Anglo-American system of measurement
The Anglo-American measurement systems have their origins in medieval England and were spread in the area of influence of the former British Empire . The Anglo-American system of measurement exists in several variants and is not a self-contained system of measurement. In addition to the largely lacking reference to the decimal system , this is the main difference to the metric system of measurement .
Todays situation
Connection to the metric system
The Anglo-American system of measurement - as it is today - is not an independent system of measurement. The Mendenhall Order issued in the United States of America in 1893 abandoned the reference to its own measuring standards and determined the corresponding metric measuring standards as the standard for the basic units of yards and pounds . With the introduction of the unified “International Yard” on July 1, 1959, all countries with the exception of Great Britain made a final changeover to metric measuring standards. Great Britain also took this step with the Weights and Measures Act 1963 .
Use in English speaking countries
In the 19th and 20th centuries, the Anglo-American systems of measurement were officially used in the United Kingdom and its colonies, as well as in the United States . In 1973, Great Britain undertook to abandon the traditional system of measurement in favor of a Europe-wide uniform system, the metric system. In order to make the changeover easier, both measurement systems were to be used in parallel in Great Britain until 2010; this exception was converted into an unlimited one in 2007. The conversion to the metric system met with various opposition in Great Britain (see the citizens' initiative Metric Martyrs ), and the units of measurement of the imperial units are still widespread, especially in everyday dealings among citizens. The situation is similar in Ireland , Canada , India , Malaysia , Australia and New Zealand . In the USA, the Anglo-American measurement system in the variant of customary units (which is based on a historical form of the British measurement system) is still in full use as the main measurement system.
International use
Some Anglo-American dimensions are also used internationally, but often not as an actually measured size, but as a nominal designation. For example, oil is traded on the exchange in the volume unit barrel , but is weighed in tons, and flight altitudes are given in feet, but are actually air pressures standardized to the same reference value. The nautical mile (nautical mile) is not specifically English unit, but a minute of arc of the rounded in the relevant measuring system earth's circumference. Even the customs (inch) is indeed in many countries for certain size constraints in the technology used, but these are almost never real measurements, but as with the 3.5-inch floppy disk , the diagonal of just 90 mm and not 88.9 mm measures, just conventional (trade) names.
Common units
Examples of important and frequently used units of Anglo-American systems of measurement are: Step (yard) mile (mile), oz (ounce), pound (pound), Stone (stone) fluid ounce (fluid ounce), pint (e) (pint) , Quart (quart), gallon (gallon) , acre . The units have been defined differently throughout history. Particularly in the area of the dimensions of the unit, differences between English and US-American variants of the units have developed from this to this day.
Even in English-language science and technology, some non-metric units are still in use today. For Newtonian mechanics, electrical engineering, etc., new units had to be formed or existing ones had to be more precisely differentiated. In part, this was done on the basis of the Anglo-American units in various so-called FPS systems (foot, pound, second), which v. a. distinguish between whether the classic weight units are used for mass (pound-mass) or force (pound-force) . In the English-speaking world there are also some units that can be assigned to the metric system (e.g. nit ) or names (mho) that have not been able to establish themselves on an international level. These belong at best to the periphery and not to the core of the Anglo-American systems of measurement.
Norms
For the metric system, there are international standards (e.g. ISO / IEC 80000 ) that describe rigid symbols (without abbreviation points) for the metric units, and these may also be applied to English units in the technical field, e.g. B. "lb F / in 2 " instead of "PSI". Overall, however, numerous different abbreviations (often with a full stop or in capital letters) are or were in use for Anglo-American quantities, which in some cases collide with the SI (e.g. 'nm' for nautical mile or nanometer). Exponentiations are usually expressed by prefixes ('sq.' And 'cu.' For square (d) and cube (d) ), while the resolution of linguistic ambiguities (e.g. 'avdp.', 'Tr.' And ' ap. 'to pound and ounce) are more likely to appear as suffixes. A plural 's' is often added to the abbreviation, while the unit symbols of SI units always remain unchanged. Few units can be denoted by non-letter symbols, v. a. the pound with # and units such as feet (′) and inches (″), which are often used with and next to each other, as well as the archaic apothecary's measurements ( scruple ℈, dram ʒ, ounce ℥, pound ℔). Since many names are monosyllabic, they are often simply spelled out in size specifications.
Units of length
Formula symbol of length : l or s
unification
Since July 1, 1959, standardized definitions apply to the Anglo-American units of length (and also units of weight). Previously, the stipulations in the states of the British Commonwealth and the USA differed extremely slightly from one another. The standardized system of measurements was given the additional designation "International", which is rarely given.
| unit | German | Abbr. | size | metric size | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| inch | inch | in. | ″ | 2.54 cm | |
| foot | foot | ft. | ′ | 12 inch | 30.48 cm |
| yard | step | yd. | 3 feet | 0.9144 m | |
| mile | mile | mi., m. | 1760 yards | 1,609.344 m | |
US land survey
In order not to have to convert the length and area data to the new international dimension due to the standardization of land and property dimensions in 1959, the old dimensions in the USA retained their validity exclusively for this purpose and are used as "survey measurement" or " surveyor's measurement ". The basic unit is the US survey foot , which is defined as 1200/3937 m ; thus the international foot is 2 ppm , about 0.6 micrometers, shorter than the US survey foot . According to the National Institute of Standards and Technology , the US survey foot is declared obsolete with effect from January 1, 2023 and should no longer be used after this date.
As an alternative system for floor measurement, " Gunter 's measurement" with the units of length link and chain was created in England in the early 17th century . Since the floor area calculated from this in square chains has a decimal relationship to the target unit acre , the area calculation with the means at that time is less cumbersome than with the conventional non-decimal units. In North America in particular, the 100-link, 66 feet (approx. 20 m) long Gunter's chain was widely used for land surveying. In addition, there was another less common classification for land surveying chains according to Jesse Ramsden , called “engineer's measurement” , in which one link in the chain corresponds to exactly one foot .
| unit | German | Abbr. | size | Metric size | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| link | Chain link | left | 0.66 feet | ≈ 0,2011684 m | |
| foot | foot | ft. | ≈ 0.3048006 m | ||
| rod / pole / perch | rod | approx. | 16.5 feet | 25 left | ≈ 5.029210 m |
| chain 1 | Chain | ch. | 66 feet | 4 rods | ≈ 20.11684 m |
| furlong | Furrow length 2 | For. | 660 feet | 10 chains | ≈ 201.1684 m |
| (statute) mile | mile | mi., m. | 5280 feet | 8 furlongs | ≈ 1,609.347 m |
Units such as link, chain or furlong are rarely used.
