Army Reconnaissance Force (Bundeswehr)
The army reconnaissance troop (HAufklTr) is a branch of service in the army of the Bundeswehr . The German Army Reconnaissance Force is one of the operational and command support forces . The main task is the reconnaissance of enemy forces and the exploration of unknown terrain.
assignment

The Army Reconnaissance Force is the main vehicle for the army's reconnaissance . It has the task of using the means available to it to cover all aspects of tactical battlefield reconnaissance and operational reconnaissance in the depths of the battlefield and thus to ensure the prerequisites for the creation of a real-time military situation report for the commanders of the combat troops. Unknown areas in the apron, traffic routes, barriers, fixed military installations and information on the strength, deployment and direction of enemy troops are of particular interest.
The majority of the army reconnaissance troops are motorized for this purpose and gain information in advance of their own combat troops , partly also behind enemy lines. The troops are equipped with special optoelectronic and other electronic reconnaissance equipment. In addition, the troops have drones that enable reconnaissance over long distances. The Army Reconnaissance Force is able to evaluate the information obtained through its own reconnaissance means. In addition, the troops can also supplement, deepen or verify the results of other reconnaissance means. The troops provide the military commanders at all levels and the joint armed forces intelligence gathering and reconnaissance network (NG&A) with the situation report obtained as quickly as possible, as required and as appropriate to the situation. The joint N&A network is also supported in the army, for example, by the “ Joint Fire Support Teams ” of infantry and artillery . To transmit the information, the Army Reconnaissance Force has special skills in the field of telecommunications .
In the course of incorporation into the Army Reconnaissance Force , the former tank reconnaissance force had to surrender its main battle tanks and is therefore no longer able to carry out reconnaissance by combat . This task therefore falls to the armored troops in conjunction with the army reconnaissance troops.
The long-distance surveillance and field intelligence forces of the Army Reconnaissance Force take on the following special assignments:
- Remote spying forces secretly gain key information far behind enemy lines. You are on your own and not motorized . You work together with the special forces of the Army and can take on the task of " Forward Air Controller ".
- Field intelligence forces create situation reports by conducting conversations, questioning people in the custody of the armed forces and observing objects and people ( HUMINT ).
history
The reorganization of the military branches in the army was announced in October 2005 by the commander's letter from the inspector of the army . This had serious consequences, especially for the previously independent armaments of the armored reconnaissance troops and teleconservation troops . These branches of service were dissolved and combined with the drone reconnaissance forces of the artillery and the field intelligence forces in the new branch of the army reconnaissance troops. The list of the type of service was completed in 2008. After that, almost all of the army's reconnaissance forces were under a common conceptual leadership for the first time. For example, the reconnaissance forces of the Army Aviation Troops , the NBC defense force and the EloKa telecommunications force were excluded from the reform .
education
The Army Reconnaissance Force offers a wide variety of training courses in these areas
- Ground-based (scouting) reconnaissance; again divided into
- Vehicle-based reconnaissance ( FENNEK ) and
- Light reconnaissance (light reconnaissance group / remote spying )
- Airborne reconnaissance ( Luna / KZO ; the latter are currently (as of January 2020) being replaced by Luna NG )
- Personal education ( field messages )
- Technical reconnaissance ( radar )
The subject-specific training and further education takes place at the Army Reconnaissance Force Training Area in Munster ; the training of Airborne reconnaissance is proportionately in Idar-Oberstein at the artillery school instead
A specialty of the recruitment and training of remote scouts and field intelligence officers is an upstream aptitude test:
- Due to the demanding training and assignments, the applicants for remote scouts are subjected to an aptitude test as with the special forces of the army . This is done as part of a selection process during the training of the light scout soldiers. In addition to the Army Reconnaissance Forces training center, the Special Operations Training Center (formerly: International Remote Scouting School) is of particular importance for the advanced training of remote scouts .
- The candidates for the field intelligence staff also go through an extended aptitude test, which is mainly about psychological resilience z. B. in questioning or interrogation .
organization
classification
The army reconnaissance troop is a branch of service in the army of the Bundeswehr . The type of service is one of the operational and command support troops . At the head of the Army Reconnaissance Force is the General of the Army Reconnaissance Force , who as commander leads the Army Reconnaissance Force Training Center and is therefore particularly responsible for the training of the armies. The Army Development Office has been responsible for the further development of the military branch since June 2013 .
The units of the Army Reconnaissance Force cover the information needs of the troop leaders at the vision and brigade level , and if necessary, also higher command authorities .
More units in the army
Combat reconnaissance forces are integrated into combat troop battalions of the Army. However, these are not part of the Army Reconnaissance Force. These are in particular the reconnaissance and liaison platoons of the staff and supply companies of the combat troop battalions , as well as the reconnaissance platoons in the heavy companies of the infantry battalions . The four reconnaissance platoons of the mountain infantry battalions are equipped with the Fennek scout car. The reconnaissance platoons in the heavy companies of the paratrooper regiments and the Jäger Battalion 1 have Wiesel 1.
