Dniester
|
Dniester Dniester |
||
|
The course of the Dnister |
||
| Data | ||
| location | Ukraine , Moldova | |
| River system | Dniester | |
| Headwaters | Ukrainian Forest Carpathians 49 ° 12 ′ 44 ″ N , 22 ° 55 ′ 40 ″ E |
|
| Source height | 900 m | |
| muzzle |
Black Sea near Majaky Coordinates: 46 ° 21 ′ 0 ″ N , 30 ° 14 ′ 0 ″ E 46 ° 21 ′ 0 ″ N , 30 ° 14 ′ 0 ″ E |
|
| Mouth height | 0 m | |
| Height difference | 900 m | |
| Bottom slope | 0.67 ‰ | |
| length | 1352 km | |
| Catchment area | 72,100 km² | |
| Drain at the Bender gauge |
MQ |
310 m³ / s |
| Left tributaries | Hnyla Lypa , Solota Lypa , Seret , Sbrutsch , Smotrych | |
| Right tributaries | Stryj , Bîc , Răut , Bystryzja | |
| Reservoirs flowed through | Dniester reservoir , Dubăsari reservoir | |
| Big cities | Tiraspol | |
| Medium-sized cities | Bender | |
| Small towns | Salishchyky , Novodnistrovsk , Chotyn | |
| Navigable | 500 km | |
|
Dniester near Horodok with the mouth of the Seret (right in the picture) |
||
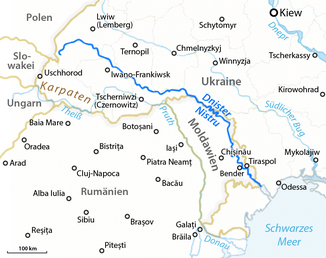
The Dniester ( Ukrainian Дністер / Dnister , Russian Днестр / Dnestr , Romanian Nistru , Polish Dniestr , sometimes also Dniester , in ancient Greek Τύρας / Týras ) is a 1352 km long tributary of the Black Sea . It flows through the Ukraine and the Republic of Moldova .
course
The river has its source at a height of about 900 m above sea level in the Ukrainian Forest Carpathians in the Turka Raion near the village of Vovche near the Ukrainian-Polish border . Over a length of about three kilometers dozens of smaller streams flow from the southwestern slopes of the Tschentyjewka Mountain (Ukrainian Чонтийовка Tschontyjowka , 923 m ) together and form the Dniester.
Many of its right tributaries, which carry clear mountain water, have their source in the Carpathian Mountains. The only exception is the small tributary Siwka , which carries wastewater from the chlorine chemical factory in the city of Kalush into the Dniester in the Lower Carpathian Plain .
In the Sub-Carpathian Plain between the cities of Stryi , Schydatschiw , Mykolaiv , Komarno and Sambir lies a large wet meadow landscape that is home to numerous endangered plant and animal species, such as large populations of the corncrake .
From the town of Salishchyky , the Dniester cuts through the Podolian Plate in the form of a valley meander up to 160 m deep and sometimes a few hundred meters wide . As the Dniester Canyon, this section of the river has the status of a national natural monument.
In Novodnistrovsk , the river is backed up by a hydropower plant over a length of up to 140 km. It then forms the natural border between Moldova and Ukraine for a few kilometers, before flowing into Moldovan territory near the municipality of Nimereuka and henceforth separating Transnistria from the rest of the country.
Flowing towards the southeast, it crosses the Dubăsari reservoir . Then the Bîc joins him and he passes Tiraspol . The Dniester flows into the Black Sea at Mayaky a few kilometers west of Odessa and a little south of the Moldovan-Ukrainian border . The river's wide estuary consists of several arms that lead into a boggy liman called Dnister-Liman (Ukrainian Дністровський лиман / Dnistrovskyj Lyman ) with dimensions of 40 × 10 km. This is separated from the Black Sea by a narrow headland.
Loop of the Dniester near the village of Pilipche between Salishchyky and Melnyzja-Podilska
The Dniester at the city of Tiraspol
Tributaries

|
right |
Left
|
Cities
The largest city on the Dniester is Tiraspol in Transnistria (Moldova). Other important cities are:
- In Ukraine:
- Staryj Sambir , Sambir , Novyi Rozdil , Zhydachiv , Khodoriv , Halych , Yezupil , Zalischyky , Chotyn , Novodnistrovsk , Sokyriany
- On the Ukrainian-Moldovan border (left bank): Mohyliw-Podilskyj , Jampil
- At the Liman: Bilhorod-Dnistrovskyi
- In Moldova:
- (right bank :) Otaci , Soroca
- Transnistrian segment (left bank): Tiraspol , Dnestrovsc , Camenca , Dubăsari , Grigoriopol , Slobozia , Crasnoe , Rîbnița , Bender
history
Its current name comes from Sarmatian * dānu nazdya 'near river'.
The Ottoman - Polish border ran along the Dniester until the partitions of Poland . After that, the upper reaches lay in the Austrian crown land of Galicia (and Lodomeria , with the Bukowina in the south). From the Sbrutsch estuary, it temporarily formed the Ottoman- Russian border, at times it ran all over Russia, with the changing affiliation of Bessarabia (today's Moldova and the Odessa-Ismail region).
economy
From the mouth, not even half of the river, at 500 km, is navigable. In winter the Dniester is frozen over for around 70 days. However, it plays an important role in the shipping of agricultural products (grain, vegetables, sunflower seeds) as well as cattle and wood that is felled in the Dniester basin. The reservoirs (e.g. at Dubăsari and the Dniester reservoir with the Dniester pumped storage power plant ) are of great importance for the local energy supply.
Large nature reserves are emerging in the Dnister Delta, which were created with the support of the EECONET Action Fund .
See also
Web links
- Dniester . In: Meyers Konversations-Lexikon . 4th edition. Volume 5, Verlag des Bibliographisches Institut, Leipzig / Vienna 1885–1892, p. 15.
- Map of the river
- Water levels in Halytsch
- Incident prevention and risk management against accidents on the Dniester and its catchment area