Atlantic hurricane season 1982
 All the storms of the season | |
| Formation of the first storm |
2th of June |
|---|---|
| Dissolution of the last storm |
October 3 |
| Strongest storm | Debby - 950 hPa ( mbar ), 115 kn (215 km / h ) |
| Storms | 6th |
| Hurricanes | 2 |
| Severe hurricanes ( Cat. 3+ ) | 1 |
| Total number of victims | 136 |
| Total damage | $ 12 million (1982) |
|
Atlantic hurricane season 1980 , 1981 , 1982 , 1983 , 1984 | |
The 1982 Atlantic hurricane season officially began on June 1, 1982 and lasted through November 30. These dates usually limit the period of the year in which most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic Basin .
Few storms formed in 1982, and those that formed were mostly weak or remained at sea. The season started early with Hurricane Alberto , which formed on the first day of the official season. Alberto threatened southwest Florida as a tropical storm, resulting in twenty-three casualties in Cuba . The next storm formed in June and affected the same area as Alberto. It resulted in property damage of ten million dollars . July was without activity.
The most momentous storm of the season was Tropical Storm Beryl, which killed 115 people as it passed over Cape Verde . Another notable storm was Hurricane Debby , which reached category four on the Saffir-Simpson hurricane wind scale , unusually far north . The season started early as Hurricane Alberto formed on the first day of the season. The last storm of the season was Tropical Storm Ernesto, which had the shortest duration of just three days and stayed far at sea.
This inactivity was caused by medium-altitude wind shear , which was unusually strong in the Caribbean Sea and the open Atlantic Ocean . The wind shear has been attributed to a number of factors. The vertical wind shear was strong enough to prevent convection in areas with disturbed weather so that they could not develop further. The El Niño that affected this hurricane season extended its effects into the 1983 Atlantic hurricane season . Tropical activity may also have been suppressed by above average concentrations of mineral dust in the air originating in Africa.
Storms
Hurricane Alberto
| Category 1 hurricane | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Duration | June 2nd - June 6th | ||
| intensity | 75 kn (140 km / h ) (1 minute) , 985 hPa | ||
- → Main article: Hurricane Alberto (1982)
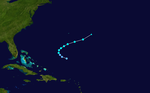
On June 1st, an existing cloud system in western Cuba developed into a tropical low pressure area. It slowly migrated northeast through the Gulf of Mexico and intensified into Tropical Storm Alberto on June 3. Alberto went on a errant course northeast and briefly intensified into a category one hurricane - one of the earliest hurricanes in June - but quickly declined in strength and turned back west. It broke up on June 6 near the Florida Keys . Alberto is a rare example of a tropical cyclone that occurs in the Gulf of Mexico without ever moving directly over land.
Nevertheless, 23 people were killed in Cuba by violent floods due to the storm. In southern Florida the rain was partly extensive, with the highest rainfall measured at 418 mm in Tavernier .
Subtropical Storm One
| Subtropical Storm ( SSHWS ) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Duration | June 18 - June 20 | ||
| intensity | 60 kn (110 km / h ) (1 minute) , 984 hPa | ||
- → Main article: Subtropical Storm One (1982)
Subtropical Storm One formed on June 18 in the east of the central area of the Gulf of Mexico and followed almost exactly a straight course in a northeast direction, which it maintained throughout its existence. He crossed the Florida Peninsula that night, where he initiated the issuance of numerous warnings of severe thunderstorms and tornadoes . The storm continued on its way, crossing the Outer Banks in North Carolina . It maintained its strength until June 20, when it went extra-tropical near Newfoundland .
Subtropical Storm One is responsible for three deaths in Florida, sank a trawler off the coast of North Carolina and caused damage of ten million US dollars .
Tropical storm Beryl
| Tropical storm | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Duration | August 28th - September 6th | ||
| intensity | 60 kn (110 km / h ) (1 minute) , 989 hPa | ||
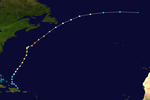
On August 27, a tropical wave broke off the west coast of Africa and quickly developed into a tropical depression. In the late evening of August 28, the low in the Tropical Storm Beryl intensified and passed directly south of Cape Verde . The storm intensified continuously and peaked on August 31 with wind speeds of 110 km / h. One eye was visible in satellite images, but quickly disappeared as the wind shear intensified at altitude. On September 2, Beryl weakened to a tropical depression and on September 6, the system north of the Lesser Antilles dissolved.
At the beginning of its existence, Beryl brought the heaviest rainfall to the Cape Verde island of Sal . The storm damage in the archipelago totaled $ 3 million (1982). Beryl caused 115 deaths in the island nation. After the storm, the United States provided humanitarian and economic aid to clean up the aftermath of Beryl.