Since some units have been redefined over the course of time, when converting historical measurements, it is important to note which definition was used at the time and how precise both are.
Nautical
The international nautical mile ( international nautical / sea mile ) since 1929 (USA until 1954) to km 1.852 set. The cable length ( cable length ), consisting of 100 Fathom ( yarn ) corresponds with one-tenth of 185.2 m nautical mile. It is used, among other things, for depth measurements. There are other definitions for the cable length , such as the almost equally long 100 fathoms (182.88 m), or 120 fathoms (219.456 m) for the US Navy . Fathoms (abbreviation f, fath, fm, fth, fthm) are only (still occasionally) used to measure the water depth or as an auxiliary unit in nautical charts (10-threadline, 20-threadline etc.) without being explicitly named; shackle or naval shot practically no longer at all, although the British measure was not increased from 12½ to 15 fathom until 1949 for the purpose of approximation .
Before the introduction of the international nautical mile in 1929, the British sea mile (also Admiralty mile ) of 1,853.184 m was in use. This sea mile is exactly 800 feet longer than the land mile .¹)
¹) In contrast, mil in nautical science means the angle measure “ line ”).
| unit | German | Abbr. | size | Metric size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| fathom | Thread (for plumbing ) or fathom | fm., fth. | 6 feet | 1.8288 m |
| shackle (UK), shot (US) | 90 feet = 15 fathom | 27,432 m | ||
| cable (length) | Cable (length) | cbl. | 600 feet = 100 fathom | 182.88 m |
| 1 ⁄ 10 sea mile | 185.2 m | |||
| nautical mile (admiralty) sea mile (admiralty) until 1929/1954 |
Nautical mile (Admiralty) | nm. (adm), sm. | 6080 feet | 1,853.184 m |
| nautical mile sea mile from 1929/1954 |
nautical mile | NM | 1,852 m | |
| nautical / sea league | nl. | 3 sea mile | 5,559,552 m |
Other length dimensions
| unit | German | Abbr. | size | meter | domain | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gauge | 1 ⁄ 100,000 inch | 0.254 µm | 0.000000254 m | Film thicknesses | ||
| twip | twp. | 1 ⁄ 1 440 inch = 1 ⁄ 20 point | 17.6 µm | 0.00001763 8 m | Typography, DTP | |
| mil (US), thou (UK) | 1 ⁄ 1000 inch | 25.4 µm | 0.0000254 m | technology | ||
| mickey | 1 ⁄ 200 inch | 127 µm | 0.000127 m | Computer technology | ||
| point | Point | pt. | 1 ⁄ 72 inch = 1 ⁄ 12 pica | 353 µm | 0.0003527 7 m | typography |
| (shoe) ounce | 1 ⁄ 64 inch | 397 µm | 0.000396875 m | (fine) leather | ||
| (shoe) iron | 1 ⁄ 48 inch | 529 µm | 0.0005291 6 m | (thick) leather | ||
| line | line | ln. | 1 ⁄ 12 inch | 2.12 mm | 0.00211 6 m | Typography, craft |
| pica | Pica | pc. | 1 ⁄ 6 inch | 4.23 mm | 0.00423 3 m | typography |
| barleycorn | Stye | 1 ⁄ 3 inch | 8.47 mm | 0.0084 6 m | old | |
| digit, nail foot | finger | 3 ⁄ 4 inch | 1.91 cm | 0.01905 m | old | |
| finger (breadth) | finger | 7 ⁄ 8 inch | 2.22 cm | 0.022225 m | old | |
| stick | 2 inch | 5.08 cm | 0.0508 m | |||
| nail yard | nail | 2 1 ⁄ 4 inch = 3 digit | 5.72 cm | 0.05715 m | ||
| palm | Hand (palm) | 3 inch = 4 digit | 7.62 cm | 0.0762 m | old | |
| hand, (palm width) | A hand's breadth | 4 inch | 10.2 cm | 0.1016 m | old, water level, horse size | |
| shaftment | (small) range | 6 inch | 15.2 cm | 0.1524 m | old, textile | |
| span | (large) span | 9 inch = 3 palm | 22.6 cm | 0.2262 m | old, textile | |
| quarter | Quarter yard | 9 inch = 1 ⁄ 4 yard | 22.6 cm | 0.2262 m | ||
| cubit | 18 inch = 1 ⁄ 2 yard | 45.7 cm | 0.4572 m | old, textile | ||
| pace (US), step (UK) | step | 30 inches = 2 1 ⁄ 2 feet | 76.2 cm | 0.762 m | military | |
| ell | Cubit | 45 inch | 1.14 m | 1.143 m | Textile | |
| grade, geometric pace | (Double) step | 60 inch = 5 foot = 2 pace | 1.52 m | 1.524 m | military | |
| rope | rope | 240 inches = 20 feet | 6.10 m | 6.096 m | Nautical | |
| skein | 4320 inches = 360 feet = 120 yards | 110 m | 109.728 m | Textile | ||
| league | League hour | lea., l. | 190080 inch = 5280 yard = 3 miles | 4.8 km | 4828.032 m | Nautical |
| spindle | (Spindle) | 518400 inch = 14400 yard = 120 skein | 13.2 km | 13,167.36 m | Textile | |
Coded length dimension designations
For the thickness of sheet metal , the diameter of wood screws , drills and electrical wires as well as the length of nails , the dimensioning of the diameter, length or thickness is not always given in units of length, but with a designation derived from a formula or a Table the actual dimensions can be determined.
- American Wire Gauge (AWG) : Wire diameter for electrical cables
- Imperial Standard Wire Gauge (SWG) : Comparable to AWG - outdated
- Drill Wire Gauge : drill diameter
- Standard Sheet Metal Gauge : sheet thickness
- Penny Size (d) : nail length
- Wood Screw Size : diameter of wood screws
- Diameter and thread pitch for screws according to the Unified Thread Standard (UNC / UNF screws)
Units of area
Formula symbols for the area : F , A
unification
The length units standardized in 1959 result in the corresponding general area units.
| unit | German | Abbr. | size | Metric size | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| square inch | Square inches | sq.in. | in² | 0.00064516 m² | |
| square foot | Square feet | sq.ft. | ft² | 144 in² | 0.09290304 m² |
| square yard | Square yards | sq.yd. | yd² | 9 ft² = 1,296 in² | 0.83612736 m² |
| square mile | Square mile | sq.mi. | mi² | 3,097,600 yd² | 2,589,988.110336 m² |
Units of land area
In practice, only the units acre or square foot are used for land areas . The unit square mile is used more in geographical contexts. All other units of land area such as square rod are no longer used and are actually only of historical importance.
