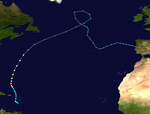
Atlantic hurricane season 2012

All the storms of the season
|
Formation of the
first storm |
May 19th |
Dissolution of the
last storm |
October 29th |
| Strongest storm |
Sandy - 940 hPa ( mbar ), 100 kn (185 km / h ) |
| Tropical lows |
19th |
| Storms |
19th |
| Hurricanes |
10 |
| Severe hurricanes ( Cat. 3+ ) |
2 |
| Total number of victims |
199 direct, 155 indirect |
| Total damage |
$ 77.97 billion (2012) |
Atlantic hurricane seasons
2010 , 2011 , 2012 , 2013 , 2014
|
The 2012 Atlantic hurricane season officially begins on June 1st and ends on November 30th. It is during this period that most hurricanes usually form , as it is only at this time that suitable conditions exist, such as warm ocean , moist air, and little wind shear , to allow tropical cyclones to form. However, the 2012 season started prematurely with the formation of Tropical Storm Alberto on May 19. The second named storm of the season, Beryl, also emerged before the official start of the season on May 26th. It was the first time since the 1951 Atlantic hurricane season that two storms formed before the official start of the season.
Storms in the Pacific Ocean are listed in the 2012 Pacific Hurricane Season article .
Season forecasts
Tropical cyclone activity predictions for the 2012 season
|
source
|
date
|
Storms
|
Number of
hurricanes
|
Cat. 3+
|
|
CSU
|
Average (1950–2000)
|
9.6
|
5.9
|
2.3
|
|
NOAA
|
Average (1950–2005)
|
11.0
|
6.2
|
2.7
|
|
|
Record values (high)
|
28
|
15th
|
8th
|
|
|
Record values (low)
|
4th
|
2
|
0
|
| ––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
|
| TSR
|
December 7, 2011
|
14th
|
7th
|
3
|
| WSI
|
December 21, 2011
|
12
|
7th
|
3
|
| CSU
|
April 4, 2012
|
10
|
4th
|
2
|
| ––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
|
|
|
Actual activity
|
19th
|
10
|
2
|
Predictions about the activity of the coming hurricane season are made every year by the hurricane experts Philip J. Klotzbach and William M. Gray and their colleagues at Colorado State University and separately by the meteorologists of NOAA and the consortium Tropical Storm Risk .
Klotzbach's team defined the average number of storms per season on average (1950-2000) at 9.6 tropical storms, 5.9 hurricanes and 2.3 severe hurricanes (ie those that are at least in on the Saffir-Simpson hurricane wind scale be classified as category 3). A normal season, as determined by NOAA, consists of 9-12 named storms, of which 5-7 become hurricane strength and 1-3 become severe hurricanes.
Forecasts before the start of the season
On December 7, 2011, Tropical Storm Risk (TSR), a public consortium of insurance, risk management and seasonal climate forecasting experts at University College London , issued a medium-term forecast that assumes an above-average hurricane season for 2012. In the report, TSR found that tropical cyclone activity could be about 49% above the 1950-2010 average, with 14.1 (± 4.2) tropical storms, 6.7 (± 3.0) hurricanes, and 3 , 3 (± 1.6) severe hurricanes and a cumulative ACE index of 117 (± 58) were expected.
On December 21, 2011, Weather Services International (WSI) issued a forecast that assumes an almost average hurricane season in 2012. In that forecast, WSI indicated that a cooler North Atlantic Oscillation , unheard of for a decade, combined with the weakening La Niña, would result in an average seasonal pattern, with 12 named storms, including seven hurricanes, three of which were Category 3 or higher. This prediction also assumed a near-average probability of a hurricane landfall in the United States, with the risk for the Gulf Coast being slightly higher and for the East Coast of the United States slightly lower than average.
Storms
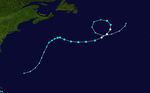
Tropical storm Alberto
| Tropical storm
|
|
|
| Duration
|
May 19 - May 22
|
| intensity
|
50 kn (95 km / h ) (1 minute) , 995 hPa
|
The first tropical storm of the season in the Atlantic Ocean formed on May 19 at 5 p.m. local time (9 p.m. UTC ) off the coast of the US state of South Carolina and was named Alberto . Its wind speed in the center was 75 km / h at an air pressure of 1007 hPa . The system initially moved in a south-westerly direction and reached its greatest strength on the same day with wind speeds of 95 km / h and an air pressure of 995 hPa. Alberto was the earliest tropical storm of the season in the Atlantic since Ana in 2003. And for the first time in history, a tropical storm formed in both the Atlantic and Eastern Pacific before the official season start on June 1. On May 21, Alberto stalled his southwest move near Jacksonville , Florida , then turned and continued moving northeast while losing strength. On the evening of the same day, Alberto was downgraded to a tropical depression. A day later, Alberto went extra-tropical.
