Potted herbs
| Potted herbs | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Giant fennel ( Ferula communis ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Ferula | ||||||||||||
| L. |
The stick herbs ( ferula ), also called rod herbs or giant fennel , are a genus of plants within the umbelliferae family (Apiaceae). The 150 to 185 species are mainly distributed in the Mediterranean region from North Africa to Southwest and Central Asia.
Naming
Ferula is derived from Latin folk etymology: ferire for "to hit", because it is guaranteed that the light, dry stick was used to hit; however, the true origin of the name is not known.
description



Appearance and leaves
Stickwort species are perennial to perennial herbaceous plants , there are both hapaxanthic species that bloom only once in their life and pollakanthic species that bloom annually. Some species reach heights of growth of up to 4 meters. The garlic-like smell of most species is noticeable . All stick herb species have tap roots , which are mostly woody . The stem is branched and the base is often covered with old fibers from the leaf sheaths.
The alternately arranged leaves are divided into leaf sheath, petiole and leaf blade. The often broad leaf sheath often envelops the stem; in some species the leaf sheaths are very durable and fray. The compound leaf blades are pinnate and two to fourfold or incised two to fourfold.
Inflorescences, flowers and fruits
Many flowers stand together in double-gold inflorescences . As a rule, there are no bracts (envelopes), but they occur in some species.
In some species there are unisexual (purely male) and hermaphrodite flowers on one specimen . The flowers are five-fold and radially symmetrical . The five petals are yellow or pale yellow (rarely greenish-yellow) and oval to lanceolate with a sharpened tip. The stylus is tapered toward sometimes enlarged or lobed to the base. The lower ovary is two-chambered.
Two -part disintegrated fruits (double achenae ) of elliptical shape are formed, in which the lateral ribs are winged. The seeds are flattened or slightly concave.
Systematics and distribution
The genus Ferula was established by Carl von Linné . Synonyms for Ferula L. are Buniotrinia Stapf & Wettst. , Leutea Pimenov , Merwia B. Fedsch . , Narthex Falc. , Schumannia Kuntze , Scorodosma Bunge , Soranthus Ledeb. , Euryangium Kauffm. , Sumbulus H.Reinsch , Talassia Korovin .
The genus Ferula belongs to the subtribe Ferulinae from the tribe Scandiceae in the subfamily Apioideae within the family Apiaceae .
Stickwort species are common in North Africa , Central and Southwest Asia, and the Mediterranean. There are also species in northern India. There are 26 species in the People's Republic of China , seven of them only there. There are 20 species in Turkey, eleven of them only there. The center of biodiversity is Central and Southwest Asia.





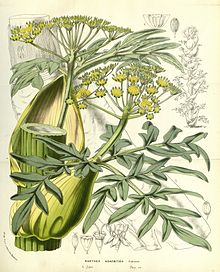

There are around 150 to 185 species of ferula :
- Ferula akitschkensis B. Fedsch . ex Koso-Pol. : It occurs in Russia , Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan and in northern Xinjiang in Altay , Bole and Tacheng .
- Ferula alaica Pimenov & Melibaev
- Ferula alliacea Boiss.
- Ferula amanicola Hub.-Mor. & Pesmen : It occurs in Turkey .
- Ferula anatolica Boiss. : It occurs in Turkey.
- Ferula angreni Korovin : It occurs in Uzbekistan and Kyrgyzstan.
- Ferula armandii Mouterde : It occurs only in Syria .
- Ferula arrigonii Bocchieri : This endemic occurs only in Sardinia .
- Asant ( Ferula assa-foetida L. )
- Ferula atlantica Elalaoui & Cauwet : It occurs only in Morocco.
- Ferula badrakema Koso-Pol. : It occurs in Iran , Afghanistan and Turkmenistan .
- Ferula baluchistanica Kitam.
- Ferula barbeyi post
- Ferula behboudiana (Rech. F. & Esfand.) DFChamb.
- Ferula bilasi post
- Ferula biverticellata J.Thiébaut : It occurs in Syria and Israel .
- Ferula blanchei Boiss.
- Ferula bolivarii Pau : It occurs in Morocco.
- Ferula botschantzevii Korovin
- Ferula brevipedicellata Peșmen ex Sağıroğlu & H.Duman : It occurs in Turkey.
- Ferula bungeana Kitag. : It thrives on stony slopes and in sandy locations at altitudes of 200 to 2500 meters in Inner Mongolia and in the Chinese provinces of Gansu , Hebei , Heilongjiang , Henan , Jilin , Liaoning , Ningxia , Shaanxi and Shanxi . It is used as a medicinal plant.