The land area units in the USA are based on the US survey foot , otherwise on the international foot . Thus there are two different systems of measurement for land areas. However, the size differences are extremely small. The square mile (≈ 2.6 km²) based on the US survey foot is around 10.36 m² larger than the international foot .
| unit | German | Abbr. | size | Metric size (US survey foot) | Metric size (international foot) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| square foot | Square feet | sq.ft. | ft² | ≈ 0.09 m² | ≈ 0.09290341 m² | see general area dimensions | ||
| square rod square perch |
Square rod | sq.rd. | rd² | 272 ¼ sq.ft. | ≈ 25.3 m² | only of historical importance | ||
| square chain | sq.ch. | 16 sq.rd. | 4,356 sq.ft. | ≈ 404.7 m² | only of historical importance | |||
| rood | Quarter morning | ro. | ¼ ac. | 10,890 sq.ft. | ≈ 1,012 m² | English plot size - historical | ||
| acre | tomorrow | ac./a. | 160 sq.rd. | 43,560 sq.ft. | ≈ 4,047 m² | ≈ 4,046.872609874 m² | 4,046.8564224 m 2 | |
| square mile | Square mile | sq.mi. | mi² | 640 ac. | ≈ 2.6 km² | ≈ 2,589,998,470 319 5 m² | see general area dimensions | |
North American land division into sections
In the greater part of the USA and western Canada, during the European settlement phase, the land areas were divided into square areas using orthogonal surveying networks aligned with the cardinal points . Due to the curvature of the earth, there are inevitably deviations from the desired values.
- Section
- The section covers a nominal area of one square mile or 640 acres (≈ 260 ha). The nominal value of the edge length is one mile (≈ 1.6 km). A section can be subdivided into further partial areas, which in turn are usually square. In the USA the section also includes the areas for the public road network, in Canada these areas are measured separately.
- Quarter Section
- The quarter section is created by quartering the section and thus comprises a nominal area of 160 acres (≈ 65 ha) with an edge length of half a mile (≈ 0.8 km). This was the standard allotment that was taken over by a settler during the American land distribution. But a homestead could also be much larger or smaller. One area for small settlers was, for example, the quarter-quarter section with 40 acres (≈ 16 ha) with an edge length of a quarter mile (≈ 0.4 km).
- Township
- A survey township consists of 36 sections in a square arrangement. The target area is therefore 23,040 acres (≈ 93.2 km²) and the target area for the edge length is 6 miles (≈ 9.6 km).
Size description for agricultural goods in medieval England
Similar to the German term Hufe or Hube, the size of an agricultural property was described with corresponding terms. These dimensions are not actually measures of area, but rather served the abstract description of the entire land area of a farm as a basis for taxes , lease payments or tribute payments . The decisive factor was less the actual size of the area than the yield. In the case of poor soils, the corresponding areas became larger. Below is a selection of the most popular size descriptions:
- Yardland, Virgate
- Approximately 30 acres in size. This was a farm that was sufficient for a full-time family.
- Hide
- Four times the size of a Virgate and thus around 120 acres (approx. 48 ha) in size.
Other areas
| unit | German | Abbr. | size | metric size | annotation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| circular mil (US) circular thou (UK) |
circ.mil | 1 ⁄ 4 • π mil 2 | ≈ 0.000506707 mm 2 | ||
| 1000 circular mils | kcmil | ≈ 0.506707 mm 2 | Wire cross-section, electrotechnical (USA, Canada etc.); obsolete abbreviation: MCM | ||
| square mil (US) square thou (UK) |
sq.mil | 1 mil 2 | = 0.00064516 mm² | ||
| circular inch | District inch | circ.in. | 1 ⁄ 4 • π inch² | ≈ 5.06707479164 cm² |
| unit | German | Abbr. | size | metric size | annotation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| square | 100 feet 2 | ≈ 9.3 m 2 | Roofing trade, historical; in Australia often for the footprint of houses |
Volume units
Formula symbol of the volume : V
| unit | German | Abbr. | size | cubic meter | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cubic inch | Cubic inches | cu.in. | 1 inch 3 | 16.4 cm 3 | 0.000016387064 m 3 |
| cubic foot | Cubic feet | cu.ft. | 1 foot 3 = 1728 inch 3 | 28.3 dm 3 | 0.028316846592 m 3 |
| perch | Manhole | 1 perch ( 16 1 ⁄ 2 feet) × 1 1 ⁄ 2 feet 2 = 24 3 ⁄ 4 feet 3 | 701 dm 3 | 0.700841953 200 m 3 | |
| cubic yard | Cubic yards | cu.yd. | 1 yard 3 = 27 feet 3 = 46656 inch 3 | 765 dm 3 | 0.764554857984 m 3 |
| freight ton | 40 feet 3 | 1.13 m 3 | 1.132673863680 m 3 | ||
| load | 50 feet 3 | 1.42 m 3 | 1.415842329600 m 3 | ||
| register tone | Register bin | RT | 100 feet 3 | 2.83 m 3 | 2.831684659200 m 3 |
| acre-inch | 1 acre × 1 inch = 3630 feet 3 | 103 m 3 | 102.790153129 m 3 | ||
| acre-foot | 1 acre × 1 foot = 43560 feet 3 | 1.23 dam 3 | 1,233.481837547 m 3 | ||
Acre-foot and acre-inch are used in agriculture and meteorology to indicate the amount of irrigation and precipitation. In the metric system, the equivalent liters per square meter and millimeter are used for this purpose (1 l / m 2 = 1 dm 3 / m 2 = 1 mm).
A perch is not only a measure of length (= pole , rod ), but (more rarely) also a measure of volume in mining.