Tropical storm Beryl
| Tropical storm
|
|
|
| Duration
|
May 26th - May 30th
|
| intensity
|
60 kn (110 km / h ) (1 minute) , 992 hPa
|
On May 23rd, an elongated depression developed over the northwestern Caribbean and moved northeast. At first there was no clear center and the wind shear was unfavorable for development. The next day, the system was on Florida Street and the National Hurricane Center advised of possible more favorable conditions within two days. The system moved further northeast and developed a well-defined circulation with convection that was below an altitude low. On May 26, the NHC therefore declared the low pressure area to be a subtropical storm Beryl . At that time, Beryl was 490 km east of Charleston , South Carolina . A high pressure ridge then turned Beryl westward and then in a southwesterly direction. A day later, Beryl intensified into a full-fledged tropical storm and reached its peak with wind speeds of 110 km / h and a minimum air pressure of 992 hPa . With that intensity, Beryl made landfall near Jacksonville Beach , Florida that day . Shortly thereafter, it weakened to a tropical depression. Over the next two days, the system moved overland, first to the southwest, north and finally northeast, dumping heavy rain over northern Florida, eastern Alabama and southern Georgia. Beryl's May 28 shore leave was the strongest in US history that did not form in the season. The storm was also responsible for 4 direct and 2 indirect deaths.
Hurricane Chris
| Category 1 hurricane
|
|
|
| Duration
|
June 18 - June 22
|
| intensity
|
75 kn (140 km / h ) (1 minute) , 974 hPa
|
On June 17, a stationary front near Bermuda developed into a depression. Over the warm waters of the Gulf Stream and as a result of low wind shear, the system gradually acquired tropical characteristics the following day, and on the afternoon of June 19, after the deep thunderstorms had persisted for a long enough time, the National Hurricane Center classified the system as tropical storm and named this Chris . On June 21, Chris intensified into the first hurricane of the season, despite the storm moving over relatively cool water with a surface temperature of less than 22 ° C. Crossing even cooler water, Chris weakened to a tropical storm just six hours later.
Early on June 22nd, under the influence of a major nontropical low south of the storm, the storm began to transition into a post-tropical cyclone . After the storm lost its tropical properties and was absorbed by the nontropical depression, the NHC issued its final warning on Chris later on June 22nd.
Chris was the third earliest tropical storm on record during the year, with only two storms forming earlier in 1887 and 1959 . Chris was also the second most northerly tropical storm since weather records began in 1851. Only Tropical Storm Alberto in 1988 was upgraded to a tropical storm further north.
Tropical storm Debby
| Tropical storm
|
|
|
| Duration
|
June 23rd - June 27th
|
| intensity
|
55 kn (100 km / h ) (1 minute) , 990 hPa
|
In mid-June, an area of low air pressure emerged in the central Caribbean that crossed the Yucatán Peninsula on June 22 and moved north into the Gulf of Mexico . The area intensified the next day into a tropical storm named Debby . Debby moved very slowly on June 24th and 25th and was almost stationary and could not strengthen himself very much. The storm was stationary on June 25, 140 km south of Apalachicola , Florida . The following day Debby weakened as the west coast of Florida approached to a weak tropical storm, which had wind speeds of 65 km / h and still had an unusually low air pressure of 992 hPa . Over Taylor County , Florida, the storm hit the mainland with winds of 40 mph, where it weakened to a tropical depression and lost almost all of its convection. On June 27th, Debby became extra-tropical. The remnants of the storm moved northeast into the open Atlantic and completely dissolved on June 30th. Debby was the earliest fourth storm of the season ever observed in the Atlantic - the earliest fourth storm formed in 2005 with Hurricane Dennis on July 5.