The artillery force has reconnaissance observation artillery , including units that ensure reconnaissance using drones.
The Army Aviation Corps has, according to the present in the feed Eurocopter Tiger , also rising above means of battlefield reconnaissance.
The Special Forces Command has its own specialized forces for reconnaissance , which (besides the airborne reconnaissance companies) are the only ones able to conduct reconnaissance in remote surveillance operations.
Although there are other reconnaissance units in the Bundeswehr outside of the army reconnaissance troops, none of the “reconnaissance troops”, which is based on its name, does not lead.
Further units in the Bundeswehr
With the Cyber and Information Room Command, a command authority was created on April 5, 2017, which is supposed to bundle the armed forces' common intelligence gathering and reconnaissance and to coordinate them over the armed forces. For this purpose, the Strategic Reconnaissance Command was subordinated, which has the units of the EloKa telecommunications force and thus special capabilities in telecommunications and electronic reconnaissance and satellite-based reconnaissance.
In a broader sense, troop units are planned especially in the armed forces base, which supplement the reconnaissance complex of the Bundeswehr on a strategic level. These include, for example, the Center for Operative Information .
With the reconnaissance company of the sea battalion and the fleet service boats , the German Navy has its own reconnaissance forces, as does the air force with the tactical air force squadron 51 "Immelmann" .
The Military Counterintelligence Service (MAD) is the defensive intelligence service of the division of the Federal Ministry of Defense .
One goal of the transformation of the Bundeswehr is to provide the reconnaissance results of all the reconnaissance forces described in the army, in the extended concept reconnaissance results of all branches of the armed forces and organizational areas (e.g. the " Forward Air Controller " or air force units), comprehensively and quickly to all military commanders across all troops To make available. In the army, for example, " Joint Fire Support Teams " were formed at the operational level , which bundle the formerly isolated reconnaissance forces of several branches of service (e.g. forward observers of the artillery troops ). The formation of the army reconnaissance force must also be seen from the perspective of combining various reconnaissance forces. The aim is also to integrate the army reconnaissance force more comprehensively into the reconnaissance groups of the Bundeswehr.
Active units
Active units are currently:
| designation | place | Association | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Battalions | ||||
| Reconnaissance Training Battalion 3 "Lüneburg" | Luneburg | Tank Training Brigade 9 | ||
| Reconnaissance Battalion 6 | Eutin | Panzer Grenadier Brigade 41 | ||
| Reconnaissance Battalion 7 | Awls | Armored Brigade 21 | ||
| Reconnaissance Battalion 8 | Freyung | Armored Brigade 12 | ||
| Reconnaissance Battalion 13 | Gotha | Panzer Grenadier Brigade 37 | ||
| Mountain Reconnaissance Battalion 230 | Feet | Mountain Infantry Brigade 23 | ||
| Companies | ||||
| Airborne Reconnaissance Company 260 | Lebach | Airborne Brigade 1 | ||
| Airborne Reconnaissance Company 310 | Seedorf | Airborne Brigade 1 | ||
| 4th / Jäger Battalion 291 * | Illkirch-Graffenstaden ( FR ) | Franco-German Brigade | ||
* The Jäger Battalion 291 set up in 2010 has, in addition to the infantry companies , a reconnaissance company that is part of the army reconnaissance force and that makes the battalion a specialty within the Bundeswehr.
| Structure of active units of the Army Reconnaissance Force |
|---|
|
Reconnaissance battalions
The army's six reconnaissance battalions are basically equipped with the same equipment. The individual scouting companies do not have their own drone platoon, which is why there is an independent drone reconnaissance company at battalion level that manages the Luna and KZO systems as well as the radar forces.
Reconnaissance Company of the Jäger Battalion 291
In order to keep the Luna skills and field messages available for use and for better training and exercise, the drone and field message train are located in AufkBtl 13 in Gotha. Airborne
|
Inactive units
The following supplementary troops are also set up without their own large equipment , which use large equipment of the specified active troop unit ( economic or non-military unit ) at the location for exercise and training of the reservists : They are the respective 5th companies of the reconnaissance training battalion 3 "Lüneburg", the reconnaissance battalion 13 and the Mountain Reconnaissance Battalion 230.
