Apulia
| Apulia | |
|---|---|
|
|
|
| Basic data | |
| Capital | Bari |
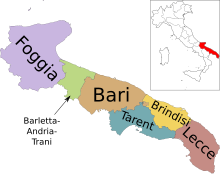
| Provinces | Foggia , Bari ( metropolitan city ) , Brindisi , Tarent ( Taranto ), Lecce , Barletta-Andria-Trani (since 2004) |
| surface | 19,365.8 km² ( 7th ) |
| Residents | 4,008,296 (Dec. 31, 2019) |
| Population density | 207 inhabitants / km² |
| Website | www.regione.puglia.it |
| ISO 3166-2 | IT-75 |
| president | Michele Emiliano ( PD ) |
 Relief map of the Apulia region |
|
Apulia ( italian Puglia [ puʎːa ] or often in the plural Puglie [ puʎːe ]; Latin Apulia ) is in southeast Italy Situated region with the capital Bari . It has 4,008,296 inhabitants (as of December 31, 2019). The Salento peninsula in the south of Apulia forms the "heel" of the so-called "Italian boot".
geography
Geographical location
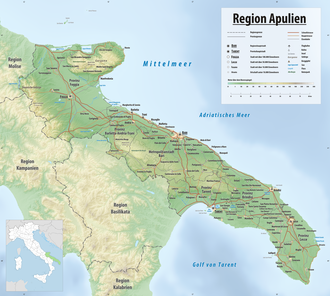
The region stretches along the Adriatic and Ionian Seas . With Punta Palascìa , the coast near Otranto reaches the easternmost point of Italy, which is only 80 km away from the Albanian coast .
Surface shape
The area consists of 53.3% plains, 45.3% hills and 1.5% mountains. This makes Apulia the flattest region in Italy. The landscapes are divided from north to south into the mountainous Gargano peninsula with the offshore Tremiti Islands , the flat Tavoliere delle Puglie , the subsequent Terra di Bari plain , the Murge limestone plateau , the Taranto coastal plain and the Valle d'Itria , the the southernmost region, which closes the largely flat Salento peninsula . The only mountain range over 1000 m next to the Gargano, the Monti della Daunia form the border with Campania and reach an altitude of 1152 m in Monte Cornacchia.
Early autumn landscape around the Castel del Monte
climate
The climate offers mild winters and hot summers .
history
The main article, History of Apulia, deals with the historical development of the southeastern Italian region of Apulia, which is roughly the heel of the Italian peninsula.
politics
Michele Emiliano ( PD ) has been President of Apulia since June 26, 2015 .
Administrative division and largest cities
Apulia consists of the provinces of Foggia , Barletta-Andria-Trani , Taranto , Brindisi , Lecce and the metropolitan city of Bari . The province of Barletta-Andria-Trani, founded in 2004, only became legally competent with the elections for the provincial assembly on June 6th and 7th, 2009.
| Province or metropolitan city | Capital | ISO | Communities | Population (December 31, 2019) |
Area (km²) | Population density (inh / km²) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bari | Bari | IT-BA | 41 | 1,249,246 | 3,825 | 327 |
| Barletta-Andria-Trani | Barletta , Andria and Trani | IT-BT | 10 | 388,390 | 1,539 | 252 |
| Brindisi | Brindisi | IT-BR | 20th | 390,456 | 1,839 | 212 |
| Foggia | Foggia | IT-FG | 61 | 616.310 | 7.175 | 86 |
| Lecce | Lecce | IT-LE | 97 | 791.122 | 2,759 | 287 |
| Tarent | Tarent | IT-TA | 29 | 572,772 | 2,437 | 235 |
| Apulia | Bari | IT-75 | 258 | 4,008,296 | 19,366 | 207 |
With an agglomeration of almost 600,000 inhabitants, Bari is the metropolis of Apulia and the second largest city in southern Italy after Naples . There are the following major cities in the region. (Population figures as of December 31, 2019) Source: ISTAT
| local community | Province or metropolitan city | Residents |
|---|---|---|
| Bari | Bari | 322,316 |
| Tarent | Tarent | 195.227 |
| Foggia | Foggia | 149.904 |
| Andria | Barletta-Andria-Trani | 99,307 |
| Lecce | Lecce | 96,534 |
| Barletta | Barletta-Andria-Trani | 94,316 |
| Brindisi | Brindisi | 85.881 |
The list of municipalities in Apulia includes all municipalities in the region with population figures.
