued after the last Nuremberg rally in 1938.

 A proposed flag for Germany that would have been used had the July 20 plot succeeded (1944)
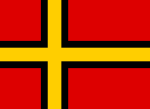
A proposed flag for Germany that would have been used had the July 20 plot succeeded (1944)On 20 July 1944, the German Resistance failed in their attempt to assassinate Hitler. If the assassination had been successful, the Resistance would have then attempted to take power in Germany via Operation Walküre (Valkyrie), disband the Nazi regime and seek peace with the Allies. Josef Wirmer, a co-conspirator in the July 20 Plot, had developed a new national flag to be used for this new post-Nazi state: a Nordic Cross Flag in black-red-gold.[34] After the July 20 Plot failed, the conspirators were executed and the flag was never used.
At the end of World War II, the first law enacted by the Allied Control Council abolished all Nazi symbols and repealed all relevant laws.[35] The possession of swastika flags is forbidden in many Western countries since then, particularly in Germany.
After World War II


 The C-Pennant (1946–49)
The C-Pennant (1946–49)After the defeat of Germany in World War II, the country was placed under Allied administration. Although there was no national German government and no German flag, German ships were required by international law to have a national ensign of some kind. As a provisional civil ensign of Germany, the Council designated the international signal pennant representing the letter C ending in a swallowtail, known as the C-Pennant (German: C-Doppelstander). The Council ruled that "no ceremonial shall be accorded this flag which shall not be dipped in salute to warships or merchant ships of any nationality".[36] Similarly, the Japanese civil ensign used immediately following World War II was the signal pennant for the letter E ending in a swallow-tail.
West of the Oder–Neisse line, the German states were reorganised along the lines of the zones of occupation and new state governments were established. Within the American zone, the northern halves of the former states of Württemberg and Baden were merged to form Württemberg-Baden in 1946. As its flag, Württemberg-Baden adopted the black-red-gold tricolour.[37] The choice of these colours was not based on the historical use of the tricolour, but the simple addition of gold to Württemberg's colours of red and black.[38] Coincidentally, Baden's colours were red and yellow, so the colour choice could be mistaken for a combination of the two flags. In 1952, Württemberg-Baden became part of the modern German state of Baden-Württemberg, whose flag is black and gold.
Two other states that were created after the war, Rhineland-Palatinate (French zone) and Lower Saxony (British zone), chose to use the black-red-gold tricolour as their flag, defaced with the state's coat of arms.[39][40] These two states were formed from parts of other states and no colour combinations from these previous states were accepted as a new state flag. This led to the use of the black-red-gold for two reasons: the colours did not relate particularly to any one of the previous states, and using the old flag from the Weimar Republic was intended to be a symbol of the new democracy.[41][42]
Divided Germany


 Flag of the Federal Republic of Germany (1949–today)
Flag of the Federal Republic of Germany (1949–today)Flag of the German Democratic Republic (1949–59)
With relations deteriorating between the Soviet Union and the United States, the three western Allies met in March 1948 to merge their zones of occupation and allow the formation of a new German nation. This was the Federal Republic of Germany, previously known as West Germany, now simply as Germany. Meanwhile, the eastern Soviet zone became the German Democratic Republic, commonly known as East Germany.
During the preparation of the new constitution for West Germany, discussions regarding its national symbols took place in August 1948 during a meeting at Herrenchiemsee. Although there were objections to the creation of a national flag before reunification with the east, it was decided to proceed. This decision was primarily motivated by the proposed constitution by the eastern SED in November 1946,[43] where black-red-gold were suggested as the colours for a future German republic.[44]
|

|
While there were suggestions for the new flag for West Germany,[45] the final choice was between two designs, both using black-red-gold. The Social Democrats proposed the re-introduction of the old Weimar flag, while the conservative parties such as the CDU/CSU and the German Party proposed a suggestion by Ernst Wirmer, a member of the Parlamentarischer Rat (parliamentary council) and future advisor of chancellor Konrad Adenauer. Wirmer suggested a variant of the 1944 "Resistance" flag designed by his brother and July 20 co-conspirator Josef.[34] The tricolour was ultimately selected, largely to illustrate the continuity between the Weimar Republic and this new German state. With the enactment of the (West) German constitution on 23 May 1949, the black-red-gold tricolour was adopted as the flag for the Federal Republic of Germany.[2]
In 1955, the inhabitants of the French-administered Saar Protectorate elected to join West Germany.[46] Since its establishment as a separate French protectorate in 1947, the Saar had a white Nordic cross on a blue and red background as its flag.[47] To demonstrate the commitment of the Saar to be a part of West Germany, a new flag was selected on 9 July 1956: the black-red-gold tricolour defaced with the new coat of arms, also proposed on this day.[48] This flag came into force on 1 January 1957, upon the establishment of the Saarland as a state of West Germany.


