German Savings Banks and Giro Association
| German Savings Banks and Giro Association V. (DSGV) |
|
|---|---|

|
|
| legal form | registered association |
| Seat | Berlin and Bonn |
| founding | 1924
|
| place |
Berlin , Germany |
| president | Helmut Schleweis |
| Board | Karl-Peter Schackmann-Fallis, Joachim Schmalzl |
| Members | 12 |
| Website | dsgv.de |
The German Savings Banks and Giro Association e. V. (DSGV) is the umbrella organization of 12 regional savings bank associations at state level and at the same time responsible for the organization of the association system of the savings bank finance group .

General
The DSGV is the counterpart to the Federal Association of Public Banks in Germany , the Federal Association of German Volksbanken and Raiffeisenbanken and the Federal Association of German Banks . As interest groups , these associations represent the interests of their affiliated members , particularly in lobbying work , ensure a uniform market presence and coordinate their members at association level. The associations issue recommendations for uniform general terms and conditions, so that these are not nationally standardized, but vary depending on the association membership.
history
As an umbrella organization, the DSGV was created in March 1924 from the merger of the “Deutsche Sparkassenverband” established in 1884, the “German Central Giro Association” established in 1916 and the “German Association of Communal Banks” established in 1921. V. “This gave the savings bank institutes, which until then had only been active locally and regionally, the opportunity to appear united and to significantly increase their political influence. The three previous associations were merged in March 1924 to form the “Arbeitsgemeinschaft Deutscher Sparkasse- und Giroverbände und Girozentralen” in the legal form of a corporation under public law , which in November 1950 assumed the legal form of a registered association (eV); From February 1951, the club had its headquarters in Bonn . Since October 1953 it has been called Deutscher Sparkassen- und Giroverband e. V. 12 regional savings bank associations are affiliated to this umbrella organization as members.
With the introduction of joint advertising for the savings banks in 1924, a Hermes head stylized from the letters “DSGV” emerged as a uniform identification symbol for the savings banks. On behalf of the association, the "Sparkassen-S" was created in 1938 with a coin slot and a point as a coin on the upper edge. The graphic designer Otl Aicher revised the uniform appearance for the savings banks in 1972, for which he modified the "Sparkassen-S" and introduced red as the corporate color of the savings banks.
In the 1920s, the DSGV ö. K. contributed to the establishment of uniform business principles, for example in giro transactions, at the savings banks. The association supported the savings banks in the further expansion of their business areas , especially in the securities, deposits and credit business. During the time of National Socialism , the DSGV was “brought into line” in terms of organization and personnel and, as the “ Economic Group of Savings Banks ” within the “ Reichsgruppe Banken ”, was subordinated to the Reich Ministry of Economics . DSGV President Ernst Kleiner, who had contributed to the “Gleichschaltung”, had to leave office in 1935. He was succeeded by Johannes Heintze , a senior official from the Reich Ministry of Economics. He died in Soviet custody in 1945. The DSGV has been based in Bonn since February 1951.
Under its first president Fritz Butschkau , the DSGV e. V. in the period of reconstruction in the Federal Republic of Germany between 1953 and 1967, the topics of monetary stability and the fight against inflation are the focus of his work. Under Butschkau's successor Ludwig Poullain , the era of increasing market orientation of the savings banks began in 1967. The professionalization and automation of savings bank operations made great strides. In 1971 the DSGV moved into a newly built administration building in Bonn , which was expanded in 1992.
Even in the period of upheaval in 1989/90, the association, under its president Helmut Geiger , who has been in office since 1972, made contacts with the GDR savings bank organization and supported them in transforming the East German savings banks into modern financial institutions. At the same time as the reunification of the two German states, the all-German Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe came into being in autumn 1990. At the Sparkasse Days of 1995 (“Responsibility in Society and Region”) and 1998 (“Future Europe - Location: Here”), Horst Köhler - DSGV President from 1993 to 1998 - underlined the future viability of the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe in competition and highlighted the regional one Responsibility and the positioning of the savings banks in Europe. The association had already started to relocate its office to Berlin in the summer of 1999. During the term of office of Dietrich H. Hoppenstedt in June 2001 an agreement was reached with the EU Commission on the change of the liability bases for savings banks and Landesbanken ( Brussels Concordance ). On this basis, the guarantor liability for new liabilities of the institutes ceased in July 2005 and the Anstaltslast was replaced.