Hurricane Ernesto
| Category 2 hurricane
|
|
|
| Duration
|
August 1st - August 10th
|
| intensity
|
85 kn (155 km / h ) (1 minute) , 973 hPa
|
Starting July 30, the National Hurricane Center observed a tropical wave and found that the system showed good signs of further development. Due to the favorable conditions, convection slowly organized. After the system showed signs of circulation, the National Hurricane Center began issuing warnings about Tropical Depression Five on August 1 . At this point the low pressure area was about 1305 km east of the island above the wind and was moving west-northwest. In the twelve hours that followed, the system was not well organized due to westerly wind shear, but on August 2, a Hurricane Hunters flight recorded gale force winds, so the National Hurricane Center upgraded the system to a tropical storm and named it Ernesto gave. The next day, the storm moved very close to St. Lucia . The station on the island reported top speeds of 100 km / h. On the same day, Ernesto moved to the Caribbean Sea and the National Hurricane Center predicted that Ernesto could potentially intensify into a Category 1 hurricane due to the good conditions for further development. Accordingly, Jamaica issued a storm warning on August 4 that Ernesto could pass dangerously close to the island. The next day, the Cayman Islands and Honduras also issued warnings. By the time Ernesto approached the western Caribbean on Monday morning August 6th and encountered an area of moderate wind shear and dry air, its rapid intensification had come to an end and Ernesto's convection disappeared. On August 7th, however, the storm began to organize again and became a Category 1 hurricane that same afternoon. At 3:15 a.m. UTC on August 8, Ernesto disembarked in Quintana Roo , Mexico on the border with Belize at top speeds of 140 km / h. Ernesto quickly lost his convection over land and weakened into a tropical storm. In Campeche Bay , however, Ernesto intensifies again into a strong tropical storm, almost a weak hurricane, and makes his second and final shore leave near Coatzacoalcos , Mexico. Ernesto weakens quickly over mountainous Mexico. Part of what was left of Ernesto moved into the Pacific and developed into tropical Storm Hector on August 11th .
The storm was classified as a Category 2 hurricane in the follow-up analysis by the National Hurricane Center.
Tropical storm Florence
| Tropical storm
|
|
|
| Duration
|
August 3 - August 6
|
| intensity
|
50 kn (95 km / h ) (1 minute) , 1002 hPa
|
On August 1st, a tropical wave broke off the coast of Africa. The next day the National Hurricane Center began monitoring them. The wave slowly began to organize and was classified as Tropical Depression Six late on August 3 . The following day it had intensified enough that it turned into tropical storm Florence . At first, the conditions were favorable for further development, so that Florence could intensify into a moderate tropical storm. When the storm moved west-northwest and hit dry and stable air, this development was over for the time being and Florence weakened into a tropical depression on August 6th. At this point Florence had lost almost all of its convection and degenerated to an extra-tropical residual low by the evening of the same day.
Tropical storm Helene
| Tropical storm
|
|
|
| Duration
|
August 9th - August 18th
|
| intensity
|
40 kn (75 km / h ) (1 minute) , 1004 hPa
|
On the evening of August 6th, the National Hurricane Center began observing a very fast moving tropical wave near the Cape Verde Islands . The system's circulation began to organize itself the next day, but the storm activity was still very unorganized. Over the next few days, the system managed to organize itself so strongly and had enough convection to be classified as Tropical Depression Seven on August 9, east of the Leeward Islands . A flight by the Hurricane Hunters on the morning of August 11th revealed that the tropical low pressure area no longer had the storm force of a low pressure area and had weakened into a tropical wave. The National Hurricane Center then issued its final warning about the system. The remnants of the low pressure area moved on and crossed Central America on August 14th. They began to organize again in Campeche Bay after being stationary for two days. On August 17th they had organized themselves to such an extent that they intensified into a tropical storm and it was named Helene . On the morning of August 18, Helene went ashore just south of Tampico as a weak tropical storm with wind speeds of 65 km / h . Overland, Helene quickly weakened to a tropical low pressure area and degenerated to a residual low late on August 18th.
Hurricane Gordon
| Category 2 hurricane
|
|
|
| Duration
|
August 15 - August 20
|
| intensity
|
95 kn (175 km / h ) (1 minute) , 965 hPa
|
At the beginning of August there was an area of convection between the Cape Verde Islands and the west coast of Africa. After moving across the islands, it moved further west-northwest, encountering cooler waters that weakened the system. The shower and thunderstorm activity also decreased. As the system moved further north, it gradually encountered an area of favorable conditions and was classified as Tropical Depression Eight on August 15 . At that time it was about 1000 km east-southeast of Bermuda . 12 hours after its formation, the low pressure area intensified into a tropical storm and was named Gordon . The next day, Gordon turned and headed east. As a result, the storm was expected to be extra-tropical near the Azores due to the vertical wind shear in this area. Although Gordon moved into the exact area on August 18, an eye developed and the storm turned into a hurricane. As the eye became more and more visible, the National Hurricane Center updated Gordon to a Category 2 hurricane on August 19th. Although Gordon was now weakening and was only a Category 1 hurricane, the storm moved early on August 20th. August directly over the island of Santa Maria , Azores. Later that day, Gordon weakened into a tropical storm and went extra-tropical on the evening of August 20.