 Flag of the German Democratic Republic (1959–90)
Flag of the German Democratic Republic (1959–90)While the use of black-red-gold had been suggested in the Soviet zone in 1946, the Second People's Congress in 1948 decided to adopt the old black-white-red tricolour as a national flag for East Germany. This choice was based on the use of these colours by the National Committee for a Free Germany,[45] a German anti-Nazi organisation that operated in the Soviet Union in the last two years of the war. In 1949, following a suggestion from Friedrich Ebert, the black-red-gold tricolour was instead selected as the flag of the German Democratic Republic upon the formation of this state on 7 October 1949.[49] From 1949 to 1959, the flags of both West and East Germany were identical. On 1 October 1959, the East German government changed its flag with the addition of its coat of arms.[50] In West Germany, these changes were seen as a deliberate attempt to divide the two Germanys. Displaying this flag in West Germany and West Berlin – where it became known as the Spalterflagge (divider-flag) – was seen as a breach of the constitution and subsequently banned until the late 1960s.
From 1956 to 1964, West and East Germany attended the Winter and Summer Olympic Games as a single team, known as the United Team of Germany. After the East German national flag was changed in 1959, neither country accepted the flag of the other. As a compromise, a new flag was used, featuring the black-red-gold tricolour defaced with the Olympic rings in white.
1989 to today

 The East German flag with the emblem cut out, displayed by many East Germans before reunification (1989)
The East German flag with the emblem cut out, displayed by many East Germans before reunification (1989)After the fall of the Berlin Wall in November 1989, many East Germans cut the coat of arms out of their flags. The inspiration for this came from Romania, where this was done during the fall of Ceauşescu. The widespread act of removing the coat of arms from the East German flag implied that the plain black-red-gold tricolour was a symbol for a united and democratic Germany and, on 3 October 1990, as the German Democratic Republic was absorbed into the Federal Republic of Germany, the black-red-gold tricolour became the flag of a reunified Germany. In 1998, the Foundation for the Reconciliation of the SED Dictatorship was formed. The duty of this organisation, directly responsible to the federal government, is to examine the consequences of the former East German regime. As its logo, the foundation uses this cut-out version of the East German flag.[51]

The old black-white-red tricolour of the German Empire is still used by monarchists and those members of German royalty who long for the peaceful reintroduction of a German democratic monarchy.[52] This use of the old flag is almost completely overshadowed by its prevalent use by the far right; since the swastika is illegal in Germany the far right have been forced to forego any Nazi flags and instead use the old tricolour – which the Nazis themselves banned in 1935.[29] The fact that Nazi symbols are banned in some countries is the main reason why many computer games related to World War II do not feature the Nazi flag, sometimes replacing it with the anachronistic flag of pre-1918 Germany. The utilisation of the old imperial tricolour by the far right and its attempts to associate the tricolour with its antidemocratic and xenophobic ideals are strongly objected to by modern German monarchists.[52]