During the presidency of Heinrich Haasis , who succeeded Hoppenstedt in 2006, the international financial market crisis fell , culminating in 2008 when the US investment bank Lehman Brothers collapsed . Due to their regional roots, their close ties with the real economy and extensive independence from the international capital markets, the German savings banks proved to be an anchor of stability in the crisis. In 2007 the DSGV organized the purchase of the Landesbank Berlin and its subsidiary Berliner Sparkasse by the savings banks. This succeeded in preventing the Sparkasse in the German capital from being privatized. Georg Fahrenschon headed the DSGV from 2012 to the end of November 2017 .
In the summer of 1999 the association moved from Bonn to Berlin . The central scientific institutions of the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe remained in Bonn: the Management Academy of the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe, the Science Fund , the Eberle Butschkau Foundation and its own, state-recognized university . Near Berlin, the DSGV has been the owner of Schloss Neuhardenberg since 1997 , and in 2001 the Foundation Schloss Neuhardenberg GmbH was responsible for the event program, conference activities and hotel operations.
tasks
In its capacity as the umbrella organization, the DSGV represents the interests of the public-law savings banks , the Landesbanken groups and DekaBank, as well as the Landesbausparkassen , primary insurance groups of the savings banks and numerous other financial service companies . The DSGV organizes the decision-making process within the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe and its market and operational strategy - from product development and processing, through risk management and overall bank control to card and payment transactions and holistic advisory approaches for all customer segments. In addition, the DSGV administers the security reserve of the Landesbanken and Girozentralen as well as the security fund of the Landesbausparkassen, which are part of the institutional security system recognized under the Deposit Protection Act (EinSiG). The DSGV is the legal entity of the institute-related guarantee system of the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe ( institute protection of the savings banks, Landesbanken and Landesbausparkassen ) recognized as a deposit guarantee system according to § 43 EinSiG and assumes the compensation of the creditors for the affiliated institutes in accordance with § § 5 to § 16 EinSiG and thus the Task of deposit insurance .
In addition, as an association partner, the DSGV represents the interests of the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe at national and international level and defines the strategic direction of the association system, such as the common corporate design . The DSGV is also the legal owner of all national and international collective brands of the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe in its capacity as a brand association .
The association is the publisher of since 1924 appearing Sparkasse newspaper that the German Sparkassenverlag is printed. The DSGV is a member of the World Institute of Savings Banks (Geneva) and the European Savings Banks Association (Brussels).
Legal issues
According to the statutes, the organs of the association are the board of directors and the general assembly . The board of directors with a full-time president is the highest decision-making body of the association in matters in which the general assembly is not responsible. He determines the lines of the association's policy in all areas of the savings and giro business. The general assembly elects and discharges the board and is responsible for determining the membership fees and approving the annual accounts . According to the statutes, the purpose of the association is to promote the common interests of its members and the affiliated savings banks through advice and the exchange of experiences. The association represents the interests of the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe on a national and international level. The association is responsible for determining the strategic direction of the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe.
The Austrian Savings Banks Association and the Association of Swiss Cantonal Banks are extraordinary members of the DSGV; conversely, the DSGV is also an extraordinary member of the two associations in Austria and Switzerland. The DSGV also represents the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe in the international savings bank committees, for example in the European Savings Banks Association in Brussels and at the World Institute of Savings Banks.
Public corporation
It is easy to confuse the DSGV e. V. with the "German Savings Banks Association public corporation " (DSGV OEK), which in June 2011 along with the "& Deka acquisition mbH & Co. KG" carrier of DekaBank German Girozentrale is a direct federal institution under public law and Association partner in the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe. On June 8, 2011, the Landesbanken that had previously been involved in DekaBank Deutsche Girozentrale left the company as shareholders. The 12 regional savings bank associations are compulsory members of the DSGV öK. According to Section 1 (1) of its Articles of Association, the DSGV öK is an amalgamation of regional associations including Landesbank Berlin Holding AG . The statutory task of the DSGV öK is to promote the savings bank system.
Association data
The association represents the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe, which consists of around 540 companies, including 385 savings banks with over 13,000 branches and 209,588 employees (as of December 31, 2018). A total of 312,800 people work in the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe. It has a business volume of € 2,840 billion. This makes the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe the largest banking group in Europe (as of December 31, 2017).