- Ferula calcarea Pimenov
- Ferula canescens (Ledeb.) Ledeb. : It occurs in western Siberia, Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan and Fuyun in northern Xinjiang.
- Ferula caspica M.Bieb. : It iswidespreadfrom Southwest Asia through the Caucasus , Ukraine , Crimea to Central Asia , Siberia, Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan, western Mongolia and northern Xinjiang .
- Ferula caucasica Korovin : It occurs in Azerbaijan and in the Caucasus region.
- Ferula ceratophylla Regel & Schmalh. : This endemic occurs only in southeastern Kazakhstan .
- Ferula clematidifolia Koso-Pol.
-
Giant fennel ( Ferula communis L. , Syn .: Ferula meoides L. ): The three subspecies are common in large parts of the Mediterranean area:
- Ferula communis L. subsp. communis : It occurs in Spain, Italy, France, Corsica , Sardinia , Sicily , Croatia , Albania , Greece , Crete , the islands of the Aegean Sea and in European and Asian Turkey.
- Ferula communis subsp. cardonae Sánchez-Cux. & M.Bernal : This endemic occurs only in Menorca .
- Ferula communis subsp. catalaunica (C.Vicioso) Sánchez-Cux. & M.Bernal : It occurs in France , the Iberian Peninsula , Mallorca , Menorca and Ibiza .
- Ferula conocaula Korovin : It only occurs in Kyrgyzstan and Wuqia in southwestern Xinjiang. It is used as a substitute for the medicinal plant Ferula assa-foetida .
- Ferula coskunii H.Duman & Sağıroğlu : It occurs in Turkey.
- Ferula cossoniana Batt. & Trot. : It occurs in Morocco, Algeria and Libya .
- Ferula costata Korovin ex Nasir
- Ferula cupularis (Boiss.) Spalik & SRDownie
- Ferula cypria Post : This endemic occurs only in Cyprus .
- Ferula czatkalensis Pimenov
- Ferula daninii Zohary
- Ferula decurrens Korovin
- Ferula dictyocarpa Rech. F.
- Ferula dissecta (Ledeb.) Ledeb. : It occurs in Kazakhstan, western Siberia and northern Xinjiang only in Altay and Tacheng.
- Ferula diversivittata Regel & Schmalh. : It occurs in northeastern Iran , Afghanistan, Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan.
- Ferula drudeana Korovin : It occurs in Turkey.
- Ferula dshizakensis Korovin
- Ferula dubjanskyi Korovin (Syn .: Ferula dshaudshamyr Korovin ): It occurs in Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, in western Mongolia and in Altay in northern Xinjiang.
- Ferula duranii Sağıroğlu & H.Duman : It occurs in Turkey.
- Ferula elaeochytris Korovin : It occurs in Turkey, Syria and Lebanon .
- Ferula elbursensis (Mozaff.) Spalik & SRDownie
- Ferula equisetacea Koso-Pol.
- Ferula euxina Pimenov
- Ferula fedoroviorum Pimenov
- Ferula fedtschenkoana Koso-Pol.
- Ferula ferganensis Lipsky ex Korovin
- Ferula ferulaeoides (Steud.) Korovin : It occurs in western Siberia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan, Mongolia and north-central Xinjiang. It is used as a substitute for the medicinal plant Ferula assa-foetida .
- Ferula flabelliloba Rech. F. & Aellen
- Ferula foetida (Bunge) rule : It occurs in Iran, Afghanistan, Pakistan , Turkmenistan , Kyrgyzstan and Uzbekistan.
- Ferula foetidissima Regel & Schmalh. : It occurs in Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan.
- Ferula fontqueri Jury : It only occurs in Morocco.
- Ferula fukanensis K.M.Shen : This endemic thrives in valleys on the border of the desert at altitudes of around 700 meters only in Fukang in north-central Xinjiang. It is used as a substitute for the medicinal plant Ferula assa-foetida .
- Ferula gabriella Rech. F. : It occurs in Iran.
- Ferula ghorana Rech. F.
- Ferula gigantea B. Fedsch.
- Ferula glaberrima Korovin
- Ferula glabra Rech. F. & Riedl
- Ferula glauca L .: It occurs in France , Italy , Sicily , Croatia , Montenegro , Albania , Greece , Crete , on other Aegean islands and in Turkey.
- Ferula glaucopruinosa (Rech. F.) Akhani
- Ferula gouliminensis Elalaoui & Cauwet : It occurs only in Morocco.