Measure of capacity
In Great Britain, the Weights and Measures Act of 1824 , the origin of the imperial units , unified the regionally different systems of measure of measure and determined the gallon as the basic unit for both liquid and dry dimensions. The starting point for the new imperial standard gallon was the English ale gallon . The size of the new imperial gallon was determined by the volume of 10 pounds of water at 62 ° F. This is roughly equal to 277.42 cubic inches. The imperial gallon was last redefined by the Weights and Measures Act of 1985 with exactly 4.54609 liters (approx. 277.4193 cubic inches). In 1963 and re-affirmed in 1976, the corresponding Weights and Measures Act adjusted the system of measure of measure and limited it to gallon, quart, pint, gill and fluid ounce.
In the USA, the capacity systems for bulk goods and liquids are in no way related to each other. The basic unit for measuring the liquid is the originally English wine gallon with 231 cubic inches (approx. 3.79 l). This is about half a liter smaller than the English gallon. The basic unit of the American dry measure has its origins in the historical English Winchester bushel , which at the time of its abolition in England in 1824 corresponded to a cylindrical volume with a diameter of 18½ inches and a height of 8 inches. The US bushel with 2150.42 cubic inches (approx. 35.2 l) was derived from this unit, which is approx. 1.1 liters smaller than the English bushel, which has since been abolished, and in contrast to this, has no relation to the gallon stands.
Most of the English denominations of measure are also used in the American system ( drachm became dram ). You also have i. d. Usually the same factors are among each other (in the respective wet or dry measure ) (exceptions are barrel and fluid ounce ). To distinguish them, the abbreviations "Imp." Or "US" may be prefixed. It is noteworthy that the British like the US oil barrel measures around 159 liters, although one is defined as 35 and the other as 42 gallons. Furthermore, the English fluid ounce and the units of measurement below it are smaller, the units above it are larger than their respective American counterparts.
In the pharmacy system only minim, scruple, drachm, ounce, pint and gallon were used.
Attention should be paid to the sometimes confusing labeling on US beverage containers, here you will find information such as "25.4 Fluid Ounces ONE PINT 9.4 FL.OZ." or ".5L (1 PT, 0.9 FL OZ)". These mean that the content corresponds to the first item (in US wet), which in turn is the sum of the last two items (in US wet).
Tables
| unit | German | Abbr. | size | metric | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fluid ounce | Fluid ounce | fl.oz., ƒ℥ | 1 ⁄ 5 gill | ≈ 2.84 cl | = 0.0284130625 L. |
| gill , noggin | Quarter pint | gi. | 1 ⁄ 4 pint | ≈ 1.42 dl | = 0.1420653125 L. |
| pint | pint | fl.pt., pt. | 1 ⁄ 2 quart | ≈ 5.68 dl | = 0.56826125 L. |
| quart | quart | qt. | 1 ⁄ 4 gallon | ≈ 1.14 l | = 1.1365225 l |
| gallon | gallon | gal. | 4.54609 L. | ≈ 4.55 l | = 4.54609 L. |
| unit | German | Abbr. | size | metric | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| minim , drop | drops | min. | 1 ⁄ 20 scruple | 59.2 µl | 0.000059193883880 L. |
| fluid scruple | Liquid cruple | fl.sc., ƒ℈ | 1 ⁄ 3 dram | 1.18 ml | 0.001183877677603 L. |
| fluid dram | Liquid drachms | fl.dr., ƒʒ | 1 ⁄ 8 ounce | 3.55 ml | 0.003551633032809 L. |
| glass | Glass | 1 ⁄ 2 gill | 7.10 cl | 0.071033 L. | |
| (petrol) barrel | barrel | bl., bbl. | 35 gallon | 1.59 hl | 159.113 l |
| unit | German | Abbr. | size | metric | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| peck | pk. | 2 gallon | 9.09 l | 9,092 1 l | |
| kenning | 4 gallon | 1.82 dal | 18.1843 l | ||
| bushel | bushel | bsh., bu. | 8 gallon | 3.64 dal | 36.3687 L. |
| sack, bag | bag | 3 bushel | 1.09 hl | 109.106 L. | |
| quarter | qr. | 8 bushel | 2.91 hl | 290.9 l | |
| chaldron | 12 sack | 1.31 kl | 1,309.2732 L. | ||
| load | load | 5 quarter | 1.45 kl | 1,454.5 L. | |
| unit | German | Abbr. | size | metric | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| minim, drop | drops | min. | 1 ⁄ 60 dram | ≈ 61.6 µl | = 0.000061611519921875 L. |
| fluid dram | Sip | fl.dr., ƒʒ | 1 ⁄ 8 ounce | ≈ 3.70 ml | = 0.0036966911953125 L. |
| fluid ounce | Fluid ounce | fl.oz., ƒ℥ | 1 ⁄ 4 gill | ≈ 2.96 cl | = 0.0295735295625 L. |
| gill | gi. | 1 ⁄ 4 pint | ≈ 1.18 dl | = 0.11829411825 L. | |
| pint | pint | pt. | 1 ⁄ 2 quart | ≈ 4.73 dl | = 0.473176473 L. |
| quart | quart | qt. | 1 ⁄ 4 gallon | ≈ 9.46 dl | = 0.946352946 l |
| gallon | gallon | gal. | 231 inch 3 | ≈ 3.79 l | = 3.785411784 L. |
| petrol barrel | Oil barrel | bl., bbl. | 42 gallon = 1 ⁄ 2 firkin | ≈ 1.59 hl | = 158.987294928 l |
| unit | German | Abbr. | size | metric | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (dry) pint | pint | pt. | 1 ⁄ 2 quart | ≈ 5.51 dl | = 0.5506104713575 L. |
| (dry) quart | 1 ⁄ 8 peck | ≈ 1.10 l | = 1.101220942715 L. | ||
| peck | pk. | 1 ⁄ 4 bushel | ≈ 8.81 l | = 8.80976754172 L. | |
| bushel 1 | bushel | bsh., bu. | 2150.42 inch 3 | 3.52 dal | = 35.23907016688 L. |
Wood
| unit | German | Abbr. | size | metric size | annotation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cord | Fathoms | CD. | 4 ft. × 4 ft. × 8 ft. | 128 cu.ft. | ≈ 3.62 stere | Space for firewood |
| long cord | 4 ft. × 4 ft. × 10 ft. | 160 cu.ft. | ≈ 4.53 stere | |||
| board foot | BF | 1 ft. × 1 ft. × 1 in. | 1 ⁄ 12 cu.ft. | ≈ 2.36 dm 3 | Calculation measure for sawn and raw wood | |
| 1000 board feet | MBF | 83 1 ⁄ 3 cu.ft. | ≈ 2.36 m 3 | MBF is more common than BF | ||
In the case of sawn timber , the billing measure board-foot refers to the rough- sawn and not yet dried board. The actual volume can therefore - depending on the processing status - also be lower. In the case of raw wood , the board-foot unit does not refer to the volume of the entire trunk, but to the equivalent amount of cut material that can be obtained after the cut. Rules are necessary for the calculation, the so-called log rules . Well-known log rules are the Doyle Rule and the Scribner Rule .