In Germany, the use of the flag and other national symbols is relatively low – a reaction against the widespread use of flags by the Nazi Party, and against the nationalistic furore of the Nazis in general.[53] The flag is used primarily by official authorities on special occasions or by citizens during international sporting events. In some states (e.g. Bavaria, Schleswig-Holstein) or sub-state historical regions (e.g. Baden, Franconia) residents may prefer the use of regional flags instead of the national flag.
During the 2006 FIFA World Cup, which took place in Germany, public use of the national flag increased dramatically.[54] Although this explosion in the flag's popularity was initially greeted by many Germans with a mixture of surprise and apprehension,[55] the decades-old fear that German flag-waving and national pride was inextricably associated with its Nazi past was dismissed by the end of the tournament by Germans and non-Germans alike.[56]
See also
- National colours of Germany
- List of German flags
- Flags of German states
- Coat of arms of Germany
- Hanseatic flags
- Flag of Prussia
- Reichskriegsflagge
References
- ^ Template:De icon Federal Parliament of Germany (2004-12-15). "Schwarz Rot Gold. Symbol der Einheit". Retrieved 2007-05-29.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ a b c Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany (23 May 1949). German version and English version (December 2000) (PDF). See Article 22. Retrieved on 24 February 2008.
- ^ a b Template:De icon Federal Government of Germany (1950-07-07). "Anordnung über die deutschen Flaggen". documentArchiv.de. Retrieved 2007-08-09.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Template:De icon Federal Government of Germany (24 May 1968). "§ 124 OWiG: Benutzen von Wappen oder Dienstflaggen". Retrieved 2008-02-24.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Template:De icon Federal Government of Germany (1996-11-13). "Anordnung über die deutschen Flaggen". Gesetze im Internet. Retrieved 2008-02-26.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Flag hoisting formats and terminology (Germany, Austria and adjacent countries)". Flags of the World. 26 October 2001. Retrieved 2008-02-24.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ a b Template:De icon Government of the German Reich (1921-04-11). "Verordnung über die deutschen Flaggen". documentArchiv.de. Retrieved 2007-08-09.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Colours of the Flag (Germany)". Flags of the World. 5 August 1998. Retrieved 2008-02-24.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) Contains a letter from the German Ministry of the Interior (30 July 1998) - ^ Template:De icon Federal Government of Germany (17 December 2007). "Primärfarben". Corporate Design Documentation. Retrieved 2008-02-26.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Template:De icon Dreyhaupt, Rüdiger F. (2000). "Flags of the Weimar Republic". Der Flaggenkurier. 11: 3–17.
- ^ a b Template:De icon Federal Court of Justice of Germany (16 November 1959). 3 StR 45/59.
- ^ Template:De icon Rabbow, Arnold (1968). "Schwarz-Rot-Gold oder Schwarz-Rot-Gelb?". Neue Heraldische Mitteilungen / Kleeblatt-Jahrbuch. 6+7. Hanover: 30–32.
- ^ a b Template:De icon Federal Government of Germany (2005-03-22). "Beflaggungserlass der Bundesregierung". Verwaltung Online. Retrieved 2008-02-24.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Flag Protocol (Germany)". Flags of the World. 6 February 2002. Retrieved 2008-02-26.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ a b "Holy Roman Empire". Flags of the World. Retrieved 2008-02-26.
- ^ "Unidentified 'Rhine Republic' Flag 1806 (Germany)". Flags of the World. Retrieved 2008-02-26.
- ^ a b c d Template:De icon Rabbow, Arnold (2007). "Schwarz-Rot-Gold: Einheit in Freiheit". Der Flaggenkurier. 25: 41–45.
- ^ Template:De icon Scheidler, Karl Hermann (1865-08-05) Illustrierte Zeitung, Leipzig, 98
- ^ a b "German Confederation". Flags of the World. Retrieved 2008-03-02.
- ^ "Austria: The Age of Metternich". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. 2008. Retrieved 2008-03-05.
- ^ "The Hambach Festival". Official website of Hambach Castle. 2007. Retrieved 2008-02-24.