Tropical Depression Three
| Tropical depression | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Duration | September 6th - September 9th | ||
| intensity | 30 kn (55 km / h ) (1 minute) | ||
The system formed on September 6, southeast of Beryl in the tropical Atlantic. On the afternoon of September 7th, the system was moving northeast of the Leeward Islands Lesser Antilles, exposed to vertical wind shear , so that it dissolved east of the Bahamas on September 9th .
Tropical storm Chris
| Tropical storm | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Duration | September 9th - September 12th | ||
| intensity | 55 kn (100 km / h ) (1 minute) , 994 hPa | ||
On September 8, a low pressure area formed near the surface in the Gulf of Mexico , which moved westward and developed into a subtropical low the next day . Under the influence of a trough , the depression turned north and after steadily developing, the system transformed into Tropical Storm Chris on late September 10th. The storm peaked at 100 km / h before moving onto the mainland near Sabine Pass , Texas . Chris continued on his way inland until it broke up over Arkansas on September 13th . Before the landfall, 6,500 people had been evacuated from southern Louisiana and a number of oil rig crews were brought ashore as a precaution.
The track from Chris recorded heavy rainfall at times, which peaked at 407 mm in Delhi , Louisiana, but also exceeded 250 mm in Mississippi and Tennessee . The rain caused local flash floods in Tennessee and Kentucky , where multiple rivers have been flooded. The storm caused nine tornadoes , four of which reached F2 or higher on the Fujita scale . At sea, Chris caused a storm surge , the water level of which was 1.5–1.8 m above normal. This caused damage to boats in the Gulf of Mexico. Chris caused a total property damage of two million US dollars along his track .
Hurricane Debby
| Category 4 hurricane | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Duration | September 13th - September 20th | ||
| intensity | 115 kn (215 km / h ) (1 minute) , 950 hPa | ||
- → Main article: Hurricane Debby (1982)
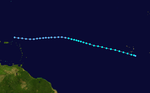
Debby began its life cycle as a tropical wave that degenerated shortly after it broke off the coast of Africa . It migrated across the Atlantic Ocean and began organizing itself into a tropical depression off the north coast of Haiti on September 13th . The low turned north and intensified into a tropical storm and then a hurricane. Hurricane Debby migrated north-northeast, blanketing Bermuda with winds the strength of a tropical storm. Debby intensified further as it moved north, reaching its top with a wind speed of 220 km / h. Winds the strength of a tropical storm were also measured at the Cape Race in Newfoundland on September 18 when Debby passed by. The storm accelerated its forward speed and began to weaken over the colder waters of the northern Atlantic. Debby joined a strong nontropical system over the British Isles on September 20th .
The leading fault at Debby brought heavy rainfall to Puerto Rico , with rainfall of up to 327 mm in the southwestern part of the island. Debby did little damage.
Tropical Depression Six
| Tropical depression | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Duration | September 16 - September 20 | ||
| intensity | 30 kn (55 km / h ) (1 minute) | ||
This tropical low pressure area formed on September 16 1450 km west of Cape Verde and moved west-northwest across the tropical Atlantic Ocean. The system disintegrated on September 20 about 1200 km east of the Lesser Antilles .
Tropical Depression Seven
| Tropical depression | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Duration | September 25th - September 27th | ||
| intensity | 30 kn (55 km / h ) (1 minute) | ||
The remaining depth of the Tropical Low Pressure Area Sieben continued its way in a west-northwest direction over the southwest North Atlantic. This developed on September 25 about 450 km west of Bermuda. The system made a curve to the north and northeast, and eventually disbanded southeast of Nova Scotia on September 27th.
Tropical storm Ernesto
| Tropical storm | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Duration | September 30th - October 2nd | ||
| intensity | 60 kn (110 km / h ) (1 minute) , 997 hPa | ||
A tropical wave formed from the coast of Africa on September 23 . The western flank of the wave expanded and was classified as a Tropical Depression on September 30th. The depression intensified and took a sharp turn on October 1st. A reconnaissance plane of the US Air Force presented wind speeds of 65 km / h and an air pressure of 1003 hPa firm, was upgraded after which the depression to Tropical Storm Ernesto. A second airplane measured a wind speed of 115 km / h and an air pressure of 997 hPa on October 2nd, but on October 3rd Ernesto connected to an extra-tropical low pressure area and was no longer identifiable afterwards. Ernesto has not approached any land area and has caused no known damage.
Accumulated Cyclone Energy (ACE)
| ACE (10 4 kt 2 ) - storm | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 18.2 | Debby | 4th | 1.65 | Ernesto | |
| 2 | 5.45 | Beryl | 5 | 1.29 | Chris | |
| 3 | 2.06 | Alberto | ||||
| Total: 28.6 | ||||||
The Accumulated Cyclone Energy is a measure that enables the comparison of hurricane seasons. The table shows the ACE for every storm of the season that reached at least the strength of a tropical storm. The wind speed measured every six hours is squared; these measurements are then added up. Longer lasting storms therefore achieve a higher ACE. In the Atlantic basin, years with an ACE below 66 are considered below average.
