1998 Atlantic hurricane season
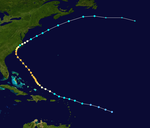
 All the storms of the season | |
| Formation of the first storm |
July 27th |
|---|---|
| Dissolution of the last storm |
December 1 |
| Strongest storm | Mitch - 905 hPa ( mbar ), 155 kn (285 km / h ) |
| Storms | 14th |
| Hurricanes | 10 |
| Severe hurricanes ( Cat. 3+ ) | 3 |
| Total number of victims | over 12,000 |
| Total damage | $ 12.2 billion (1998) |
|
Atlantic hurricane season 1996 , 1997 , 1998 , 1999 , 2000 | |
The 1998 Atlantic hurricane season officially began on June 1 and lasted through November 30, 1998. These dates conventionally limit the time of year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic Ocean ; however, the season didn't actually end until Hurricane Nicole dissolved on December 1st. The major storms of the season were Hurricane Georges and Hurricane Mitch ; Georges caused severe damage in the Caribbean and the Gulf Coast of the United States , killing 603 people, mostly in the Dominican Republic and Haiti . Mitch killed at least 11,000 people, mostly in Honduras and Nicaragua , making it the Atlantic hurricane with the highest number of casualties in modern times. Only the number of victims of the Great Hurricane of 1780 are higher.
Season overview
The season started late because the first system didn't develop until late July and early August was also rather quiet. The rest of the season was quite active until the beginning of October. Five storms reached hurricane status in September and the month was among the most active on record, with seven total. There were also two storms in November, one of which developed into a hurricane. In 1998, a total of seven tropical systems moved overland along the shores of the Atlantic Ocean, four of them as a hurricane. With six tropical cyclones in the Gulf of Mexico , this region was relatively badly affected.
An extremely unusual event occurred during the course of the season when, on September 26, four hurricanes hit the Atlantic basin simultaneously, Georges, Ivan, Karl and Jeanne. Such an encounter has never been recorded since the 1893 Atlantic hurricane season . Even the simultaneous existence of three hurricanes is quite rare; between 1950 and 2005 this occurred only seven times.
Storms
Tropical storm Alex
| Tropical storm | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Duration | July 27th - August 2nd | ||
| intensity | 45 kn (85 km / h ) (1 minute) , 1002 hPa | ||
On July 26, a tropical wave broke off the coast of West Africa and migrated westward. The wave, which was already quite well organized, quickly entered an area with favorable conditions for further development. On July 27th, about 550 km south-southwest of Cape Verde, Tropical Low Pressure Area One was formed. After nearly 24 hours of silence, during which the system maintained poor organization and minimal convection activity, satellite imagery revealed strong convection near the center of the now intensifying low. Around midnight on July 29th, the depression was upgraded to a tropical storm.
Alex stayed on a west-northwest course but struggled with wind shear and a subtropical trough that nearly tore the storm apart. According to the assumptions of the NHC, Alex reached its greatest intensity in the early morning of July 31 with a central air pressure of 1002 hPa and wind speeds of 80 km / h. The wind shear increased, creating near-impossible conditions for further development, and so the system quickly disintegrated as it turned in a northwest direction on August 2nd. Alex was initially the last storm to form in July, as there was no tropical cyclone in the Atlantic basin that month in 1999-2001. The next July tower was Arthur , which formed on July 15, 2002.
Hurricane Bonnie
| Category 3 hurricane | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Duration | August 19 - August 30 | ||
| intensity | 100 kn (185 km / h ) (1 minute) , 954 hPa | ||
Bonnie emerged on August 19 from a poorly organized tropical depression east of the Leeward Islands . The tropical storm moved west-northwest, passed the Antilles arc and reached hurricane strength north of Puerto Rico on August 22nd. At that time, the storm turned northwest, away from the Bahamas and Florida , towards the Carolina States. Bonnie intensified into a Category 3 hurricane with winds of 185 km / h and maintained this strength until shortly before crossing the coast through the Eye on August 27 at Wilmington , North Carolina . Over land, Bonnie continued an east turn that the hurricane had begun above water and came back over the surface of the sea as a tropical storm. So Bonnie was able to intensify again into a minimal hurricane before the system weakened rapidly on the way to the northeast. Bonnie became extra-tropical on August 30 about 450 km south-southeast of Newfoundland .