- ^ Template:De icon Frankfurt Parliament (1848-11-12). "Gesetz betreffend die Einführung einer deutschen Kriegs- und Handelsflagge". documentArchiv.de. Retrieved 2007-08-09.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Template:De icon "Constitution of the North German Confederation". documentArchiv.de. 1867-06-27. Retrieved 2008-02-24.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) See Article 55. - ^ Template:De icon "Constitution of the German Empire". documentArchiv.de. 1871-04-16. Retrieved 2008-02-24.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) See Article 55. - ^ Template:De icon "Constitution of the Weimar Republic". documentArchiv.de. 1919-08-11. Retrieved 2008-02-24.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) See Article 3. - ^ Template:De icon von Hindenburg, Paul (1933-03-12). "Erlaß des Reichspräsidenten über die vorläufige Regelung der Flaggenhissung". documentArchiv.de. Retrieved 2008-02-09.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ a b Template:De icon Government of the German Reich (1935-09-15). "Reichsflaggengesetz". documentArchiv.de. Retrieved 2007-12-23.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Template:De icon Statement by Hermann Göring, in the Völkischer Beobachter (17 September 1935)
- ^ Speer, Albert (1970). Inside the Third Reich. New York: Macmillan. ISBN 0-684-82949-5.
- ^ Template:De icon Government of the German Reich (1933-12-20). "Verordnung über die vorläufige Regelung der Flaggenführung auf Kauffahrteischiffen". documentArchiv.de. Retrieved 2007-12-23.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Centred vs. Offset Disc and Swastika 1933-1945 (Germany)". Flags of the World. Retrieved 2008-02-24.
- ^ a b Rabbow, Arnold (1983). "A Flag Against Hitler. The 1944 National Flag Proposal of the German Resistance Movement". Flag Bulletin. 100.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Allied Control Council (1945-08-30). "Law N° 1 from the Control Council for Germany: Repealing of Nazi Laws". European NAvigator. Retrieved 2007-12-23.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Allied Control Council (30 November 1946). "Law No. 39 of the Allied Control Commission". Flags of the World. Retrieved 2008-02-26.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) See Article 1 #3. - ^ Template:De icon "Constitution of Württemberg-Baden". Verfassungen der Welt. 1946-11-30. Retrieved 2008-02-24.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) See Article 45 - ^ "Württemberg-Baden 1947-1952 (Germany)". Flags of the World. Retrieved 2008-02-24. Contains quotation from discussion of the constitution committee.
- ^ Template:De icon "Constitution of Rhineland-Palatinate". Verfassungen der Welt. 1947-05-18. Retrieved 2008-02-24.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Template:De icon "Preliminary constitution of Lower Saxony". Verfassungen der Welt. 1951-04-13. Retrieved 2008-02-24.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) See Article 1 #2 - ^ "Rhineland-Palatinate (Germany)". Flags of the World. Retrieved 2008-03-03.
- ^ "Lower Saxony (Germany)". Flags of the World. Retrieved 2008-03-03.
- ^ Template:De icon Friedel, Alois (1968). Deutsche Staatssymbole. Athenäum-Verlag. ISBN 9783761051153.
- ^ Template:De icon "SED-proposed constitution of the German Democratic Republic". documentArchiv.de. 1946-11-14. Retrieved 2008-02-24.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ a b "Proposals 1944-1949 (Germany)". Flags of the World. Retrieved 2008-02-24.
- ^ "The Saar referendum". European Navigator. 1955-10-23. Retrieved 2008-02-24.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Template:De icon "Constitution of the Saarland". documentArchiv.de. 1947-12-15. Retrieved 2008-02-24.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) See Article 61. - ^ Template:De icon Government of the Saarland (1956-07-09) Gesetz Nr. 508 über die Flagge des Saarlandes and Gesetz Nr. 509 über das Wappen des Saarlandes
- ^ Template:De icon "Constitution of the German Democratic Republic". documentArchiv.de. 1949-10-07. Retrieved 2008-02-24.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) See Article 2. - ^ Template:De icon Government of the German Democratic Republic (1959-10-01). "Gesetz zur Änderung des Gesetzes über das Staatswappen und die Staatsflagge der Deutschen Demokratischen Republik". documentArchiv.de. Retrieved 2008-02-24.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Information pamphlet by the Foundation for the Reconciliation of the SED Dictatorship. Retrieved on 9 March 2008.
- ^ a b Home page of monarchist organisation Tradition und Leben. See German section for more detailed text. Retrieved on 24 February 2008.
- ^ Sontheimer, Michael (2006-06-29). "Dr. Strangelove: How Germans Learned to Stop Worrying and Love the Flag". Spiegel Online. Retrieved 2008-03-05.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Young, Marc (2006-06-14). "Germany flies the flag". Spiegel Online. Retrieved 2008-02-24.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Bernstein, Richard (2006-06-14). "In World Cup Surprise, Flags Fly With German Pride". The New York Times. Retrieved 2008-03-05.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Crossland, David (2006-07-10). "Germany's World Cup Recovery: From Humorless to Carefree in 30 Days". Spiegel Online. Retrieved 2008-03-05.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help)
External links