Storm names
The following list of names was used for named storms that formed in the North Atlantic during the 1982 hurricane season. No names were removed from this list, so it was reused unchanged during the 1988 Atlantic hurricane season . These names were first used, with the exception of Florence and Helene, which were given in 1954, 1958, 1960 and 1964. Unused names are marked here with the note (unused) .
|
|
|
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ Gilbert B. Clark. Atlantic Hurricane Season of 1982. (PDF; 1.0 MB) Retrieved November 15, 2008 (English).
- ^ William S. Kessler. Southern Oscillation Index. Retrieved November 15, 2008 (English).
- ↑ Amato T. Evan, Jason Dunion, Jonathan A. Foley, Andrew K. Heidinger, Christopher S. Velden .: New Evidence For a Relationship Between Atlantic Tropical Cyclone Activity and African Dust Outbreaks Archived from the original on September 11, 2008 (PDF ) In: American Geophysical Union (Ed.): Geophysical Research Letters . Vol. 33, 2006. doi : 10.1029 / 2006GL026408 . Retrieved August 10, 2015.
- ↑ David Roth . Hurricane Alberto Rainfall Totals. Retrieved October 21, 2006.
- ↑ Miles B. Lawrence. Hurricane Albero Report. Retrieved October 21, 2006.
- ↑ Joseph Pelissier. Subtropical Storm One Report Retrieved October 21, 2006.
- ^ National Hurricane Center: Tropical Storm Beryl (1982) Preliminary Report Page 1 . National Hurricane Center. 1983. Retrieved April 5, 2007.
- ^ National Hurricane Center: Tropical Storm Beryl (1982) Preliminary Report - Section 2 - Storm History II ( English , GIF) National Hurricane Center. 1983. Retrieved April 5, 2007.
- ^ EM-DAT: the International Disaster Database: Disaster List for Cape Verde . Center for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters. 2007. Archived from the original on May 12, 2016. Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. Retrieved August 10, 2015.
- ↑ Geography IQ: US-CAPE VERDEAN RELATIONS ( English ) Geography IQ. 2007. Retrieved April 5, 2007.
- ^ David M. Roth . CLIQR tropical cyclone database. Retrieved November 15 (English).
- ^ A b Gilbert B. Clark: Tropical Storm Chris Preliminary Report . National Hurricane Center. September 27, 1982. Retrieved March 28, 2007.
- ^ David Roth : Tropical Cyclone Rainfall: Tropical Storm Chris . Hydrometeorological Prediction Center. 2007. Retrieved March 28, 2007.
- ^ US Geological Survey Kansas Water Science Center: Summary of Significant Floods in the United States, Puerto Rico, and the Virgin Islands, 1970 Through 1989-1982 . US Geological Survey Kansas Water Science Center. 2007. Retrieved March 28, 2007.
- ↑ Tom Grazulis of The Tornado Project and Bill McCaul of USRA Huntsville: List of Known Tropical Cyclones Which Have Spawned Tornadoes . Tornado Project. 2007. Retrieved March 28, 2007.
- ↑ David Roth . Hurricane Debby Rainfall Totals. ( Memento of October 8, 2006 in the Internet Archive ) Retrieved October 21, 2006.
- ^ National Hurricane Center . Hurricane Debby Report. Retrieved October 21, 2006.
- ↑ Associated Press: A Wandering Hurricane Brushes Past Bermuda ( English ) The New York Times. September 17, 1982. Retrieved August 10, 2015.
- ^ Associated Press : Hurricane Debby threatens shipping interests (English) , Galveston Daily News . September 19, 1982. Retrieved May 23, 2008.
- ↑ Associated Press : Debby weakens; depression forms. (English) , Galveston Daily News . September 20, 1982. Retrieved May 23, 2008.
- ^ Associated Press : Tropical Winds Threaten Shipping (English) , Syracuse Herald Journal . September 26, 1982. Retrieved May 23, 2008.
- ↑ Associated Press : Tornado kills one (English) , Galveston Daily News . September 27, 1982. Retrieved May 23, 2008.
- ^ Associated Press : Tropical storm loses ferocity (English) , Indiana Gazette . September 27, 1982. Retrieved May 23, 2008.
- ↑ Miles B. Lawrence. Tropical Storm Ernesto Report. Retrieved October 21, 2006.
literature
- Gilbert B. Clark: NHC. "Atlantic Hurrican Season 1982". In: Monthly Weather Review 1983 (PDF; 1.0 MB). Pp. 1071-1079.