President of the German Savings Banks and Giro Association
- 1924–1935: Ernst Eberhard Kleiner
- 1935–1945: Johannes Heintze (appointed by the Reich Ministry of Economics )
- 1953–1967: Fritz Butschkau (1945–1953 Managing Director, since 1967 Honorary President DSGV)
- 1967–1972: Ludwig Poullain
- 1972–1993: Helmut Geiger
- 1993–1998: Horst Köhler
- 1998-2006: Dietrich H. Hoppenstedt
- 2006–2012: Heinrich Haasis
- 2012–2017: Georg Fahrenschon
- since 2017: Helmut Schleweis
Facilities
- The state-recognized university of the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe in Bonn offers the possibility of a Bachelor and MBA course. The course is aimed at young professionals in the financial sector.
- The Management Academy is the central training center of the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe and takes on association-political tasks in the area of human resource management and personnel development.
- Science funding initiates and deepens the dialogue between science and the Savings Banks Finance Group. It supports research and teaching in the field of money, banking and stock exchange as well as the history of the savings banks and promotes the transfer of knowledge from science to practice.
- The Financial Institutions Risk and Rating System GmbH supports with methods and procedures for risk management , for capital planning and risk-bearing capacity calculation as well as the subjects reporting and internal reporting.
- The European service of the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe offers small and medium-sized enterprises information and advice on the European single market, its economic, legal and social effects as well as its future expansion - on all questions that are of interest to companies. EuropaService is a facility for customers and institutes of the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe. It cooperates with the EU Commission and its “Enterprise Europe Network” consisting of 500 institutions in 40 countries.
-
Sparkassenstiftung für Internationale Zusammenarbeit e. V. based in Bonn: The Sparkassenstiftung mainly focuses on six project types:
- Development of retail banks, e.g. B. in the area of risk management.
- Credit lines for SMEs ("down-scaling"), e. B. German-Azerbaijanian Fund in Azerbaijan.
- Microfinance, e.g. B. Transformation of unregulated microfinance institutions into formal (microfinance) banks.
- Personnel development and training, e.g. B. Establishment of banking academies, the development of curricula and training courses and the organization of seminars and conferences (bank simulation games).
- Financial sector development, e.g. B. Advising microfinance associations and central banks.
- Basic financial education and mobilization of savings, e.g. B. Introduction of World Savings Day and accompanying campaigns.
- Advice service money and budget: supports consumers in their private financial planning with free offers. The aim is to provide financial education and prevention of over-indebtedness.
- Neuhardenberg Castle Foundation
- Arbitration Board
Savings Banks Finance Group
The Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe consists of several regional associations, network partners and service companies.
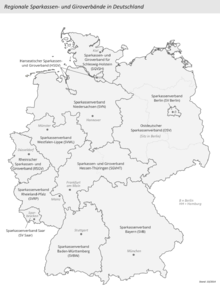
Regional savings and giro associations
- Savings Banks Association Baden-Württemberg (SVBW, seat: Stuttgart)
- Savings Banks Association of Bavaria (SVB, seat: Munich)
- Savings Bank Association Berlin (SV Berlin, seat: Berlin)
- Hanseatic Savings Banks and Giro Association (HSGV, seat: Hamburg)
- Savings Banks and Giro Association Hessen-Thuringia (SGVHT, seat: Frankfurt am Main and Erfurt)
- Savings Bank Association Lower Saxony (SVN, seat: Hanover)
- East German Savings Bank Association (OSV, seat: Berlin)
- Rheinischer Sparkassen- und Giroverband (RSGV, seat: Düsseldorf)
- Sparkassenverband Rheinland-Pfalz (SVRP, seat: Mainz)
- Savings Bank Association Saar (SV Saar, seat: Saarbrücken)
- Savings Banks Association Westphalia-Lippe (SVWL, seat: Münster)
- Savings Banks and Giro Association for Schleswig-Holstein (SGVSH, seat: Kiel)
There are a total of 12 regional associations in the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe with 2,698 employees.
Landesbanken
6 Landesbanken (excluding DekaBank Deutsche Girozentrale) (as of December 31, 2017); Employees (in Germany and abroad) approx. 34,836 (as of December 31, 2017).
