Plantain family
| Plantain family | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Germander speedwell ( Veronica chamaedrys ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Plantaginaceae | ||||||||||||
| Yuss. |
The plantain family (Plantaginaceae), sometimes also referred to as speedwell family (Veronicaceae), are a family of plants in the order of the mint family (Lamiales). They are represented worldwide in all climate zones .
description

The Plantaginaceae sl family is morphologically very heterogeneous .
Vegetative characteristics
They are mostly annual or herbaceous plants , rarely shrubs ( Veronica subg. Hebe , Aragoa ). Some genera are aquatic plants ( Hippuris , Callitriche ). Parasites or semi-parasites are absent from this family.
Hair ( trichomes ) are usually simple, often glandular, sometimes star-shaped. The lack of vertical structure in the hair is considered to be a common derived characteristic of the family ( synapomorphism ). The leaves are opposite, alternate or screwy, rarely whorled. In most species the leaf blades are simple, less often composed; whole to pinnate. The veins are pinnate, but in Plantago mainly parallel. Stipules are missing.
Generative characteristics
The inflorescences are very diverse and include both open and closed inflorescences; in some species the flowers are solitary.
The mostly hermaphrodite flowers are zygomorphic and usually five-fold with a double flower envelope . Some genera have radial symmetry flowers ( e.g. Bacopa , Sibthorpia ), in others the flowers are reduced ( Callitriche ). As an exception, Hippuris species are single sexed ( monoecious ), and some species of Plantago and Veronica subg. Hebe are dioecious, separate sexes ( diocesan ) or gynodioces .
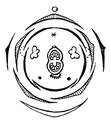
Flowering diagram of Veronica
There are usually five, sometimes four sepals that are free to fused. There are usually five fused petals , sometimes only four due to the merging of the two upper corolla lobes. The fusion can go on to only two lobes ( lagotis ). Sibthorpia, on the other hand, also has corolla lobes. The corolla tube can either be inconspicuous or very long compared to the corolla lobes. In some Veronica species, which were previously placed with Besseya , the crown is completely absent. The flowers can grow to several centimeters and can be pollinated by wind, bees, flies or birds. Some flowers have a nectar spur, in others a protrusion of the lower lip covers the entrance (mask flower). For others, the entrance is blocked by hair. A nectar slice is present in most genera.
The androeceum forms early compared to the corolla tube. This is possibly another synapomorphism . Usually there are four stamens , rarely only two or one ( Hippuris, Callitriche ). A fifth stamen is sometimes reduced as staminodium . The stamens are connected to the corolla tube (adnat). The anthers are arrow-shaped, because the pollen sacs diverge below. The pollen is usually tricolpat to tricolporat and has a reticulate exine .
The gynoeceum consists of two fused carpels . Plantago subg. Littorella has only one carpel. The ovary is on top and is characterized by central angular placentation with large, undivided placentas. The ovules are numerous, more rarely the number is reduced to one per compartment, such as in Lagotis . The ovules are anatropic to hemitropic, have an integument and a thin-walled mega sporangium . There is a stylus with a bilobed or cephalic scar .
The capsule fruits are usually septicidal or loculicidal , more rarely poricidal or circumscissile and contain one to many seeds. The egg-shaped seeds can be winged. In winged seeds, the inner walls of the Exotesta cells are thickened.
The basic number of chromosomes varies between x = 6 and x = 11.
ingredients
The secondary ingredients are diverse. Iridoids are predominant . In some groups they are missing and are then often replaced by various glycosides ( e.g. in Gratioleae, Sibthorpia , Ellisiophyllum , Digitalis ). The Antirrhineae and Monttea have antirrhinoside . Bacopa , Gratiola and Stemodia contain di- and triterpene glucosides. Most genera form amorphous or globular protein bodies in the cell nucleus .



Systematics
Of the Central European genera , only plantain ( Plantago ) and Strandling ( Littorella ) traditionally belong to the plantain family. Most of the genera and species used to be counted among the figwort family (Scrophulariaceae).