Units decommissioned
equipment
Large device
The Army Reconnaissance Force has the following large equipment:
- Drone systems
- Armored vehicles
- Fennek scout car
- Waffträger Wiesel 1 (reconnaissance variant of the airborne reconnaissance units)
- Transport tank Fuchs
- GTK boxers
- ATF dingo
- Mowag Duro
- Radar systems
- RASIT (loaded on TPz Fuchs )
- LeGAR (light battlefield reconnaissance radar; only used by airborne reconnaissance companies)
uniform
The weapon color of the Army Reconnaissance Troops, shown for example as the color of the braids and collar tabs , is golden yellow . The color of the beret is black . In contrast to this, soldiers of the Army Reconnaissance Troops of the Rapid Forces Division wear the burgundy-colored beret. The beret badge shows two crossed rider lances framed by oak leaves .
The combination of black beret and golden yellow weapon color also marked the army's field intelligence forces, which in turn had adopted this combination from the armored reconnaissance force when it was founded. For the longest time of its existence, golden yellow was also the color of the weapons used by televised scouts. A slightly lighter yellow (lemon yellow) indicates the telecommunications force . The black beret shared the armored reconnaissance force with the original armored combat troops , which included the armored reconnaissance troops . As there too, e.g. B. in the tank troops , the black beret is also often worn in combat service. The rider lances in the beret badge were already included, along with other symbols, in the beret badges of the remote scout and tank reconnaissance troops. They are a traditional symbol of the cavalry , in whose relationship the army reconnaissance troops see themselves. Incidentally, the color of the weapons used by the cavalry in the Reichswehr and Wehrmacht was golden yellow .
Military symbol
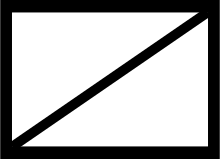
The military symbol of the Army Reconnaissance Force shows the usual NATO conventions as a line running from bottom left to top right.
Military symbol (basic symbol ) of the NATO reconnaissance force
See also
literature
- Reinhard Scholzen : Army reconnaissance. Motorbuch-Verlag, Stuttgart 2012, ISBN 978-3-613-03408-2 .
- Freundeskreis Heeresaufklärer (Ed.): The Panzerspähtrupp - Narchrichterblatt for the Freundeskreis Heeresaufklärer . so far 48 issues (1984–2010). Munster ( heeresaufklaerungstruppe.de ( memento of July 10, 2011 in the Internet Archive ) [accessed on January 20, 2011] overview and ordering information).
- Cord Schwier (Ed.): ... and the scouts are always there .... On the history of the German tank reconnaissance troops . Munster 2005, ISBN 3-00-013145-0 ( heeresaufklaerungstruppe.de ( Memento of July 10, 2011 in the Internet Archive ) [accessed on January 20, 2011]).
Web links
- The Army Reconnaissance Force. Federal Ministry of Defense , the head of the press and information staff, accessed on January 20, 2011 .
- Jürgen Engelhardt: New type of troops in the army - Army reconnaissance troops set up. (pdf) Federal Ministry of Defense, Head of the Press and Information Staff, 2008, accessed on January 20, 2011 .
- pzaufkl.de - The golden yellow pages of the German tank reconnaissance and army reconnaissance. Wolfgang Schmid, accessed January 20, 2011 .
- Website Freundeskreis Army Reconnaissance Party. Army Reconnaissance School, accessed January 20, 2011 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ What is the mission of the Army Reconnaissance Force? Federal Ministry of Defense , the head of the press and information staff, accessed on January 20, 2011 .
- ↑ Formations of the Army. (No longer available online.) The Federal Archives, archived from the original on September 14, 2015 ; Retrieved February 20, 2011 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ The Army Reconnaissance Force. Federal Ministry of Defense, head of the press and information staff, 2018, accessed on July 26, 2018 .
- ↑ The history of the Army Reconnaissance Force. Federal Ministry of Defense, the head of the press and information staff, accessed on January 20, 2011 .
- ↑ Reinhard Scholzen : Reconnaissance Artillery. In: Troop service. 2, 2014, pp. 146-150.
- ↑ Which units are part of the Army Reconnaissance Force? Federal Ministry of Defense, the head of the press and information staff, accessed on January 20, 2011 .
- ^ Franco-German Brigade - Jägerbataillon 291st German-French Brigade , Bureau presse / press and public relations, archived from the original on March 23, 2010 ; Retrieved January 20, 2011 .
- ^ Antje Jungmann: German soldiers are stationed in France. Federal Ministry of Defense, head of the press and information staff, 2010, accessed on January 20, 2011 .
- ↑ the reserve of the army
- ↑ What equipment and technology does the Army Reconnaissance Force use? Federal Ministry of Defense, the head of the press and information staff, accessed on July 2, 2019 .
- ↑ Airborne Reconnaissance Company 310 - structure. Federal Ministry of Defense, the head of the press and information staff, accessed on January 20, 2011 .
- ↑ Light battlefield reconnaissance radar (LeGAR) / BOR-A 550. pzaufkl.de/heeresaufklärer.de, July 3, 2017, accessed on April 12, 2020 .