A measuring station eleven kilometers north of Wilmington recorded a rainfall of 370 mm in connection with Bonnie. The effects of Hurricane Bonnie left three dead and $ 720 million in property damage (1998; $ 1,127 million, adjusted for inflation), most of it in Hampton Roads , Virginia . Bonnie was the third hurricane to hit North Carolina directly in three years.
Tropical Storm Charley
| Tropical storm | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Duration | August 21st - August 24th | ||
| intensity | 60 kn (110 km / h ) (1 minute) , 1000 hPa | ||
Charley formed on August 21 in the western Gulf of Mexico from a tropical wave that broke off the coast of Africa on August 9. The system moved westward and intensified until landfall with winds of 115 km / h near Port Aransas on August 22nd. Charley continued on his way overland until the system broke up on August 25 at Del Rio .
Charley created dangerous flooding in and around Val Verde County , Texas . Thirteen people died in the state and another seven victims were from the south of the Mexican border lies Ciudad Acuña , Coahuila reported. Between 300 and 1500 houses, caravans, businesses and apartments were either damaged or destroyed by the floods. The property damage totaled up to 50 million US dollars (1998; inflation-adjusted US $ 78 million). Del Rio reported around 430mm of rainfall in 24 hours related to Charley. This rainfall was a record for the city and the highest amount from a tropical cyclone in Texas since Tropical Storm Claudette passed through in 1979.
Hurricane Danielle
| Category 2 hurricane | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Duration | August 24th - September 3rd | ||
| intensity | 92.5 kn (170 km / h ) (1 minute) , 960 hPa | ||
Danielle got her name on August 24th when the center of the storm was about 1100 km west-southwest of Cape Verde . The storm moved in a west-northwest direction and intensified into a hurricane. For the next nearly six days, Danielle moved on almost straight. The strength of the hurricane fluctuated between a weak Category 1 hurricane and a strong Category 2 hurricane. As she approached mainland North America , Danielle turned first to the north and then to the northeast. Bonnie had retired to the open ocean after crossing the Carolina coast on August 28th, and the US public's attention was now on Danielle, who was named a Category 2 hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane. Wind scale reached continuous wind speeds of 160 km / h.
Danielle continued to move quickly northwest. However, a trough in the jet stream off the east coast of the United States prevented Danielle from passing over Bermuda . When Danielle got across cooler water because of this, the loss of tropical properties began. Danielle was found extratropical south of Cape Race , Newfoundland on September 4th . At the time, Danielle's wind speeds were still quite similar to those of a hurricane, and the system retained its organization as it moved further east. The extra-tropical storm was pursued until it merged with another system north of Ireland on September 8th .
Danielle caused no loss of life, but the British Isles were clearly feeling the effects of the residual depression on September 6th. Some people had to be rescued from distress at sea. Danielle caused property damage on the west coast of Great Britain ; in Cornwall , people were brought to safety on the coast.
Hurricane Earl
| Category 2 hurricane | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Duration | August 31st - September 3rd | ||
| intensity | 85 kn (155 km / h ) (1 minute) , 985 hPa | ||
Earl became a named system on August 31 in the southwestern Gulf of Mexico. Earl moved in a generally northeastern direction and intensified to hurricane about 230 km southeast of New Orleans on September 2 , although it had a more sub-tropical system-like structure similar to a comma with a dry section. When it landed near Panama City , Florida on September 3, the hurricane was classified in category one. Earl moved overland and went extra-tropical via Georgia before returning to the sea and running his train path across the northern Atlantic. He was finally absorbed by the extratropical remnants of Danielle on September 8th.
Hurricane Earl killed three people. Most of the property damage estimated at $ 79 million (1998; adjusted for inflation, $ 124 million) was caused by the 7.3 m high storm surge . The rainfall when crossing Florida was heavy and reached its highest value about 8 km northeast of Panama City at 416 mm.