| unit | German | Abbr. | size | metric size | annotation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hoppus foot | 4 / π cu.ft. | ≈ 1.273 cu.ft. | ≈ 0.0361 m 3 | Calculation: (circumference [in] / 4) ² x length [ft] / 144 | ||
| hoppus sound | HT | 50 hoppus foot | ≈ 63,662 cu.ft. | ≈ 1.8027 m 3 | ||
The accounting measure hoppus foot for round wood was introduced in England by Edward Hoppus in 1736 and was the predominant round wood unit in the British Empire. In the meantime, this unit is to be regarded as historical and is only rarely used in Asian tropical wood, mainly in Myanmar (Burma) in the form of the hoppus clay .
Beer and wine
Historically, there were different standardized barrel sizes for wine and beer, some with the same name ( barrel, hogshead, puncheon, butt, tun ). In addition, before 1824, beer in Great Britain made a distinction between beer and ale . As with other sizes, these room dimensions were also used like units. In particular, the (petrol) barrel , which is still in use today, developed from the tierce (159 l) - and not from one of the barrels (164 l or 119 l) . The wine measures in the UK and the USA are equivalent for all practical purposes, although they are based on the different gallons and therefore there are arithmetical differences of just under one per mille.
The German equivalents Eimer , Ohm and Oxhoft , for example, were very similar in size and definition in Prussia .
| unit | German | Abbr. | size | liter | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| gallon | gallon | gal. | 277.42 inch 3 | 4.55 l | 4.54609 L. |
| pin code | 4½ gallon = 1 ⁄ 2 firkin | 2.05 dal | 20.4574 L. | ||
| firkin | keg | 9 gallon = 1 ⁄ 2 kilderkin | 4.09 dal | 40.9148 L. | |
| kilderkin | 18 gallon = 1 ⁄ 2 barrel | 8.18 dal | 81.8296 L. | ||
| barrel | (Barrel) | 36 gallon | 1.64 hl | 163.6592 L. | |
| hogshead | hd., hhd. | 54 gallon = 1 1 ⁄ 2 barrel | 2.45 hl | 245.489 L. | |
| puncheon | 72 gallons = 2 barrels | 3.27 hl | 327.3185 L. | ||
| butt | 108 gallon = 2 hogshead | 4.91 hl | 490.978 L. | ||
| do, tone | (Ton) | 216 gallon = 3 puncheon = 2 butt | 9.82 hl | 981.9554 L. | |
| unit | German | Abbr. | Size (UK) | Size (US) | Liter (UK) | Liter (US) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| gallon | gallon | gal. | 277.42 inch 3 | 231 inch 3 | 4.55 l | 4.54609 L. | 3.79 l | 3.78541 L. |
| rundlet | bucket | 15 gallon = 1 ⁄ 7 pipe | 18 gallon = 1 ⁄ 7 pipe | 6.82 dal | 68.19135 L. | 6.81 dal | 68.1374 L. | |
| barrel | barrel | bl. | 26 1 ⁄ 4 gal. = 1 ⁄ 4 pipe | 31 1 ⁄ 2 gal. = 1 ⁄ 4 pipe | 1.19 hl | 119.335 L. | 1.19 hl | 119.240 L. |
| tierce | Ohm, third | 35 gallon = 1 ⁄ 3 pipe = 1 ⁄ 2 firkin | 42 gallon = 1 ⁄ 3 pipe = 1 ⁄ 2 firkin | 1.59 hl | 159.113 l | 1.59 hl | 158.987 L. | |
| hogshead | Oxhoft | hd., hhd. | 52 1 ⁄ 2 gal. = 1 ⁄ 4 do | 63 gallon = 1 ⁄ 4 do | 2.39 hl | 238.670 L. | 2.38 hl | 238,481 L. |
| firkin, puncheon / pon, tertian | 70 gallons = 1 ⁄ 3 do | 84 gallon = 1 ⁄ 3 do | 3.18 hl | 318.226 L. | 3.18 hl | 317.975 L. | ||
| pipe, butt | 105 gallon = 1 ⁄ 2 do | 126 gallon = 1 ⁄ 2 do | 4.77 hl | 477,339 L. | 4.77 hl | 476,962 L. | ||
| to do | (Ton) | 210 gallons | 252 gallons | 9.55 hl | 954.68 L. | 9.54 hl | 953.924 L. | |
kitchen
Particularly in the North American cuisine, the sizes of scoops (are spoon ) and measuring cup ( cup ) well defined, although has the appropriate containers, especially in the UK are often metric. The US version is sometimes rounded using a “metric fluid ounce” of 30 ml: 1.25 ml / ssp., 5 ml / tsp., 10 ml / dsp., 15 ml / tbsp., 180 ml / tc., 240 ml / c. They differ from the European kitchen dimensions for z. B. Teaspoon and tablespoon .
Some chefs and cookbooks use definitions other than those listed in the table, e.g. B. for the British tablespoon half a fluid ounce (14.2 ml) as is common in the American system. The names dessertspoon , saltspoon and tea cup are rare. Measuring spoons or markings of the corresponding sizes are common, but are referred to as fractions of another measure. In addition, there are usually markings for quarter , third and half cup in measuring cups .