- Ferula gracilis (Ledeb.) Ledeb. : It occurs in western Siberia and in Altay in northern Xinjiang.
- Ferula grigoriewii B. Fedsch.
- Ferula groessingii Riedl & Riedl-Dorn
- Ferula gummosa Boiss. : It occurs in Iran and possibly also in Turkmenistan.
- Ferula gypsacea Korovin
- Ferula halophila Peşmen : It occurs in Turkey.
- Ferula haussknechtii H.Wolff ex Rech. F.
- Ferula hedgeana Pimenov & Kljuykov
- Ferula heratensis Rech. F.
- Ferula Hermonis Boiss. : It occurs in Lebanon and Syria.
- Ferula heuffelii Griseb. ex Heuff. : It occurs in Croatia , Serbia , Bulgaria and Romania .
- Ferula hexiensis K.M.Shen : This endemic thrives in humid locations on mountain slopes only in Sunan in northern Gansu.
- Ferula hezarlalehzarica Ajani
- Ferula hindukushensis Kitam.
- Ferula huber-morathii Peşmen
- Ferula iliensis Krasn. ex Korovin : It only occurs in Kazakhstan.
- Ferula inciso-serrata Pimenov & JVBaranova
- Ferula jaeschkeana Vatke : It is common in Central Asia (Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan), Afghanistan , Bhutan , northeast India, western Pakistan and western Tibet (only in Ngari , Zanda ).
- Ferula juniperina Forovin
- Ferula kandaharica Rech. F.
- Ferula karakalensis Korovin
- Ferula karatavica Regel & Schmalh. : It occurs in southeastern Kazakhstan, in Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan in the Altai , Pamir and Tian Shan and in Xinyuan in western Xinjiang.
- Ferula karataviensis (Regel & Schmalh.) Korovin ex Pavlov
- Ferula karategina Lipsky ex Korovin
- Ferula karelinii Bunge (Syn .: Schumannia karelinii (Bunge) Korovin , at FOC 2005 this is the only species of the genus Schumannia Kuntze ): It occurs in Iran, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan and Xinjiang.
- Ferula kashanica Rech. F.
- Ferula kelifi Korovin
- Ferula kelleri Koso-Pol.
- Ferula kingdon-wardii H.Wolff : This endemic thrives in gaps between stones on grassy slopes at altitudes of 2700 to 3300 meters only in northwestern Yunnan .
- Ferula kirialovii Pimenov : It only thrives in Tian Shan in Xinjiang, Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan.
- Ferula kokanica Regel & Schmalh.
- Ferula korshinskyi Korovin
- Ferula koso-polyanskyi Korovin
- Ferula krylovii Korovin
- Ferula kuhistanica Korovin : It occurs in Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan.
- Ferula kyzylkumica Korovin
- Ferula lancerotensis Parl. Ex Hartung : It occurs only on Lanzarote and Fuerteventura .
- Ferula lapidosa Korovin
- Ferula laseroides (Akhani) Spalik & SRDownie
- Ferula latiloba Korovin
- Ferula latipinna A.Santos : It occurs only on La Palma and Gomera .
- Ferula latisecta Rech. F. & Aellen
- Ferula lehmannii Boiss.
- Ferula leiophylla Korovin
- Ferula leucographa Korovin
- Ferula licentiana Hand.-Mazz.
- Ferula linczevskii Korovin
- Ferula linkii Webb : It occurs in the Canary Islands of Tenerife , Gran Canaria , La Palma , Gomera , Fuerteventura and Hierro .
- Ferula lipskyi Korovin
- Ferula lithophila Pimenov
- Ferula litwinowiana Koso-Pol. : It occurs in Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan.
- Ferula longipedunculata Peşmen : It occurs in Turkey.
- Ferula longipes Coss. ex Bonnier & Maury
- Ferula loscosii (Lange) Willk. : It occurs in Spain .
- Ferula lutensis Rech. F.
- Ferula lycia Boiss. : It occurs in Turkey.
- Ferula macrocolea Boiss.
- Ferula malacophylla Pimenov & JVBaranova
- Ferula marmarica Ash. & Deaf. ex ash. & Schweinf. : It occurs in Libya and Egypt .
- Ferula mervynii Sağıroğlu & H.Duman : It occurs in Turkey.
- Ferula microcolea (Boiss.) Boiss.
- Ferula mogoltavica Lipsky ex Korovin
- Ferula mollis Korovin
- Ferula mongolica (V.MVinogr. & Kamelin) VMVinogr. & Camel
- Ferula moschata (H. Reinsch) Koso-Pol.