Tropical Storm Frances
| Tropical storm | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Duration | September 8th - September 13th | ||
| intensity | 55 kn (100 km / h ) (1 minute) , 990 hPa | ||
Frances formed on September 8th in the western Gulf of Mexico. The system hit south for a moment, but then took a northern and finally northwestern trajectory. The landfall north of Corpus Christi on September 11th came as a moderate tropical storm. This weakened into a tropical depression that migrated northward over land and dissolved north of Dallas , Texas.
The storm was relatively large; the radius of the winds at gale force was 485 km from the center of circulation. A storm surge of up to 7.3 m was recorded on the Texas coast, and some areas saw more than 250 mm of rainfall.
Tropical Storm Frances was by a tornado a direct victim in Lafourche Parish of Louisiana responsible. Heavy rain caused widespread flooding damage in southeast Texas and southwest Louisiana, valued at $ 500 million (1998; $ 783 million when adjusted for inflation).
Hurricane Georges
| Category 4 hurricane | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Duration | September 15 - October 1 | ||
| intensity | 135 kn (250 km / h ) (1 minute) , 937 hPa | ||
A tropical wave broke away from the coast of Africa and organized itself on September 15 about 550 km south-southwest of Cape Verde into a tropical low pressure area. It developed into a tropical storm the next day around 1150 west-southwest of Cape Verde. Georges took a course typical of a Cape Verde-type hurricane and followed an almost straight west-northwest track. Georges intensified steadily and on September 20 almost reached category five on the Saffir-Simpson hurricane wind scale, about 530 km east of Guadeloupe . Georges steadily weakened from then on, but remained on course for the Leeward Islands and the Greater Antilles .
On September 21st, Georges reached the archipelago. He moved across several small Antilles islands, initially via Antigua . After leaving the Leeward Islands behind, Puerto Rico followed and, after a slight intensification, Hispaniola . There it lost some of its strength over the mountains and came back over water as a minimal hurricane. Georges then moved along the north coast of Cuba and crossed Key West , Florida as a Category 2 hurricane. The hurricane turned slightly north over the Gulf of Mexico and crossed the mainland coast at Biloxi on September 28. Over the south of the state of Mississippi , the storm then weakened and slowly meandered east, where it dispersed over northern Florida on October 1.
The damage done by Georges was immense. There were 602 victims directly caused by the hurricane, almost all of them in the Dominican Republic and Haiti . Property damage in and around the United States was estimated at $ 5.9 billion (1998; $ 9.2 billion when adjusted for inflation). The property damage in the other affected areas in monetary terms is not available. Around 185,000 people in the Dominican Republic and another 167,000 in Haiti were left homeless. Cuba reported the destruction of 3,500 houses. Hurricane Georges was a very devastating hurricane, the number of casualties ranks 19th in the 20th century. Georges was one of four active hurricanes on September 26th.
Tropical storm Hermione
| Tropical storm | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Duration | September 17th - September 20th | ||
| intensity | 40 kn (75 km / h ) (1 minute) , 999 hPa | ||
Hermione became a tropical depression a few hundred kilometers south of Louisiana on September 17th. The low circled offshore before moving north. On September 19, it was upgraded to Tropical Storm Hermione, and landed at this intensity near Cocodrie , Louisiana the next day. The storm generated two tornadoes but caused only minor property damage. One person was injured by the effects of the storm.
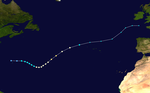
Hurricane Ivan
| Category 1 hurricane | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Duration | September 19 - September 27 | ||
| intensity | 80 kn (150 km / h ) (1 minute) , 975 hPa | ||
A tropical wave just off Cape Verde organized itself into a tropical depression on September 19, which moved in a west-northwest direction before intensifying into Tropical Storm Ivan. Ivan then migrated north and intensified into a hurricane. Little by little, Ivan turned east and passed the Azores just north on September 26th. The next day, Hurricane Ivan lost its tropical properties. Ivan caused no damage and there are no reports of measuring stations on land where Ivan reached the strength of a tropical storm. Ivan was one of four active hurricanes on September 26th.