Phylogenetic investigations using molecular biological methods have led to a division of the Scrophulariaceae family and a considerable expansion of the Plantaginaceae. The Plantaginaceae family comprises twelve tribes with 92 genera, which together include around 2000 species. The structure follows Albach et al. 2005. The correct nomenclature name of the family according to the ICBN is Plantaginaceae, but in 2008 it was proposed to instead define Veronicaceae as the noun conservandum in order to clearly differentiate the family as described here from the Plantaginaceae in the narrow sense, as they existed until 1998 and how they are circumscribed by some authors who divide the Plantaginaceae into several families in the scope shown here.
The taxa of the earlier families: Antirrhinaceae, Aragoaceae, Callitrichaceae, Chelonaceae, Digitalidaceae, Ellisiophyllaceae, Erinaceae, Linariaceae, Littorellaceae, Oxycladaceae, Psylliaceae, Scopariaceae, Sibthorponicaceae belong to this family today, Trapellaceae.
Here are the twelve tribes of the Plantaginaceae with the included genera:
- Tribus Angelonieae
Pennell : It contains about six genera:
- Angelonia Humb. & Bonpl. : The approximately 25 species are common in the Neotropic .
- Base monkey Turcz. : The seven or so species are common in the Neotropic.
-
Melosperma Benth. : It contains only one type:
- Melosperma andicola Benth. : It only occurs in Chile .
- Monopera Barringer : The roughly two types are common in South America.
- Monttea Gay : The three or so species occur in Chile.
- Ourisia Comm. ex Juss. : The 26 to 30 species are common in the Andes , New Zealand and Tasmania .




- Tribe Antirrhineae Dumort. : It contains about 29 genera:
- Acanthorrhinum Rothm. : The only two species occur in Spain and North Africa .
- Albraunia Speta : The three or so species occur in Southwest Asia .
-
Lochschlund ( Anarrhinum Desf. ): There are about twelve species in the Mediterranean , one of which:
- Daisy throat ( Anarrhinum bellidifolium (L.) Willd. ) Also occurs in Central Europe (Rhineland-Palatinate).
- Snapdragons ( Antirrhinum L. ): The 20 to 30 species are common in North America and the Mediterranean.
-
Gloxinia Winds ( Asarina Mill. ): Up to 15 species are common in North America and only one occurs in Europe:
- Gloxinia bindweed ( Asarina procumbens Mill. ): It occurs only in northeastern Spain and in southern France .
- Klaffmund ( Chaenorrhinum (DC.) Rchb. ): The 20 or so species are common in Europe, the Mediterranean and Western Asia.
- Cymbal herbs ( Cymbalaria Hill ): The ten or so species are common in Western Europe and the Mediterranean.
-
Epixiphium (Engelm. Ex A.Gray) Munz : It contains only one species:
- Epixiphium wislizeni (Engelm. Ex A.Gray) Munz : It occurs in Mexico .
- Galvezia Dombey ex Juss. : The approximately five species are distributed from California via Mexico to Ecuador and Peru.
- Gambelia Nutt. : The four or so species are distributed from California to Mexico.
-
Holmgrenanthe Elisens : It contains only one species:
- Holgrenanthe petrophila (Coville & CVMorton) Elisens : It is only found in California.
- Holzneria Speta : One or two species are common in Southwest Asia.
-
Howelliella Rothm. : It contains only one type:
- Howelliella ovata (Eastw.) Rothm. : It only occurs in California.
- Tännelkräuter ( Kickxia Dum. ): The approximately 25 species are distributed from Europe over the Mediterranean area to India .
- Lafuentea Lag . : The roughly two species occur in Spain and Morocco .
- Flax herbs ( Linaria Mill. ): The approximately 150 species thrive in the temperate areas of the northern hemisphere, especially in the Mediterranean area.
- Lophospermum D.Don : The ten or so species are mainly found in Mexico.
- Mabrya Elisens : The six or so species are distributed from the southern USA to Mexico.
- Maurandella (A. Gray) Rothm. : Up to three species are distributed from the USA to Mexico.
- Maurandya Ortega : Up to six species are distributed from North America to Mexico.
- Misopates Raf. : The roughly two species are common in Eurasia and Africa.
- Mohavea A. Gray : One or two species are found in the southwestern United States.
- Neogaerrhinum Rothm. : One or two species occur in the southwestern United States.