- Ferula myrioloba Rech. F.
- Ferula narthex Boiss. : It occurs in India, Pakistan and Afghanistan.
- Ferula negevensis Zohary
- Ferula nevskii Korovin
- Ferula nuda Spreng.
- Ferula nuratavica Pimenov
- Ferula nuristanica Rech. F.
- Ferula olivacea (Diels) H.Wolff
- Ferula oopoda (Boiss. & Buhse) Boiss. : It occurs in Iran, Afghanistan, northern Iraq, Pakistan, southern Turkmenistan and Armenia.
- Ferula orbicularis Post ex Beauverd & Zohary
- Ferula orientalis L .: It occurs in southeastern Bulgaria, in Ukraine, in eastern Turkey, in northern Iraq, in western Iran and in Azerbaijan.
- Ferula ovczinnikovii Pimenov
- Ferula ovina (Boiss.) Boiss. : It occurs in Iran, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan and Xinjiang.
- Ferula pachycaulos Rech. F.
- Ferula pachyphylla Korovin
- Ferula pallida Korovin
- Ferula palmyrensis Post & Beauverd
- Ferula parva Freyn & Bornm. : It occurs in Turkey.
- Ferula penninervis Regel & Schmalh. : It occurs in Kyrgyzstan and Turkmenistan.
- Ferula persica Willd. Of this kind was serapinum (also seraphin resin (called) Serapinharz won). It occurs in Iran, Azerbaijan and Armenia.
- Ferula pimenovii Lazkov
- Ferula plurivittata Korovin
- Ferula potaninii Korovin ex Pavlov
- Ferula prangifolia Korovin : It occurs in eastern Uzbekistan.
- Ferula pratovii F.O.Khasanov & IIMal'tsev
- Ferula pseudalliacea Rech. F. : It occurs in Iran.
- Ferula racemosoumbellata (Gilli) Rech. F.
- Ferula rechingeri D.F. Chamb.
- Ferula renardii (Regel & Schmalh.) Pimenov
- Ferula rigidula fish. ex DC.
- Ferula rubricaulis Boiss.
- Ferula rubroarenosa Korovin
- Ferula rutbaensis C.C. Towns .
- Ferula sadleriana Ledeb. : It occurs in Hungary , Slovakia and Romania.
- Ferula samariae Zohary & PHDavis
- Ferula samarkandica Korovin
- Ferula sauvagei Elalaoui & Cauwet : It occurs only in Morocco.
- Ferula schchurowskiana Regel & Schmalh.
- Ferula seravschanica Pimenov & JVBaranova
- Ferula serpentinica Rech. F.
- Ferula sharifii Rech. F. & Esfand.
- Ferula sibirica Willd.
- Ferula sinaica Boiss.
- Ferula sinkiangensis K.M.Shen : It occurs in Xinjiang.
- Ferula sjugatensis Bjat.
- Ferula soongarica Pall. ex Schult. : It occurs in Kazakhstan and Siberia.
- Ferula sphenobasis C.C.Towns.
- Ferula stenocarpa Boiss. & Hausskn.
- Ferula stenoloba Rech. F.
- Ferula stewartiana O.E. Schulz
- Ferula subtilis Korovin
- Ferula sugatensis Bajtenov
- Ferula sumbul (Kauffm.) Hook. f. : It occurs in Kyrgyzstan.
- Ferula syreitschikowii Koso-Pol.
- Ferula szowitsiana DC. : It occurs in Iran, Turkey, Afghanistan, Turkmenistan and Armenia.
- Ferula tabasensis Rech. F. : It was first described from Iran.
- Ferula tadshikorum Pimenov
- Ferula tatarica fish. ex explos.
- Ferula taucumica Baitenov
- Ferula tenuisecta Korovin
- Ferula tenuissima Hub.-Mor. & Pesmen : It occurs in Turkey.
- Ferula teterrima Kar. & Kir.
- Ferula thomsonii C.B. Clarke
- Ferula tingitana L .: It occurs in Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia , Libya, Portugal , Spain, Gibraltar , on the Aegean islands, in Turkey, Syria, Jordan and Israel.
- Ferula trachelocarpa Rech. F. : It was first described from Afghanistan.
- Ferula trachyphylla Rech.f. & Riedl : It was first described from Afghanistan.
- Ferula transiliensis (Herder) Pimenov
- Ferula tschimganica Lipsky ex Korovin
- Ferula Tschuiliensis Bajtenov
- Ferula tuberifera Korovin
- Ferula tunetana Pomel ex Batt. : It only occurs in Tunisia.