Hurricane Jeanne
| Category 2 hurricane | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Duration | September 21st - October 1st | ||
| intensity | 92.5 kn (170 km / h ) (1 minute) , 969 hPa | ||
Jeanne developed into a tropical depression about 260 km off the coast of Guinea-Bissau . Jeanne formed further east than any other recorded Atlantic tropical cyclone before, with the exception of Christine 1973 . The system moved in a west-northwest direction and was named Jeanne on September 21 . The storm continued to intensify, becoming a category two hurricane. On September 25th, Jeanne made an arc to the right and two days later Jeanne moved eastward as a weakening tropical storm over the Azores. Leaving the Azores behind, the system became extra-tropical. As an extra-tropical storm, the system reached Portugal with winds at hurricane strength on October 4th and dissolved over Spain . No damage was reported in connection with Jeanne. Jeanne was one of four active hurricanes on September 26th.
Hurricane Karl
| Category 2 hurricane | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Duration | September 23rd - September 28th | ||
| intensity | 92.5 kn (170 km / h ) (1 minute) , 970 hPa | ||
Hurricane Karl generally moved northeast and weakened to a tropical storm as it passed the Azores. Karl became extratropical on September 28th and disbanded south of Ireland the next day. Karl was one of four active hurricanes on September 26th.
Hurricane Lisa
| Category 1 hurricane | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Duration | October 5th - October 9th | ||
| intensity | 65 kn (120 km / h ) (1 minute) , 995 hPa | ||
Lisa formed into a tropical storm with wind speeds of 85 km / h on October 5th, about halfway between Africa and the Leeward Islands . The storm moved essentially north and began accelerating forward on October 9. In the afternoon of that day, the train speed was over 90 km / h, unusually fast for a tropical wind system. Lisa briefly reached the strength of a light hurricane, but then united with a cold front over the northern Atlantic. The next day, the system was no longer identifiable as a storm. Hurricane Lisa had no impact on land or caused any damage at sea.
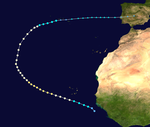
Hurricane Mitch
| Category 5 hurricane | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Duration | October 22nd - November 5th | ||
| intensity | 155.5 kn (290 km / h ) (1 minute) , 905 hPa | ||
With sustained winds of 290 km / h, Hurricane Mitch was one of the strongest Atlantic hurricanes ever observed. Mitch had a major impact in Honduras and Nicaragua, killing more than 11,000 people there. Mitch was thus the most casualty Atlantic hurricane for more than two hundred years and was only beaten by the Great Hurricane of 1780.
The deaths are largely due to flooding, as the slow-moving storm dumped nearly 900mm of precipitation . Tens of thousands of houses have been damaged or destroyed, and more than three million residents have been left homeless. The property damage was estimated at more than five billion US dollars (1998; adjusted for inflation 8).
As a significantly weaker storm, Mitch later crossed the Yucatán Peninsula and Florida before moving to the northern Atlantic and was observed as far north as Great Britain .
Hurricane Nicole
| Category 1 hurricane | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Duration | November 24th - December 1st | ||
| intensity | 75 kn (140 km / h ) (1 minute) , 979 hPa | ||
Nicole was a hurricane that formed late in the season from a nontropical system in the eastern Atlantic. The depression intensified into a tropical storm when it was well west of the Canary Islands on November 24th . The storm moved west-southwest for a few days. Wind shear weakened the system on November 26th, so the NHC initially did not continue the storm warnings. However, the system was able to regenerate and was re-classified as a tropical storm on November 27th.
Nicole then started unexpectedly with a slow turn and followed a north-easterly course towards the Azores as a minimal hurricane on November 30th . However, the storm returned to a northerly migratory direction and was classified as extratropical on December 1st . Hurricane Nicole had no direct land impact and no damage was recorded from Nicole.
Other storms
On April 1, an extensive subtropical circulation developed with a center about 370 km northeast of Antigua. It intensified and built up convection . The system moved steadily northeast and the wind speeds reached storm strength. The system developed tropical properties in that the heat released latently in thunderstorms was the primary energy source of the system. The National Hurricane Center issued a special statement on April 2 about the formation of a tropical disturbance, but the system began to weaken the next day as the convection collapsed. The low continued to weaken on April 4 as it accelerated northeast. Several ships passing through the system reported wind speeds of 65 km / h and wave heights of 7.3 m. The Tropical Prediction Center classified the system as a hybrid low, and the National Hurricane Center reviewed its data to see if it had developed into a subtropical storm. Ultimately, it was decided not to include it in the hurricane database.