- Nuttallanthus D.A.Sutton : The four or so species are distributed from North to Central and South America.
-
Pseudorontium (A. Gray) Rothm. : It contains only one type:
- Pseudorontium cyathiferum (Benth.) Rothm. : It only occurs in California.
- Rhodochiton Zucc. ex Otto & A. Dietr. : There are about two species in Mexico.
- Sairocarpus D.A.Sutton : The up to twelve species are mainly found in North America.
- Schweinfurthia L .: Up to six species are distributed from North Africa to India.
- Tribus Callitricheae Dumort. : It contains only two genera and up to 41 species:
- Water stars ( Callitriche L. ): The 25 to 40 species are distributed almost worldwide.
-
Fir fronds ( Hippuris L. ): The only two species are widespread in waters in the temperate areas mainly of the northern hemisphere, including:
- Common fir frond ( Hippuris vulgaris L. )
- Tribe Cheloneae Benth. : It contains about nine genera:
 Tribe Cheloneae: Penstemon triflorus
Tribe Cheloneae: Penstemon triflorus- Brookea Benth. : The four or so species occur only on Borneo .
- Shield flowers , also called snakeheads ( Chelone L. ): The five or so species are common in North America.
- Chionophila Benth. : There are about two species only in the Rocky Mountains .
- Collinsia Nutt. : The approximately 20 species are common in North America.
- Keckiella Straw : The seven or so species are common in North America.
-
Nothochelone (A.Gray) Straw : It contains only one species:
- Nothochelone nemorosa (Douglas ex Lindl.) Straw : It occurs in western North America.
- Beard thread ( Penstemon Schmidel , including Pennellianthus Crosswh. ): The approximately 250 species are common in North America and northeastern Asia.
- Tonella Nutt. ex A.Gray : The roughly two species are common in western North America.
- Uroskinnera Lindl. : The four or so species are distributed from Mexico to Central America .

- Tribe Digitalideae Dumort. : It contains three types:
- Thimbles ( Digitalis L. ): The approximately 18 species are distributed from Europe to Central Asia.
- Alpenbalsam ( Erinus L. ): The roughly two types are native to North Africa , the Pyrenees and the Alps .
- Isoplexis (Lindl.) Loudon (sometimes included in Digitalis ): The two to three species are common in Macaronesia .

- Tribus Globularieae Rchb. : It contains three types:
- Campylanthus Roth : The approximately 17 species are distributed in Macaronesia, northeastern Africa and the Persian Gulf.
- Globularia ( Globularia L. ): The 20 to 25 species in Europe, Asia Minor to the Canary Islands disseminated and in Cape Verde.
- Poskea Vatke : The two or so species only occur in Somalia and Socotra .






- Tribe Gratioleae Benth. It contains 16 to 40 genera with around 320 species that occur almost worldwide, with a focus on the Neotropic and adjacent temperate areas .:
- Achetaria Cham. & Schltdl. : The seven or so species are common in the Neotropic.
- Adenosma R.Br. : The 15 to 27 species are common in Asia and Australia .
- Bacopa ( Bacopa Aubl. , Including Brami Adans. , Bramia Lam. , Herpestis Gaertn. , Hydrant Helium Kunth , Macuillamia Raf. , Moniera P.Browne , Monocardia Pennell , Sinobacopa D.Y.Hong ): The approximately 60 species are mainly used in the New World .
-
Benjaminia Mart. ex benj. : It contains only one type:
- Benjaminia reflexa (Benth.) D'Arcy : It is common in the New World.
-
Boelckea Rossow : It is a monotypical genus with the only species:
- Boelckea beckii Rossow : The home is Bolivia .
-
Braunblanquetia Eskuche : It contains only one type:
- Braunblanquetia littoralis Eskuche : It occurs in Argentina .
- Capraria L .: The three to seven species are common in the New World.
- Cheilophyllum Pennell ex Britton : The eight or so species are common in Central America .
- Conobea Aubl. : The seven or so species are common in the New World.
- Darcya B.L. Turner & CCCowan : The three or so species are common in Central and South America.
- Deinostema T.Yamaz. : The roughly two types are common in East Asia.
- Dizygostemon (Benth.) Radlk. ex competition : The roughly two types are common in Brazil .