| unit | German | Abbr. | Size (UK) | Size (US) | Liter (UK) | Liter (US) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| saltspoon | Salt spoon | ssp. | 1 ⁄ 4 teaspoon | 1.11 ml | 0.0011098 L. | 1.23 ml | 0.001232230399 L. | |
| teaspoon | teaspoon | tsp. | 1 ⁄ 4 tablespoon | 1 ⁄ 3 tablespoon | 4.44 ml | 0.004439 L. | 4.93 ml | 0.004928921595 L. |
| dessert spoon | dsp. | 2 teaspoon | 8.88 ml | 0.008 879 L. | 9.86 ml | 0.009857843190 L. | ||
| tablespoon | tablespoon | tbsp. | 1 ⁄ 16 cup | 1.78 cl | 0.017758 L. | 1.48 cl | 0.0147867647825 L. | |
| tea cup | Teacup | tc. | 1 ⁄ 3 pint | 3 ⁄ 4 cup | 1.89 dl | 0.18942 L. | 1.77 dl | 0.177441177 L. |
| cup | Cup | c., cu. | 1 ⁄ 2 pint = 10 ounce | 1 ⁄ 2 pint = 8 ounce | 2.84 dl | 0.28413 L. | 2.37 dl | 0.2365882365 L. |
Bottles
Since 1979, the quantities given for (foam) wine bottles in the USA have been based on three quarters of a liter instead of one fifth of a gallon, which corresponds to a nominal reduction of around 1%. However, at the same time the larger bottles were changed more and shrank by around 25%, only shawl manasar only by around 15%.
| Surname | German | size | Liter until 1979 |
Liters since 1979 |
gallon | fifth | ¾L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| glass | Glass | 4 ounce | 0.118 | ||||
| split | 1.6 glass | 0.189 | 0.1875 | 0.05 | 0.25 | ||
| tenth | Tenth (gallon) | 2 split | 0.379 | 0.375 | 0.1 | 0.5 | |
| fifth, bottle | Fifth (gallon), bottle | 0.757 | 0.75 | 0.2 | 1 | ||
| magnum | Magnum | 1.89 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 2.5 | 2 | |
| jeroboam | Jeroboam | 2 magnum | 3.79 | 3 | 1 | 5 | 4th |
| rehoboam | Rehaboam | 3 magnum | 5.68 | 4.5 | 1.5 | 7.5 | 6th |
| methuselah | Methuselah | 4 magnum | 7.57 | 6th | 2 | 10 | 8th |
| shalmanazar | Shawl Manasar | 10.6 | 9 | 3 | 14th | 12 | |
| balthazar | Balthazar | 8 magnum | 15.1 | 12 | 4th | 20th | 16 |
| nebuchadnezzar | Nebuchadnezzar | 10 magnum | 18.9 | 15th | 5 | 25th | 20th |
Weight units
Symbol of the mass : m
The basic unit of the weight system, which originally came from France (around the 15th century), is the Avoirdupois pound of 7000 grains , which since July 1, 1959 has been standardized at exactly 453.59237 g of the metric system. From 1853 to 1959 this pound was defined in Great Britain by a weight of approx. 453.592338 g, while in the USA it was defined in the metric system with the Mendenhall Order as early as 1893: According to this, the Avoirdupois pound was exactly 453.5924277 g .
In the coin and precious metal industry, the Troy system is used with one pound, which weighs 5760 instead of 7000 grains , and until the 19th century (UK Medical Act of 1858) a pharmacy system that also uses the lighter pound (Troy) at 12 ounces but used scruple and dram instead of pennyweight .
Usually the system used is determined by the context; when in doubt it is the Avoirdupois system, short in the US and long in the UK. To differentiate, short or long (seldom also net and large ) are placed before and - often abbreviated - (Avoirdupois) , (Troy) or (apothecaries) after the unit.
The units stone and hundredweight were abolished in British trade decades before the metric system was introduced; The British and Irish often give their body weight in stones and pounds and their height in feet and inches . The long (long) units resulting from the subsequent introduction of the stone to 14 pounds in the UK and were more common there than in the colonies. According to other sources that are short units the result of a partial transfer decimation of the system in North America of the 18th century, following the example of several hundredweight (centner) and quintals to 100 pounds on the European continent.
The slug is constructed as a consistent unit of mass in feet (ft) and pound-force (lb f ) in one of the English engineering systems: a mass of 1 slug is accelerated by 1 ft / s² by the force 1 lb f , where the value of Acceleration due to gravity is not standardized, cf. 1 hyl = 9.80665 kg for the technical mass unit .
| unit | German | Abbr. | size | Grain | Gram | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| grain | Gran , grain | gr. | 1 | 64.8 mg | 0.06479891 | |
| Commercial weights , Avoirdupois | ||||||
| dram | drachma | dr. | 1 ⁄ 16 ounce | 27.34375 | 1.77 g | 1.7718451953125 |
| ounce , coll. lid | ounce | oz. | 1 ⁄ 16 pounds | 437.5 | 2.83 dag | 28.349523125 |
| pound | lb | lb., pd., #, lb m . | 7000 grain | 7,000 | 4.54 hg | 453,59237 |
| short Avoirdupois | ||||||
| quarter | Quarter penny | 1 ⁄ 4 hundredweight | 175,000 | 11.3 kg | 11,339.80925 | |
| hundredweight , cental | Hundredweight | cwt. | 100 pounds | 700,000 | 45.4 kg | 45,359.237 |
| volume | ton | T., to., T. | 20 hundredweight | 14,000,000 | 0.907 t | 907,184.74 |
| long Avoirdupois | ||||||
| stone | stone | st. | 14 pounds | 98,000 | 6.35 kg | 6,350,29318 |
| quarter | Quarter penny | qu., qr. l. | 2 stone | 196,000 | 12.7 kg | 12,700.58636 |
| hundredweight | Hundredweight | cwt. | 4 quarters | 784,000 | 50.8 kg | 50,802.34544 |
| volume | ton | T., to., T. | 20 hundredweight | 15,680,000 | 1.02 t | 1,016,046.9088 |
| Coin Weights, Troy | ||||||
| pennyweight | Penny weight | dwt. | 24 grain | 24 | 1.56 g | 1.55517384 |
| ounce | Troy ounce | oz., tr.oz., oz.t. | 20 pennyweight | 480 | 3.11 dag | 31.1034768 |
| pound | Troy pound | lb., tr.lb., lb.t. | 12 ounce | 5,760 | 3.73 hg | 373.2417216 |
| Apothecary weights, apothecaries , until 1858 | ||||||
| scruple | Scruple | s., s.ap., ℈ | 20 grain | 20th | 1.30 g | 1.2959782 |
| dram | Drachma, penny | dr., dr.ap., ap.dr., ʒ | 3 scruple | 60 | 3.89 g | 3.8879346 |
| ounce | Troy ounce | oz., oz.ap., ap.oz., ℥ | 8 dram = 1 troy ounce | 480 | 3.11 dag | 31.1034768 |
| pound | Troy pound | lb., lb.ap., ap.lb. | 12 ounce = 1 troy pound | 5,760 | 3.73 hg | 373.2417216 |
| Engineering technology | ||||||
| slug | 1 lb F · s 2 / ft | 32.174048 lb | 225,218,336 | 14.6 kg | 14,593.9029372 | |
Wool
For sheep and cotton, separate weights were used in Great Britain until the 19th century. Only hundredweight and stone also exist in the normal, "long" English weight system (see above).