- Ferula ugamica Korovin : It occurs in Kyrgyzstan and in eastern Uzbekistan.
- Ferula varia (Schrenk) Trautv. : It occurs in Kazakhstan and in Kyrgyz people.
- Ferula vesceritensis Coss. & Durieu ex trot. : It occurs in Algeria and Tunisia.
- Ferula vicaria Korovin
- Ferula violacea Korovin
- Ferula xanthocarpa Rech. F. : It was first described from Afghanistan.
- Ferula xeromorpha Korovin
- Ferula xylorhachis Rech. F.
- Silphium , a plant found in Libya, was probably a species of the genus Ferula (Ferula historica). It is probably extinct.
use
Ferula persica supplies the serapine resin. In Sicily, bee houses were made from ferula sticks, illustration in: Walter Brinkmann, Beehive and apiary in the Romanic countries of Hamburg 1938, panel VII, 1.
swell
- Renata Kurzyna-Młynik, Alexei A. Oskolski, Stephen R. Downie, Rafał Kopacz, Aneta Wojewódzka, Krzysztof Spalik: Phylogenetic position of the genus Ferula (Apiaceae) and its placement in tribe Scandiceae as inferred from nrDNA ITS sequence variation. In: Plant Systematics and Evolution , Volume 274, 2008, pp. 47-66. doi : 10.1007 / s00606-008-0022-2 PDF. (Section systematics)
- She Menglan (佘孟兰 Sheh Meng-lan), Mark F. Watson: Ferula , p. 174 - online with the same text as the printed work , In: Wu Zheng-yi, Peter H. Raven (ed.): Flora of China , Volume 14 - Apiaceae through Ericaceae , Science Press and Missouri Botanical Garden Press, Beijing and St. Louis, 2005, ISBN 1-930723-41-5 . (Sections Description and Systematics)
- Zeynep Elibol, Yusuf Menemen, Mehmet Sağiroğlu, Hayri Duman, Fen Edebiyat: A molecular phylogenetic study on some Turkish Ferula L. (Apiaceae) species using nrDNA ITS sequences. In: Pakistan Journal of Botany , Volume 44, Issue 2, 2012, pp. 589–594: full text PDF. (Section systematics)
Individual evidence
- ↑ Helmut Genaust: Etymological dictionary of botanical plant names. 3rd, completely revised and expanded edition. Birkhäuser, Basel / Boston / Berlin 1996, ISBN 3-7643-2390-6 , p. 247.
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag She Menglan (佘孟兰 Sheh Meng-lan), Mark F. Watson: Ferula , P. 174 - online with the same text as the printed work , In: Wu Zheng-yi, Peter H. Raven (Ed.): Flora of China , Volume 14 - Apiaceae through Ericaceae , Science Press and Missouri Botanical Garden Press, Beijing and St. Louis, 2005, ISBN 1-930723-41-5 .
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af Ferula in the Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN), USDA , ARS , National Genetic Resources Program. National Germplasm Resources Laboratory, Beltsville, Maryland. Retrieved May 25, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc bd be bf R. Hand, 2011: Apiaceae. : Ferula data sheet In: Euro + Med Plantbase - the information resource for Euro-Mediterranean plant diversity.
- ↑ Mehrnoush Panahi, Łukasz Banasiak, Marcin Piwczyński, Radosław Puchałka, Alexei A. Oskolski, Krzysztof Spalik: Phylogenetic relationships among Dorema, Ferula and Leutea (Apiaceae: Scandiceae: Ferulinae) inferred noncoding sequences from nr .DNA ITNAS In: Taxon , Volume 64, Issue 4, August 2015. doi : 10.12705 / 644.8
- ↑ Dieter Lehmann: Two medical prescription books of the 15th century from the Upper Rhine. Part I: Text and Glossary. Horst Wellm, Pattensen / Han. 1985, now at Königshausen & Neumann, Würzburg (= Würzburg medical-historical research , 34), ISBN 3-921456-63-0 , p. 254.
Web links
further reading
- Marcin Piwczyński, Dominika WyborskaJoanna Gołębiewska, Radosław Puchałka: Phylogenetic positions of seven poorly known species of Ferula (Apiaceae) with remarks on the phylogenetic utility of the plastid trnH-psbA, trnS-trnG, and atpB-rbcL inter. In: Systematics and Biodiversity March 2018. doi : 10.1080 / 14772000.2018.1442374