-
Dodartia L .: It contains only one species:
- Dodartia orientalis L .: It is common in southern Russia and western Asia.
- Dopatrium Buch.-Ham. ex Benth. : The 12 to 14 species are common in the tropics.
-
Fonkia Phil .: It contains only one species:
- Fonkia uliginosa Phil . : It occurs in Chile.
-
Geochorda Cham. & Schltdl. : It contains only one type:
- Geochorda glechomoides (Spreng.) Kuntze : It occurs in South America.
- Gratiola ( Gratiola L. ): Including Amphianthus Torr. , Sophronanthe Benth. , Tragiola Small & Pennell : There are about 25 species.
- Hydrotriche Zucc. ( Water hair ): The one to four species occur in Madagascar .
-
Ildefonsia Gardner : It contains only one species:
- Ildefonsia bibracteata Gardner : It occurs in Brazil.
-
Leucospora Nutt. : It contains only one type:
- Leucospora multifida (Michx.) Nutt. : It occurs in eastern North America.
- Limnophila R.Br. : The 5 to 36 species are common in the tropics (some species such as Limnophila aromatica arecalled swamp friends and are used as aquarium plants ).
-
Maeviella Rossow : It is a monotypical genus with the only species:
- Maeviella cochlearia (Huber) Rossow : It occurs in Brazil.
- Mecardonia Ruiz & Pav .: The 10 to 15 species are common in the New World.
- Otacanthus Lindl. : The three to four types are common in Brazil.
- Philcoxia P.Taylor & VCSouza : The three or so species are common in Brazil.
- Schistophragma Benth. ex Endl. : The four or so species are common in the New World.
-
Schizosepala G.M.Barroso : It is a monotypical genus with the only species:
- Schizosepala glandulosa G.M.Barroso : It isnative to Mato Grosso in Brazil.
- Scoparia L .: The 10 to 20 species are common in the Neotropic.
- Stemodia L. (Including Chodaphyton Minod , Lendneria Minod , Morgania R.Br. , Poarium Desv. Ex Ham. ): The 30 to 35 species are common in the Neotropic.
-
Tetraulacium Turcz. : It contains only one type:
- Tetraulacium veroniciforme Turcz. : It occurs in Brazil.
- Tribus Hemiphragmeae Wall. : It contains only one monotypical genus:
-
Hemiphragma Wall. : It contains a type:
- Hemiphragma heterophyllum Wall. : It occurs from the Himalayas to Assam .
-
Hemiphragma Wall. : It contains a type:
- Tribe Plantagineae Dumort. : It contains two to three genera:
- Aragoa Kunth : The 5 to 19 species thrive in the Andes.
- Littorella P.J.Bergius : Of the approximately three species, two occur in America and one occurs in Europe; the latter is the Strandling ( Littorella uniflora (L.) Asch. ), which is sometimes placed with Plantago .
- Plantain ( Plantago L. ): The approximately 275 species distributed worldwide; sometimes including littorella .
- Tribus Russelieae Pennell : It contains only two genera:
- Tribus Sibthorpieae Benth. : It contains only two genera:
-
Ellisiophyllum Maxim. : It contains only one type:
- Ellisiophyllum pinnatum (Wall. Ex Benth.) Makino : It is distributed from India via China and the Philippines to Japan and New Guinea.
- Sibthorpia L .: The two to five species occur in America, Africa, Europe and Macaronesia.
-
Ellisiophyllum Maxim. : It contains only one type:
- Tribe Veroniceae Duby : It contains 9 to 16 genera , depending on the extent of the genus Veronica :
-
Kashmiria D.Y. Hong (Syn .: Falconeria Hook f. , Wulfenia auct. Non Jacq. ): It contains only one species:
- Kashmiria himalaica (Hook. F.) DYHong : It occurs in the Himalayas.
- Lagotis Gardens. : The approximately 20 species occur in Asia from the Caucasus to central China and in Eastern Europe.
- Mänderle ( Paederota L. ): The only two species occur in southern Europe and the Alps.
- Picrorhiza Royle ex Benth. (including Neopicrorhiza D.Y. Hong ): The two or so species occur in South Asia.
-
Scrofella Maxim. : It contains only one type:
- Scrofella chinensis Maxim. : It occurs in China.