| unit | German | Abbr. | size | Pound | Gram | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| clove , nail | 7 pounds | 7th | 3.18 kg | 3,175.146590 | ||
| stone | st. | 2 clove | 14th | 6.35 kg | 6.350.293180 | |
| death | 2 stone | 28 | 12.7 kg | 12,700.586360 | ||
| hundredweight | Hundredweight | cwt. | 4 death = 8 stones | 112 | 50.8 kg | 50,802,345440 |
| wey , weight | 1 5 ⁄ 8 hundredweight = 13 stones | 182 | 82.6 kg | 82,553.811340 | ||
| bag | bag | 2 wey | 364 | 165 kg | 165.107,622680 | |
| last, load | load | 12 sack | 4368 | 1.98 t | 1,981,291.472160 |
Grain
The bushel unit as a measure for determining a quantity of grain was originally a pure measure of volume. This unit has been an equivalent measure of mass since the 19th century. The reference point for a "bushel" is - depending on the type of grain - a certain weight that is determined at a reference moisture content and is then referred to as "standard weight / bu". Depending on the moisture content, the weight of a "bushel" grain is therefore different.
| unit | German | Abbr. | Size (and humidity) | Kilograms (and moisture) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bushel (corn) | Bushel (corn) | bu | 56 pounds at 15.5% | 25.401172720 kg at 15.5% |
| bushel (rye) | Bushel (rye) | bu | 56 pounds at 14.0% | 25.401172720 kg at 14.0% |
| bushel (wheat) | Bushel (wheat) | bu | 60 pounds at 13.5% | 27.215542200 kg at 13.5% |
| bushel (soybean) | Bushel (soybeans) | bu | 60 pounds at 13.0% | 27.215542200 kg at 13.0% |
time
Symbol of the time : t
The only English unit of time that is often found in Great Britain these days (but rarely in the US) is fortnight (from "fourteen nights"), for example in biweekly television programs. In addition, the term fortnight is often used in Australia, where the salary and pension are usually paid every fortnight.
The other English time measures come mainly from seafaring.
| unit | German | Abbr. | size | Seconds | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ounce | (Ounce) | 1 ⁄ 12 moment | 7.5 s | ||
| moment | (Moment) | 1 ⁄ 40 h | 1.5 min | 90 s | |
| bell | ( Bell ) | 1 ⁄ 8 watch | 30 min | 1800 s | |
| watch | (Guard) | 4 h | 240 min | 14,400 s | |
| sennight | 1 week | 7 days | 604,800 s | ||
| fortnight | 2 weeks | 14 days | 1,209,600 s | ||
temperature
Formula symbol for temperature : T or θ
Traditionally, in the English-speaking world, the Fahrenheit temperature scale is more common than that of Celsius . They differ in the starting point
- 0 ° C corresponds to 32 ° F corresponds to 273.15 K ,
- 0 ° F corresponds to −17 7 ⁄ 9 ° C ≈ - 17.78 ° C corresponds to 255.37 K.
and in the size of a degree (temperature difference), which, however, are in a simple linear relationship to one another:
- A temperature difference of 1 ° F corresponds to 5 ⁄ 9 ° C or 5 ⁄ 9 K.
So the conversions of a temperature from Fahrenheit to Celsius and back are:
- t ° C corresponds to ( 9 ⁄ 5 t + 32) ° F.
- t ° F corresponds to 5 ⁄ 9 (t - 32) ° C.
Analogous to the Kelvin scale , the Rankine scale is used accordingly in science .
Derived units
speed
Formula symbol for speed : v
| unit | German | Abbr. | size | km / h | m / s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Knot | node | kn, nm / h | 1 nm ÷ 1 h | 1.852 km / h | 0.5144444 m / s |
| Admiralty knot | Knot (admiralty) | kn, nm adm / h | 1 sm adm ÷ 1 h | 1.853184 km / h | 0.514773 m / s |
| Mile per hour | miles per hour | mph, mi / h | 1 mi ÷ 1 h | 1.609344 km / h | 0.447040 m / s |
| Foot per second | Feet per second | fps, ft / s | 1 ft ÷ 1 s | 1.097280 km / h | 0.304800 m / s |
With the international nautical mile, a knot only sinks by 1.184 m / h or 0.329 mm / s.
force
Symbol of force : F
| unit | German | Abbr. | size | Newton | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pound-force | lb | lbf, lb F | 1 pound g N = 196 133 ÷ 6096 lb ft / s 2 | 4.45 N | 4.448221615260500 kg m / s 2 |
| poundal | pdl | 1 lb ft / s 2 | 1.38 dN | 0.138254954376 kg m / s 2 | |
Colloquially, the distinction between pound and pound-force (like kilogram to kilopond ) is often neglected, and the definition is not official. In addition, a technical pound-foot-second system was introduced in the first half of the 20th century, in which pound is the unit of force and the unit of mass is called slug . The poundal has been around since at least 1879.
pressure
Symbol of the pressure : p
| unit | German | Abbr. | size | Pascal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pound-force per square inch | PSI | psi, lb F / in 2 | 1 pound-force / inch 2 | 6.89 kPa | 6894.757293168370 kg / ms 2 |
| Pound-force per square foot | lb F / ft 2 | 1 pound-force / foot 2 | 47.9 Pa | 47.880258980336 kg / ms 2 | |
| Poundal per square foot | pdl / ft 2 | 1 poundal / foot 2 | 1.49 Pa | 1.488163943570 kg / ms 2 | |
| Torr, mmHg | Torr , millimeters of mercury | mmHg, mmHg | 1 ⁄ 760 atm = 101,325 / 760 Pa | 1.33 hPa | 133.322368 kg / ms 2 |
| Inch mercury | Inches of mercury | inHg, in Hg | 25.4 mm Hg | 3.39 kPa | 3386.388157894730 kg / ms 2 |
energy
Symbol of energy or work : W or E
| unit | German | Abbr. | size | Joules | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| calorie (15 ° C) | calorie | cal, cal 15 | 1 g H 2 O @ 1 atm , 14.5 → 15.5 ° C | 4,186 J. | 4.185 5 kg m 2 / s 2 |
| Calorie (15 ° C) | Kilocalorie | C, kcal | 1000 calorie | 4.186 kJ | 4185.5 kg m 2 / s 2 |
| British thermal unit | Btu, BTU | 1 pound H 2 O.63 → 64 ° F ~ = 778 ft lb F | 1.055 kJ | ||
| therm | 100,000 Btu | 105.5 MJ | |||
| quad | 10,000,000,000 therm | 1.055 EJ | |||
In addition to the 15-degree calorie, there are a few more, see Calorie . The quad means quadrillion BTU , whereby the American quadrillion is meant, i.e. 10 15 BTU.