Hurricane Isaac
| Category 1 hurricane
|
|
|
| Duration
|
August 21st - September 1st
|
| intensity
|
70 kn (130 km / h ) (1 minute) , 965 hPa
|
On August 17, the National Hurricane Center began observing a tropical wave that was found on the west coast of Africa. The next day the wave began to organize and slowly built up a circulation. After she developed convection on August 21, the National Hurricane Center classified her as Tropical Depression Nine that same day . At that time, the low pressure area was 1,150 km east of the Leeward Islands . On the evening of the same day, a flight of the Hurricane Hunters observed winds at gale force, so the National Hurricane Center upgraded the low pressure area to a tropical storm and named it Isaac . Despite this reinforcement, Isaac remained disorganized and was just a weak tropical storm with top speeds of 75 km / h as it was still in an area of dry air. On the afternoon of August 22nd, Isaac moved just south of Guadeloupe into the Caribbean Sea and gradually began to organize. Late on August 24th, the Hurricane Hunters observed a well-defined circulation, prompting the National Hurricane Center to upgrade Isaac to a strong tropical storm with winds of 110 km / h and a minimum air pressure of 990 hPa . Early on August 25, Isaac developed a weak eye but remained below the threshold of a hurricane before sweeping across Haiti . While the storm was overland, Isaac's circulation largely dissolved and Isaac was nothing but a weak tropical storm with little convection. When the tropical storm moved north-west, it moved right along the north coast of Cuba . Early on August 26th, Isaac re-established convection and intensified into a strong tropical storm on Florida Street. The following day, Isaac lowered his air pressure very much so that at wind speeds of 110 km / h he had a minimum air pressure of 975 hPa. At 16:20 UTC on the same day, the storm reached hurricane status 115 km south-southeast of the mouth of the Mississippi River . After intensifying rapidly, Isaac went ashore at 11:45 p.m. UTC on August 28 with winds of 130 km / h southwest of the mouth of the Mississippi River. After going ashore, Isaac crossed the water again and made his second and final shore leave on August 29 at 7:15 am UTC over Lafourche Parish , Louisiana . On the afternoon of August 29th, Isaac weakened into a tropical storm over southern Louisiana. As Isaac moved further inland, the storm weakened over Arkansas to a tropical depression on the evening of August 30th . Over the next two days, Isaac moved across Arkansas to Missouri . Isaac weakened further and further and only had wind speeds of 45 km / h. Even so, its outer rainbands reached through Iowa and Illinois to Wisconsin and brought rain there. On September 1, Isaac lost its tropical properties and completely disintegrated 115 km west-southwest of Columbia , Missouri.
The approaching tropical storm meant, among other things, that a hearing of alleged conspirators of the 9/11 terrorist attacks before a military tribunal had to be canceled at the Guantanamo Bay Naval Base in Cuba for security reasons .
Tropical storm Joyce
| Tropical storm
|
|
|
| Duration
|
August 22nd - August 24th
|
| intensity
|
35 kn (65 km / h ) (1 minute) , 1006 hPa
|
Early on August 20, the National Hurricane Center reported that a tropical wave with showers and thunderstorms was between the west coast of Africa and the Cape Verde Islands . In the course of the next day, the wave was able to organize itself more and more, so that on August 22nd, 1450 km west-southwest of the Cape Verde Islands, it was classified as Tropical Low Pressure Area Ten . The depression was able to develop further on August 23, so that it intensified into a tropical storm and was named Joyce . However, Joyce moved to an area of high wind shear that same day and was unable to develop. The storm then weakened to a tropical low pressure area and degenerated to a residual low on August 24th.
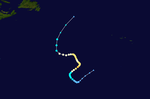
Hurricane Kirk
| Category 2 hurricane
|
|
|
| Duration
|
August 28th - September 2nd
|
| intensity
|
90 kn (165 km / h ) (1 minute) , 970 hPa
|
On August 22nd, the National Hurricane Center began observing a strong tropical wave breaking off the coast of Africa. The wave migrated west-northwest into the central Atlantic, developing slowly until, on August 28, it had organized itself enough to be classified as Tropical Depression Elf , about halfway between the Leeward Islands and the Azores . Six hours later, the system was upgraded to a tropical storm and named Kirk . On August 30, Kirk intensified into a Category 1 hurricane. The following day, the hurricane peaked as a Category 2 hurricane with wind speeds of 165 km / h and a minimum air pressure of 970 hPa . Because of very cooler waters and strong wind shear Kirk began to weaken. On September 2, Kirk went extra-tropical.