- Ehrenpreis ( Veronica L .; including Besseya Rydb. , Detzneria Schltr. Ex Diels , Hebe Comm. Ex Juss. , Paederotella (E. Wulff) Kem.-Nath. , Parahebe W.RB Oliv. , Pseudolysimachion Opiz , Synthyris Benth. ) : This genus in the broader sense is divided into sub-genera and contains about 450 species.
- Veronicastrum Heist. ex Fabr .: Up to 13 species are common in Asia and North America.
- Wulfenia ( Wulfenia Jacq. ): Around two species occur in Southeastern Europe, one species in Asia Minor and around three species in North America.
-
Wulfeniopsis D.Y.Hong : It contains only one kind or two kinds:
- Wulfeniopsis amherstiana (Benth.) DYHong : It occurs only in the western Himalayas.
-
Kashmiria D.Y. Hong (Syn .: Falconeria Hook f. , Wulfenia auct. Non Jacq. ): It contains only one species:
swell
- The Plantaginaceae family on the AP website . (Sections systematics and description)
- DC Albach, HM Meudt, B. Oxelman: Piecing together the "new" Plantaginaceae. In: American Journal of Botany. Volume 92, 2005, pp. 297-315. Full text online.
- David C. Tank, Paul M. Beardsley, Scot A. Kelchner, Richard G. Olmstead: LAS JOHNSON REVIEW No. 7. Review of the systematics of Scrophulariaceae sl and their current disposition. In: Australian Systematic Botany. Volume 19, pp. 289-307. (there Veronicaceae = Plantaginaceae to the extent shown here)
Individual evidence
- ^ Richard G. Olmstead et al.: Disintegration of the Scrophulariaceae. In: American Journal of Botany. Volume 88, 2001, pp. 348–361, (full text online.)
- ↑ James L. Reveal, Richard Olmstead, Walter S. Judd: Proposals to conserve the name Veronicaceae (Magnoliophytina) , and to conserve it against Plantaginaceae , a "superconservation" proposal. In: Taxon. Volume 57, 2008, pp. 643-644.
- ↑ Plantaginaceae in the Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN), USDA , ARS , National Genetic Resources Program. National Germplasm Resources Laboratory, Beltsville, Maryland.
- ↑ Pertti Johannes Uotila, 2009+: Hippuris. Data sheet Hippuris. In: Euro + Med Plantbase - the information resource for Euro-Mediterranean plant diversity.
- ↑ Jiarui Chen, Michele Funston: Hippuridaceae. Hippuris Linnaeus. In: Wu Zheng-yi, Peter H. Raven, Deyuan Hong (Eds.): Flora of China. Volume 13: Clusiaceae through Araliaceae. Science Press and Missouri Botanical Garden Press, Beijing and St. Louis 2007, ISBN 978-1-930723-59-7 .
- ↑ Dwayne Estes, Randall L. Small: Phylogenetic Relationships of the Monotypic Genus Amphianthus (Plantaginaceae Tribe Gratioleae) Inferred from Chloroplast DNA Sequences. In: Systematic Botany. Volume 33, Issue 1, 2008, pp. 176-182. doi: 10.1600 / 036364408783887375
- ^ Hans-Georg Kramer: Plant aquaristics á la Kramer. Tetra-Verlag, Berlin-Velten 2009, ISBN 978-3-89745-190-2 , pp. 162-171 (Limnophila aquatica, L. aromaticoides, L. browni, L. hippuroides, L. indica).
- ↑ PW Fritsch, F. Almeda, AB Martins, BC Cruz, D. Estes: Rediscovery and Phylogenetic Placement of Philcoxia minensis (Plantaginaceae), with a Test of Carnivory. In: Proceedings of the California Academy of Science. Volume 58, 2007, pp. 447-467 ISSN 0068-547X .
- ↑ a b c d e f g Classification of Veroniceae online.
- ↑ DC Albach, Heidi M. Meudt: Phylogeny of Veronica in the Southern and Northern Hemispheres based on plastid, nuclear ribosomal and nuclear low-copy DNA. In: Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. Volume 54, 2010, pp. 457-471.
Web links
- The Plantaginaceae family at DELTA . (engl.)