- Bayerische Landesbank (BayernLB) (seat: Munich)
- Landesbank Baden-Württemberg (LBBW) (seat: Stuttgart)
- Landesbank Hessen-Thüringen Girozentrale (Helaba) (seat: Frankfurt am Main and Erfurt)
- Norddeutsche Landesbank - Girozentrale - (Nord / LB) (seat: Hanover)
- Landesbank Saar (SaarLB) (seat: Saarbrücken)
Former Landesbanken
- Hamburg Commercial Bank AG (formerly HSH Nordbank AG )
- Hamburgische Landesbank (predecessor institution of HSH Nordbank )
- Landesbank Schleswig-Holstein Girozentrale (LB Kiel) (predecessor institute of HSH Nordbank )
- Bremer Landesbank Kreditanstalt Oldenburg - Girozentrale (taken over by NORD / LB)
- WestLB (since July 1, 2012)
- Landesbank Berlin (LBB) (no longer owned by a federal state since it was sold by the state of Berlin to the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe )
-
Südwestdeutsche Landesbank Girozentrale (SüdwestLB; merged in 1999 with Landesgirokasse Stuttgart and the market section of Landeskreditbank Baden-Württemberg to form Landesbank Baden-Württemberg)
- Landesbank Stuttgart (merged with Südwestdeutsche Landesbank Girozentrale in 1988)
- Badische Kommunale Landesbank (merged into the Südwestdeutsche Landesbank Girozentrale in 1988)
- LRP Landesbank Rheinland-Pfalz (merged with Landesbank Baden-Württemberg in 2008)
- Landesbank Sachsen (merged with Landesbank Baden-Württemberg in 2008)
Landesbausparkassen
8 Landesbausparkassen (LBS), employees approx. 6,800 (as of December 31, 2019).
- LBS Bayerische Landesbausparkasse (seat: Munich)
- Landesbausparkasse Hessen-Thüringen (Headquarters: Offenbach am Main)
- LBS Norddeutsche Landesbausparkasse Berlin-Hanover (seat: Hanover)
- LBS Ostdeutsche Landesbausparkasse AG (seat: Potsdam)
- LBS Landesbausparkasse Saar (seat: Saarbrücken)
- LBS Bausparkasse Schleswig-Holstein-Hamburg AG (seat: Hamburg and Kiel)
- LBS Landesbausparkasse Südwest (seat: Stuttgart)
- LBS Westdeutsche Landesbausparkasse (seat: Münster)
Savings banks
377 savings banks (as of April 15, 2020) with around 210,000 employees in over 13,000 branches (as of December 31, 2018)
Public regional primary insurers
11 institutes, employees approx. 30,000.
DekaBank Deutsche Girozentrale
- DekaBank Deutsche Girozentrale , central asset manager of the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe, around 4.7 million managed custody accounts, total assets 276 billion euros (as of December 31, 2018). (Headquarters: Frankfurt am Main and Berlin)
Savings Bank Broker
- Sparkassen Broker (S Broker AG & Co. KG), central online broker of the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe (seat: Wiesbaden)
Deutsche Leasing Group
- Deutsche Leasing AG (registered office: Bad Homburg vd Höhe)
Financial informatics
- Finanz Informatik , central IT service provider of the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe (seat: Frankfurt am Main)
DSV Group (Deutscher Sparkassenverlag)
- DSV Group , central product and solution provider in the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe (seat: Stuttgart)
Social commitment of the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe and the DSGV
Like the savings banks, the German Savings Banks and Giro Association is committed to the common good in a wide variety of ways . In its "Report to Society", the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe documents its contributions to sustainable development in Germany. With its entrepreneurial attitude, its products and social initiatives, it is committed - following its public mandate - on site in a complex manner. For the savings banks, their respective business area is the focus of promotion.
Associations from the fields of art, sport and culture, environmental and social projects as well as institutions for academic and economic further education, such as B. the financial advisory service " Money and Budget " or the stock market simulation game . Furthermore, there are numerous foundations in the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe that support certain projects. The Sparkassen-Kulturfonds of the German Savings Banks and Giro Association is a regular partner for the institutes and foundations of the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe in promoting culture .
Examples of previous and ongoing projects
- The Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe has supported the Dresden State Art Collections since 2006, and has been the main sponsor since 2011; Since 2011 she has also been the main sponsor of the Staatliche Museen zu Berlin .
- In the anniversary year of the Bauhaus , the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe supports numerous individual projects, events and series
- In Schloss Neuhardenberg , the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe has set up a center for art and culture, science and business ethics.
- The Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe has supported the " Jugend musiziert " competition on all three levels from the start, and has been the main sponsor since 1991
- Under the motto “Experience is simple”, the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe was the main sponsor of Documenta 14 in Kassel and the Skulptur.Projekte Münster in 2017 , and was also a partner of the German Pavilion at the 57th International Art Exhibition - La Biennale di Venezia
- The association was the main sponsor of RUHR.2010 and added the "Ruhrblicke" to the cultural program.