Hurricane Leslie
| Category 1 hurricane
|
|
|
| Duration
|
August 30th - September 11th
|
| intensity
|
70 kn (130 km / h ) (1 minute) , 968 hPa
|
On August 27, a tropical wave broke off the west coast of Africa and moved into the Atlantic . After being very disorganized in the beginning, the system formed convection early on August 30th. Later that day, the NHC upgraded the wave to Tropical Depression Twelve . At that time, the low pressure area was about 1905 km east of the Leeward Islands . Due to good conditions, the system intensified into tropical storm Leslie that same evening . After Leslie developed into a powerful tropical storm on August 31, wind shear began to weaken her. Leslie held status as a tropical storm for 6 days until it formed an eye on September 5 and the NHC updated it to a hurricane. On September 11th, Leslie hit Newfoundland as a strong tropical storm with winds of 110 km / h and quickly went extra-tropical.
Hurricane Michael
| Category 3 hurricane
|
|
|
| Duration
|
September 3 - September 11
|
| intensity
|
100 kn (185 km / h ) (1 minute) , 964 hPa
|
On September 2, the NHC began monitoring a tropical wave located northwest of the Cape Verde Islands . Later that day the wave became more and more organized and formed a circulation. The following day, the system was organized enough to be classified as Tropical Depression Thirteen on the same day . On September 4, the low pressure area continued its rapid development and initially intensified into a tropical storm that was named Michael . On September 5th, Michael began a rapid intensification and in just a few hours he turned into a Category 3 hurricane with a well-defined eye. After Michael's peak, the hurricane began a phase of weakening on September 6 and then weakened into a strong Category 2 hurricane. Michael remained a Category 2 hurricane through September 9, when it weakened into a Category 1 hurricane that day. The following day the hurricane rapidly weakened into a tropical storm and became extra-tropical over cool waters on September 11th.
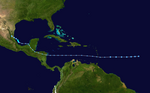
Hurricane Nadine
| Category 1 hurricane
|
|
|
| Duration
|
September 10th - October 3rd
|
| intensity
|
80 kn (150 km / h ) (1 minute) , 978 hPa
|
Late on September 7th, a large tropical wave broke off the west coast of Africa and moved into the Atlantic. The thunderstorm activity of the tropical wave organized itself more and more on the following day, so that the NHC gave a medium chance of forming a tropical depression. Although the wave hit an area of dry air over the next few days, the NHC gave the system a high chance on September 10th. On September 11th, the disturbance had organized itself to such an extent that it was classified as Tropical Low Pressure Area Fourteen at 15:00 UTC that day . On the night of September 12, the low pressure area increasingly formed convection, so that it was upgraded to Tropical Storm Nadine in the early morning . After Nadine was forced to move to the northwest due to a subtropical ridge in the southwest, the storm was able to intensify more and more and developed continuous wind speeds of 110 km / h, which corresponds to a strong tropical storm. However, when moderate wind shear set in late on September 13th, Nadine weakened a little. Nevertheless, on September 15, at 3:00 a.m. UTC, the storm was able to intensify into a Category 1 hurricane. After the reinforcement, wind shear increased in Nadine's area, which weakened the hurricane into a tropical storm in the early morning of September 17th. The storm continued its eastward course and slowly moved south along the Azores . At 10:00 UTC on September 18, the first warnings for the islands of Flores and Corvo were issued. On September 20, Flores reported wind speeds of 75 km / h. On September 21, Nadine lost much of its tropical properties and was therefore reclassified as a major subtropical storm before the system was declared post-tropical early on September 22. However, from the early morning of September 23, Nadine began to show increasingly tropical characteristics and was therefore declared a tropical storm again at 15:00 UTC. Shortly afterwards, Nadine turned her direction and from then on moved westwards south of the Azores, and thus also moved against the Gulf Stream . On September 28, Nadine was able to intensify into a hurricane for a second time before weakening into a tropical storm again on the same day. In the course of the afternoon Nadine was able to step into a hurricane a third time and on September 30th had a wind speed of 150 km / h at an air pressure of 979 hPa . On October 1st, however, Nadine experienced a rapid weakening and was just a tropical storm. Due to cool waters and moderate wind shear, the storm could no longer develop in the following 2 days and continued to weaken. On October 4th, Nadine only had wind speeds of 75 km / h and was just a weak tropical storm. Later that same day, Nadine was merged with a cold front north of the Azores and became an extra-tropical cyclone.