Castel del Monte , one of the landmarks and sights of the region
Trulli in Alberobello near the metropolitan city of Bari
economy
Compared with the per capita GDP of the EU ( adjusted for purchasing power ) Puglia reached in 2015 an index of 63 (EU 28: 100). With a value of 0.852, Puglia ranks 17th among the 20 regions of Italy in the Human Development Index .
In 2017 the unemployment rate was 18.8%.
Agriculture
In addition to almonds , olives , cereals and tomatoes , prickly pears , grapes , figs and citrus fruits also thrive in the fertile coastal plains . The mild winter is ideal for Stem carbon , which in wild broccoli recalls and the base of the famous Apulian Court Orecchiette con cima di rapa forms.
Puglia is an important wine-growing region with predominantly full-bodied red wines. Important grape varieties are Primitivo , Negroamaro and Nero di Troia . A total production of 7,580,000 hectoliters ( DOC production: 259,900 hl) is produced on a cultivated area of 107,571 hectares . Well-known wine-growing regions are Manduria , the Salento peninsula , the areas around Castel del Monte , Canosa di Puglia , Locorotondo and Foggia .
In 2013, Puglia was the first European region to be affected by olive tree death and was divided into corresponding protection zones.
Airports
In terms of aviation history, Puglia was Italy's stepping stone to the Orient. Because of this, there is a strong concentration of civil and military airfields in this region. In addition to the Bari-Palese airport, the operating company Aeroporti di Puglia also operates the Brindisi-Casale airport and the Taranto-Grottaglie and Foggia airports . The airport of Bari, together with the airport of Brindisi-Casale, is the most important in the Apulia region;
Bari Airport is located eight kilometers northwest of Bari, the capital of the Apulia region. It was named at the end of 2005 after the real name of the late Pope John Paul II Karol Wojtyła .
Steel industry
The huge steel factory ILVA SpA in Taranto produces more than 30% of Italy's steel and employs 25,000 people. It is the largest of its kind in Europe. Due to massive environmental pollution with many deaths in the region, however, parts of the plant are currently closed and the Italian state has taken control of the most important employer in the region.
See also
literature
- Pina Belli D'Elia: Romanesque Apulia , Echter, Würzburg 1989, ISBN 3-429-01242-2 .
- Christian Hülsen : Apuli, Apulia . In: Paulys Realencyclopadie der classischen Antiquity Science (RE). Volume II, 1, Stuttgart 1895, Col. 288-290.
- Ekkehart Rotter: Apulia . Trips to Byzantine grotto churches, Norman cathedrals, Hohenstaufen forts and baroque buildings in Lecce. (= DuMont art travel guide ). 6th edition. Dumont Reise Verlag, Ostfildern 2012, ISBN 3-7701-4314-0 .
- Gianni Farneti: 1000 oasi e parchi naturali da vedere in Italia. Rizzoli, 2011, pp. 690-727.
- Kathleen M. Lynch: Introduction , in: Thomas H. Carpenter, Kathleen M. Lynch, Edward GD Robinson (Eds.): The Italic People of Ancient Apulia: New Evidence from Pottery for Workshops, Markets, and Customs , Cambridge University Press, 2014, pp. 1–9. ( academia.edu )
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Statistiche demografiche ISTAT. Monthly population statistics of the Istituto Nazionale di Statistica , as of December 31 of 2019.
- ↑ EUROSTAT Newsrelease , 52/2017 - March 30, 2017
- ^ Sub-national HDI - Area Database - Global Data Lab. Retrieved August 12, 2018 .
- ↑ Unemployment rate, by NUTS 2 regions. Retrieved November 5, 2018 .
- ↑ Rachel Donadio: Ilva Steel Mill: The Pink Dust That Brings Death. In: welt.de . January 3, 2013, accessed October 7, 2018 .
- ↑ http://industriemagazin.at/a/ilva-verstaatlicht
Coordinates: 41 ° 0 ' N , 16 ° 43' E