power
Formula symbol for performance : P
| unit | German | Abbr. | size | watt | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manpower | (Manpower) | 1 ⁄ 10 horsepower | 7.46 daW | 74.569987158227 kg m 2 / s 3 | |
| Horsepower | Horsepower | hp, BHP | 550 lb F ft / s = 550 196 133 ÷ 6096 lb ft 2 / s 3 | 7.46 hW | 745.699871582270 kg m 2 / s 3 |
The German horse power is defined as 75 kp · m / s and, at 735.49875 watts, is somewhat smaller than the British horse power ; it is sometimes called metric horsepower , so as metric horsepower referred.
Torque
Formula symbol for the torque : M
| unit | German | Abbr. | size | Newton meter | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foot-pound | Pound foot | lb-ft, lb F ft | 1 lb F x 1 ft | 1.36 Nm | 1.355817948331400 4 kg m 2 / s 2 |
| Inch-pound | lb-in, lb F · in | 1 lb F 1 in = 1 ⁄ 12 lb-ft | 1.13 dN m | 0.1129848290276167 kg m 2 / s 2 | |
| Inch-ounce | oz-in, oz F in | 1 oz F 1 in = 1 ⁄ 192 lb-ft | 7.06 mN m | 0.007061551814226 kg m 2 / s 2 | |
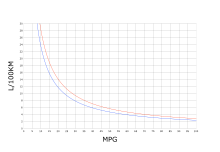
Fuel consumption
Route-related fuel consumption: In the case of vehicles, the metric system of measurements indicates the amount of fuel (in liters) that is consumed per 100 km of route. In the Anglo-American system of measurement, the reverse relationship is established. This shows the distance (in miles) that can be covered with one gallon of fuel, i.e. the fuel efficiency . Since the gallon in the US Customary Units variant is smaller than in the Imperial Units (UK) variant , there are also two different sized units.
| unit | German | Abbr. | size | Conversion factor mpg (US) | Conversion factor mpg (UK) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Miles per gallon | Miles per gallon | mpg, MPG, mi / gal | 1 mile / gallon | 235.2145833 mpg (US) ⁄ l / 100 km | 282.4809363 mpg (UK) ⁄ l / 100 km |
| Conversion accuracy: 1 place after the decimal point: | 235 mpg (US) ⁄ l / 100 km | 282 mpg (UK) ⁄ l / 100 km | |||
Because the metric consumption in liters per 100 kilometers - i.e. H. as SI unit without numerical factors: cl / km or dal / Mm - reciprocal to the Anglo-American efficiency specification in miles per gallon (mpg, MPG, mi / gal), the conversion factor must be divided by the original unit for the conversion into the respective target unit . The following examples should explain this:
- 5.3 l ⁄ 100 km → mpg (US): 235 ⁄ 5.3 l ⁄ 100 km = 44.3 mpg (US)
- 25 mpg (US) → l ⁄ 100 km : 235 ⁄ 25 mpg (US) = 9.4 l ⁄ 100 km
After petrol stations in Great Britain were converted to liters, but distances are still given in miles, the indication of miles per liter (mi / l) also appears there. In Canada, both l ⁄ 100 km and mpg (UK) are possible. The unit kilometer per liter is rarely used there, especially in the NWT . The general rule is that the consumption information is determined worldwide according to different standards and a conversion is therefore only of limited informative value (see also fuel consumption ).
| L / 100 km | mi / gal (US) |
|---|---|
| 2.35 | 100 |
| 3 | 78.4 |
| 3.14 | 75 |
| 4th | 58.8 |
| 4.70 | 50 |
| 5 | 47.0 |
| 6th | 39.2 |
| 7th | 33.6 |
| 8th | 29.4 |
| 10 | 23.5 |
| 11.8 | 20th |
Illuminance
In the USA, at the consumer, production and retail level up to the engineering level, the illuminance is specified according to the United States customary units system using the unit foot-candle ( lumens per square foot). The unit is used in occupational safety regulations for the illumination of workplaces, paths and rooms, as well as for the illumination of streets, squares and public spaces. But it is also predominant in the field of photography and the specification of photo sensors. On the other hand, at the internationally cooperating scientific level, the SI unit Lux is predominantly used .
| unit | German | Abbr. | size | Metric size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foot-candle | Foot candle (rarely used) | fc, ftc, ft-c | 1 fc = 1 lm / ft 2 | 10.76391 lx = 10.76391 lm / m 2 |
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ Ronald Edward Zupko: Revolution in measurement: Western European weights and measures since the age of science . American Philosophical Society, 1990, ISBN 978-0-87169-186-6 , p. 261 (accessed October 13, 2012).
- ↑ Alanna Mitchell: America Has Two Feet. It's About to Lose One of Them. ( en ) In: New York Times . August 18, 2020. Retrieved August 19, 2020.
- ↑ Weights and Measures Act of 1985 (UK) Page 76: Definition of the English gallon.
- ↑ Weights and Measures Act of 1976 (UK) page 14: List of the valid English measures of measure.
- ↑ pound avoirdupois. Retrieved March 7, 2017 .
Web links
General
- Imperial Measure (English)
- History of the metric system as opposed to the old units in the United States (English)
More specific details
- UK laws on "Imperial Units":
- Units of Measurement Regulations 1995 (PDF)
- Weight and Measure Act 1824 (PDF; 4.1 MB)
- Publications of the "National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) on" US Customary Units ":
- Handbook No. 44, Appendix C (PDF; 401 kB)
- Publication 811: Guide for the Use of the International System of Units (SI) (PDF; 2.0 MB)
- Publication 447: Weights and Measure Standards of the United States (PDF; 1.4 MB)