Tropical storm Oscar
| Tropical storm
|
|
|
| Duration
|
October 3rd - October 5th
|
| intensity
|
45 kn (85 km / h ) (1 minute) , 994 hPa
|
On September 30, an area of low air pressure formed west of the Cape Verde Islands . The following day the area was able to organize itself better and better because of the good conditions, so that on that day it had a high chance of becoming a tropical depression. By October 2, the area was organized enough to be classified as Tropical Depression Fifteen the next day . In the night of October 4, the low pressure area was able to intensify further and became tropical storm Oscar in the early morning of October 4 . During the day Oscar was able to organize himself further and until evening he had wind speeds of 75 km / h and a minimum air pressure of 1000 hPa , which corresponds to a weak tropical storm. On October 5th, Oscar reached its peak with wind speeds of 85 km / h and a minimum air pressure of 994 hPa, before it was absorbed by a large extra-tropical low pressure area that same day.
Tropical storm patty
| Tropical storm
|
|
|
| Duration
|
October 11th - October 13th
|
| intensity
|
40 kn (75 km / h ) (1 minute) , 1005 hPa
|
In early October, an area of low air pressure was created northeast of the Bahamas . At first, the system was able to develop slowly and slowly built up convection. But after strong wind shear set in, the rapid intensification of the system was initially over. When the NHC had already ceased observing the area, it organized rapidly and developed a closed circulation on October 11, prompting the NHC to classify it as Tropical Depression Sixteen at 15:00 UTC . Just 6 hours later, the NHC upgraded the depression to a tropical storm named Patty . The storm reached its climax early on October 12th with sustained wind speeds of 75 km / h and a minimum air pressure of 1005 hPa . On the same evening, however, strong wind shear ensured that Patty weakened into a tropical depression. The following day the storm had lost almost all of its convection and was only a weak circulation. The NHC issued the final warning on Patty at 15:00 UTC that day.
Hurricane Rafael
| Category 1 hurricane
|
|
|
| Duration
|
October 12th - October 17th
|
| intensity
|
80 kn (150 km / h ) (1 minute) , 969 hPa
|
On October 5th, there was a tropical wave on the west coast of Africa. Three days later, on October 8th, the NHC began observing the tropical wave. At that point she was halfway between Cape Verde and the coast of South America . In the course of the next few days the system organized itself better and better, so that convection developed and the thunderstorm activity was well concentrated. Early on October 12, the area moved into the eastern Caribbean Sea , moving right past St. Lucia . Later that day, Hurricane Hunters observed closed circulation in the system, so the NHC started issuing warnings about Tropical Storm Rafael . At the time of the update, Rafael was approximately 200 km west-southwest of Dominica . The greatest convection at that moment was concentrated in the east and southeast of Rafael, as there was an altitude low near Puerto Rico that caused southwest wind shear. A weak subtropical ridge allowed Rafael to move north-northwest and strengthen himself. On the morning of October 14th, Rafael was observed moving northwest and gradually building better circulation. When Rafael left the Caribbean Sea between the British Virgin Islands and Anguilla at the same time and moved into the open Atlantic , the already strong tropical storm intensified into a category 1 hurricane. In the afternoon and evening hours of October 16, Rafael reached its peak with Wind speeds of 150 km / h as it moved close to Bermuda . On October 17th, the storm slowly lost strength as conditions gradually set in. During the day, Rafael transformed into an extra-tropical cyclone, but it remained strong and still had hurricane winds.