Another extensive depression formed over the northwestern Caribbean Sea on October 19. It moved northwest and developed well-organized convection as it crossed the Yucatán Peninsula. On October 21, the system recalled the development stages of Hurricane Earl and Tropical Storm Francis, which had developed earlier in the season. A strong cold front in the north pushed the system to the southwest, with convection developing near the circulation center near the ground. Despite the effects of the cold front, the system organized itself better, so that a reconnaissance flight into the low-pressure area was scheduled. On October 23, the system moved across the coast near Veracruz before the hurricane hunters could reach the low pressure area. The low weakened over mainland Mexico and resolved on October 24th. The nature of the system is unknown; the state of the organization shortly before landfall suggests tropical characteristics; the interaction with the cold front suggests non-tropical properties. Ultimately, the Tropical Prediction Center classified the system as a hybrid / tropical low.
Season course

Accumulated Cyclone Energy (ACE)
| ACE (10 4 kn 2 ) - storm | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 39.4 | Georges | 8th | 7.45 | Karl |
| 2 | 35.9 | Mitch | 9 | 5.00 | Lisa |
| 3 | 24.8 | Bonnie | 10 | 3.90 | Earl |
| 4th | 23.1 | Danielle | 11 | 2.83 | Alex |
| 5 | 18.8 | Jeanne | 12 | 1.63 | Frances |
| 6th | 9.92 | Ivan | 13 | 0.845 | Charley |
| 7th | 7.63 | Nicole | 14th | 0.565 | Hermione |
| Total = 182 (181.77) | |||||
The table opposite shows the ACE for every storm this year. The ACE describes the energy of a tropical storm by multiplying the maximum wind speed of a storm by its duration, i.e. long-lasting storms as well as strong storms have a high ACE value. Traditionally, the NOAA only records named storms with wind speeds of over 34 knots (63 km / h), but not in phases in which they were classified as subtropical.
Storm names
The following names were used in 1998 to refer to tropical cyclones in the Atlantic basin. The list is identical to the list of names for the 1992 season , with the exception of the name Alex, who replaced Andrew . Unused names are grayed out.
|
|
The names Alex, Lisa, Mitch and Nicole were first used in 1998. The World Meteorological Organization removed two names from the list of tropical cyclones in the spring of 1999 , Georges and Mitch. These were replaced by Gaston and Matthew in the 2004 Atlantic hurricane season .
See also
- 1998 Pacific hurricane season
- 1998 Pacific typhoon season
- 1998 North Indian cyclone season
- Cyclone season in the southwestern index 1997–1998 , 1998–1999
- Australian cyclone seasons 1997-1998 , 1998-1999
- South Pacific cyclone seasons 1997-1998 , 1998-1999
Individual evidence
- ^ Hurricane Charley Preliminary Cyclone Report ( English ) National Hurricane Center. 1998. Retrieved July 12, 2009.
- ↑ a b c Jack Beven: Mariners Weather Log September 1998 – December 1998 ( English , PDF; 3.0 MB) Tropical Prediction Center. 1999. Retrieved February 21, 2007.
- ^ Tropical Storm Lisa Advisory Number 1 ( English ) 1998. Retrieved July 12, 2009.
- ↑ Mitch: The Deadliest Atlantic Hurricane Since 1780 ( English ) National Climatic Data Center. 1998. Archived from the original on July 17, 2012. Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. Retrieved July 10, 2009.
- ↑ a b Tropical Atlantic and Tropical East Pacific Areas: January to April 1998 ( English , PDF; 1.8 MB) In: Mariners Weather Log . NOAA. 1998. Retrieved July 10, 2009.
- ^ A b Gary Padgett: Tropical Weather Summary for April 1998 ( English ) 1998. Retrieved July 12, 2009.
- ^ Gary Padgett: Tropical Weather Summary for October 1998 ( English ) 1998. Retrieved July 12, 2009.
- ↑ 2007 Atlantic Ocean Tropical Cyclones . NOAA . June 1, 2007. Archived from the original on December 25, 2007. Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. Retrieved June 3, 2007.