Olympia partner Germany
As "Olympia Partner Germany", the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe has been supporting the German Olympic team since 2008 . The Paralympic teams have also been supported since 2012 . The focus is also on promoting young athletes and mass sports. With around 90 million euros, the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe is the largest non-governmental sports sponsor in Germany.
Report to society
In July 2014, the German Savings Banks and Giro Association presented the first report to the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe company. The aim of the report is to promote sustainable development in Germany and to improve awareness of the commitment of public savings banks. In cooperation with the German Council for Sustainable Development , the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe was the first banking association in Germany to cooperate with the German Sustainability Code. A separate indicator system for sustainability reporting was developed for the savings banks and was recognized by the German Council for Sustainable Development. The savings banks can use 61 indicators to show their contributions to sustainable development and their performance in fulfilling their public mandate.
Memberships
The association is a member of the European Movement Network . The DSGV is also an extraordinary member of the Austrian Association of Savings Banks and the Association of Swiss Cantonal Banks . In return, both associations are also extraordinary members of the DSGV.
Web links
- www.dsgv.de Website of the DSGV
- Early documents and newspaper articles on the German Savings Banks and Giro Association in the 20th Century press kit of the ZBW - Leibniz Information Center for Economics .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Henner Schierenbeck (Ed.): Bank- und Versicherungslexikon , 1994, p. 75
- ^ Peter Linder, Associations of Private Banks and Savings Banks in Germany , 1968, p. 46
- ↑ Christian Thiemann, Legal Problems of the Sparkasse Brand , 2008, p. 52
- ↑ Hans Pohl / Bernd Rudolph / Günther Schulz, Economic and Social History of the German Savings Banks in the 20th Century , 2005, pp. 160 ff.
- ↑ Jürgen Mura, Development Lines of German Savings Bank Stories , 1987, pp. 58 ff.
- ↑ Thorsten Wehber, Fritz Buschkau , in: Hans Pohl (Ed.): Deutsche Bankiers des 20. Jahrhundert . 2008, p. 35 ff.
- ↑ Hans Pohl / Bernd Rudolph / Günther Schulz, Economic and Social History of the German Savings Banks in the 20th Century , 2005, p. 336 ff.
- ↑ Hans-Georg Günther / Walter Geiger, Reorganization of the East German Savings Bank System 1990–1995 , 1998, pp. 45 ff., 155 ff.
- ↑ Horst Köhler, German Sparkasse Organization: Responsibility in Society and Region , Deutscher Sparkassentag 1995 in Hanover, 1995, pp. 205 ff.
- ↑ Hans-Peter Burghof , Expiry of guarantor liability for savings banks and Landesbanken , in: Dieter Lindenlaub / Carsten Burhop / Joachim Scholtysek (eds.): Key events in German banking history , 2013, p. 464 ff.
- ↑ Norbert Schwaldt: Sparkassen assume the Landesbank Berlin . In: Die Welt , June 16, 2007
- ↑ Sparkassen buy LBB
- ↑ Fahrenschon resigns president. Retrieved December 11, 2017 .
- ↑ History of Neuhardenberg Castle /
- ↑ cf. § 5 trademark statutes of the DSGV
- ↑ Henner Schierenbeck (Ed.): Bank- und Versicherungslexikon , 1994, p. 75
- ↑ Henner Schierenbeck (Ed.): Bank- und Versicherungslexikon , 1994, p. 76
- ^ Deutscher Sparkassen- und Giroverband KöR, press release No. 55 of June 8, 2011
- ↑ According to Section 3 (5) sentence 1 of the Berlin Savings Banks Act, it is a separate regional association.
- ↑ Deutscher Sparkassen- und Giroverband e. V .: Press release on the annual press conference of the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe. Retrieved April 18, 2019 .
- ↑ PDF document: "The Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe in Figures 2017"
- ↑ S-Risk and Rating System GmbH
- ↑ Savings Banks. In: dsgv.de. Retrieved April 18, 2019 .
- ^ Association of public insurers
- ↑ "On behalf of the company"
- ↑ Press release: Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe promotes the common good in 2018 with 422 million euros
- ^ DSGV, museum cooperation
- ↑ Sparkasse.de: 100 years of Bauhaus
- ↑ Music funding from the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe
- ↑ dsgv.de
- ↑ DSGV, Our responsibility to society
- ↑ Swiss cantonal banks become members of the DSGV . dsgv.de, accessed on August 22, 2014.