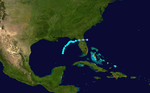
Hurricane Sandy
| Category 3 hurricane
|
|
|
| Duration
|
October 22nd - October 29th
|
| intensity
|
100 kn (185 km / h ) (1 minute) , 940 hPa
|
In mid-October, a tropical wave moved west into the Caribbean . On October 19, the NHC began monitoring the low pressure area in the eastern Caribbean, north of the coast of South America . This developed very rapidly, and the NHC determined a high chance of a tropical cyclone developing on the following day . The system was able to organize itself slowly over the course of the next few days, so that on the evening of October 21st it built up strong convection and formed a closed circulation. By October 22nd, it had intensified to such an extent that it was classified as Tropical Depression Eighteen at 3:00 p.m. UTC with its center about 350 miles south of Kingston , Jamaica . That same evening, during a reconnaissance flight by the Hurricane Hunters, it was found that the persistent winds on the surface had reached storm strength and the NHC declared the system to be a tropical storm. The storm was named Sandy . The following day the storm intensified and drifted northwards. One eye formed during October 24, causing Sandy to be upgraded to a Category 1 hurricane at 3:00 p.m. UTC. At the time, the storm was about 65 miles south of Kingston. At 19:00 UTC, Sandy's Eye reached the south coast of the island with sustained winds of 130 km / h. After crossing Jamaica, Sandy moved further north and intensified rapidly, so that the hurricane intensified into a Category 2 hurricane before reaching the Cuban coast province of Santiago de Cuba . Sandy's center landed in the early morning (local time) of October 25 at Playa Mar Verde , a good ten kilometers west of the city of Santiago de Cuba , quickly crossed the island in a north-northeast direction and reached Cabo Lucrecia , Municipio , just five hours later Banes over water again. The hurricane caused severe damage in the provinces of Santiago de Cuba, Guantánamo and Holguín . Numerous roofs were covered, trees were uprooted, electricity and telephone poles were broken. Entire houses were also destroyed. The electricity supply in Santiago completely collapsed. The cyclone continued to move roughly north across the Bahamas. It was not until the early morning of October 26 that Sandy weakened and was classified as a Category 1 hurricane northeast of the Bahamas due to her poorly visible eye . The hurricane became more and more disorganized and weakened to a strong tropical storm on October 27 at 09:00 UTC, but only intensified into a hurricane a few hours later. On October 29, 2012, the extreme wind field Sandys hit the east coast of the United States. The center of the cyclone reached the coast near Atlantic City in New Jersey , but Boston , New York City and Washington, DC / Baltimore were also in the area of the strong winds . The governors declared a state of emergency in several US states. In New York, the evacuation of low-lying neighborhoods in Manhattan and Brooklyn was ordered, affecting 375,000 residents. In addition, the port was closed. Local public transport and numerous Amtrak connections in the region have been discontinued . The exchange trading on Wall Street was discontinued. President Barack Obama canceled all campaign events and stayed in Washington, DC
Serious damage occurred in many places. The power went out in up to 7.5 million households, in New York a construction crane buckled and electricity substations exploded. A fire broke out in the borough of Queens. The subway was flooded in places and streets were blocked. A storm surge of up to 4 m high put large parts of Manhattan under water. In the Atlantic, the film ship Bounty sank in the storm, a woman died and 14 people were rescued. The captain is still missing. At least 285 people have been killed in association with Sandy in the Caribbean and North America.
Tropical storm Tony
| Tropical storm
|
|
|
| Duration
|
October 22nd - October 25th
|
| intensity
|
45 kn (85 km / h ) (1 minute) , 1000 hPa
|
On October 19, the NHC began monitoring an area of showers and thunderstorms located east-northeast of the Leeward Islands . In the course of the next day, however, the system remained very disorganized and had only little convection and shower and thunderstorm activity. However, that changed on October 21st when the area formed poor circulation and the NHC saw a medium chance of developing a tropical low. The following day, the system had organized itself to such an extent that it was classified as tropical depression nineteen at 21:00 UTC . However, this could not organize itself on October 23 and remained below the storm force. However, when the low pressure area began to circulate on October 24, the NHC updated it at 03:00 UTC for Tropical Storm Tony . This was able to intensify quickly, so that it reached its peak on the same day with wind speeds of 85 km / h and a minimum air pressure of 1000 hPa . After the climax, however, Tony quickly weakened again due to poor conditions and became extra-tropical on the evening of October 25, southwest of the Azores .
Season course
Storm names
The following names will be used in the 2012 Atlantic hurricane season. This list will be used again in 2018, subject to names that the World Meteorological Organization may replace in spring 2013. This list is identical to the list for the 2006 Atlantic hurricane season .
- Alberto
- Beryl
- Chris
- Debby
- Ernesto
- Florence
- Gordon
|
- Helene
- Isaac
- Joyce
- Kirk
- Leslie
- Michael
- Nadine
|
- Oscar
- Patty
- Rafael
- Sandy
- Tony
- Valerie (unused)
- William (unused)
|
See also
Web links
Individual evidence
-
↑ a b Philip J. Klotzbach and William M. Gray: Extended Range Forecast of Atlantic Seasonal Hurricane Activity and US Landfall Strike Probability for 2009 ( English , PDF; 849 kB) Colorado State University. December 10, 2008. Retrieved January 15, 2009.
-
↑ a b Climate Prediction Center: BACKGROUND INFORMATION: THE NORTH ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON . National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. August 8, 2006. Archived from the original on November 15, 2010. Retrieved January 22, 2008.
-
↑ a b Mark Saunders: Extended Range Forecast for Atlantic Hurricane Activity in 2012 ( English , PDF; 198 kB) Tropical Storm Risk. December 7, 2011. Retrieved April 11, 2012.
-
↑ a b Linda Maynard: WSI: Cooler Atlantic, Waning La Nina Suggest Relatively Tame 2012 Tropical Season ( English ) WSI Corporation. Retrieved April 11, 2012.
-
↑ FORECAST OF ATLANTIC HURRICANE ACTIVITY FOR OCTOBER 2005 AND SEASONAL UPDATE THROUGH SEPTEMBER ( English , PDF, 1,769,472 bytes; 1.8 MB). Retrieved October 19, 2012.
-
↑ Blake, Franklin: Tropical Storm ALBERTO Tropical Cyclone Update , NHC, May 19, 2012
-
↑ Brennan: Tropical Storm ALBERTO Forecast Discussion 1 , National Hurricane Center, May 19, 2012
-
↑ Pasch: TROPICAL STORM ALBERTO ADVISORY NUMBER 9 , NHC from May 21, 2012
-
↑ Stewart: TROPICAL STORM ALBERTO ADVISORY NUMBER 10 , NHC, May 21, 2012
-
↑ Pasch: TROPICAL STORM ALBERTO ADVISORY NUMBER 12 , NHC from May 22, 2012
-
^ Atlantic graphical weather outlook ( English ) National Hurricane Center. May 23, 2012. Retrieved May 29, 2012.
-
^ Richard Pasch: Special Tropical Weather Outlook (TXT) National Hurricane Center. May 23, 2012. Retrieved May 25, 2012.
-
↑ Michael Brennan: Special Tropical Weather Outlook ( English , TXT) National Hurricane Center. May 24, 2012. Retrieved May 25, 2012.
-
^ A b Todd Kimberlain: Subtropical Storm Beryl Discussion One ( English ) National Hurricane Center. May 26, 2012. Retrieved May 29, 2012.
-
^ Daniel Brown: Tropical Weather Outlook ( English ) National Hurricane Center. June 17, 2012. Retrieved August 22, 2012.
-
↑ Christopher Landsea: Tropical Weather Outlook ( English ) National Hurricane Center. June 18, 2012. Retrieved August 22, 2012.
-
↑ Tropical Storm CHRIS Forecast Discussion Number 1 . National Hurricane Center . June 19, 2012. Retrieved June 20, 2012.
-
↑ Tropical Storm CHRIS Discussion Number 7 , National Hurricane Center from June 21, 2012
-
↑ Dave Roberts: Hurricane Chris Discussion Number 9 ( English ) National Hurricane Center. June 21, 2012. Retrieved August 22, 2012.
-
↑ Dave Roberts: Tropical Storm Chris Discussion Number 9 ( English ) National Hurricane Center. June 21, 2012. Retrieved August 22, 2012.
-
^ John Cangialosi: Tropical Storm Chris Discussion Number 11 ( English ) National Hurricane Center. June 22, 2012. Retrieved August 22, 2012.
-
^ Robbie Berg: Post-tropical cyclone Chris Discussion # 12 ( English ) National Hurricane Center. June 22, 2012. Retrieved August 22, 2012.
-
^ Tropical Depression Nine Discussion 1 , NHC, August 21, 2012.
-
^ Tropical Storm Isaac Discussion 3 , NHC, Aug. 21, 2012.
-
↑ Court cancels 9/11 hearings due to tropical storm , Spiegel Online from August 22, 2012.
-
^ Robbie Berg: Graphical Tropical Weather Outlook for TD11 ( English ) National Hurricane Center. August 22, 2012. Retrieved August 29, 2012.
-
↑ Michael Brennan: Eleven Forecast Discussion # 1 ( English ) National Hurricane Center. August 28, 2012. Retrieved August 29, 2012.
-
↑ Tropical Storm Forecast Discussion KIRK 2 , NHC of August 28, 2012
-
↑ Hurricane “Sandy” raged in eastern Cuba ( memento from October 22, 2013 in the Internet Archive ) , Granma Internacional from October 25, 2012
-
^ Hurricane "Sandy": New York is preparing for a monster storm at Spiegel Online, October 28, 2012 (accessed October 28, 2012).