Clotrimazole
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
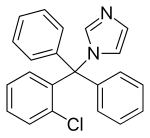
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Clotrimazole | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 22 H 17 ClN 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | |||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action |
Inhibition of ergosterol synthesis, damage to the membrane structure |
||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 344.84 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
147-149 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Clotrimazole is a drug , in the form of tinctures , ointments, vaginal - tablets or powders against mycosis is applied (fungal) of the skin. Among the most common of these infections are known as athlete's foot called skin fungus in the toes and vaginal yeast infections . Clotrimazole is considered a broad spectrum antifungal agent , so it is effective against a large number of different fungi .
Clotrimazole was developed at the end of the 1960s by Bayer AG by Karl Heinz Büchel and came onto the market in Germany after approval in 1973 under the Canesten ® brand . For external use and for short-term vaginal use, clotrimazole preparations are available in Germany without a prescription . Generics are numerous .
history
Clotrimazole was developed between 1967 and 1969 in the research department of Bayer AG under the name Bay b 5097 . Between 1970 and 1972, experimental and clinical studies on efficacy and tolerability were published. Relevant U.S. Patents 3,660,576 and 3,660,577 were issued on May 2, 1972. In 1973 the first drug based on clotrimazole was approved in Germany under the brand name Canesten ® . The first approved dosage forms included a cream, a solution and vaginal tablets. Four years later it was released as a drug without a prescription due to its good tolerability. In the early 1980s, the mechanism of action was elucidated in several studies.
Even today, clotrimazole is still the agent of choice and reference substance for the treatment of most skin fungal infections.
properties
Pharmacodynamics
On the one hand, clotrimazole works by inhibiting the synthesis of ergosterol , especially the inhibition of the enzyme lanosterol demethylase, which is essential for the intermediate step in the formation of desmethylsterol from lanosterol . Since ergosterol is an important component of the cell membrane of fungi, this effect damages the membrane structure.
On the other hand, clotrimazole binds directly to phospholipids in the cell membrane and in this way also causes disturbances in the membrane structure and a change in the permeability of the membrane. Both effects either inhibit fungal growth at low concentrations of one to five milligrams per liter (fungistatic effect) or at higher concentrations from ten to 20 milligrams per liter to kill the fungi (fungicidal effect).
Furthermore, a stimulation of the immune system , i.e. an immunostimulatory effect, is postulated.
Pharmacokinetics
In experimental studies that clotrimazole after oral administration to about 90 percent was demonstrated absorbed is and within four hours in most tissues distributed. The highest concentrations are measured in adipose tissue , adrenal glands , liver and skin after 25 hours . The inactivation takes place in the liver, excretion to about 90 percent over the bile into the gastrointestinal tract and thus through the feces and to about 10 percent over the urine . The main metabolites are:
- 2-chlorophenyl-4-hydroxyphenyl-phenyl-methane
- 2-chlorophenyl-4-hydroxyphenyl-phenyl-methanol
- 2-chlorophenyl-bis-phenyl-methane
- 2-chlorophenyl-bis-phenyl-methanol
- Benzophenone
toxicology
The lethal dose LD 50 as a measure of the acute toxicity after a single intake is 708 to 761 milligrams per kilogram of body weight for oral intake and 108 to 445 milligrams per kilogram of body weight for intraperitoneal administration for mice and rats . A carcinogenic , i.e. carcinogenic, effect was not observed in long-term experimental studies; an embryotoxic effect was detectable when 100 times the usual therapeutic dose was administered. Clotrimazole is therefore classified as harmful and is therefore marked with H302 ("Harmful if swallowed"). No information is available on the transfer into breast milk .
Chemical properties and synthesis
Clotrimazole is a weak base that is hardly soluble in water and toluene , but readily soluble in acetone , chloroform and ethyl acetate . Optimal stability is guaranteed at a pH value of 7 to 8, a pH value below 5 deactivates the active ingredient through hydrolytic decomposition. The substance is weakly hygroscopic (water-attracting).
The chemical name of clotrimazole according to IUPAC nomenclature is 1 - [(2-chlorophenyl) diphenylmethyl] -1 H -imidazole, the common name is 1- (2-chlorotrityl) imidazole. It belongs to the group of imidazole derivatives . Antimycotics chemically related to clotrimazole are itraconazole and ketoconazole .
The synthesis takes place through a nucleophilic substitution of imidazole ( 1 ) with o - chlorotrityl chloride ( 2 ). The final product clotrimazole ( 3 ) is purified by adding activated charcoal and then pressure filtration . When the acetone solution cools, 3 crystallizes out and is then washed several times with acetone and water.
Ecological aspects
During production and processing, there are no significant releases of clotrimazole into the environment under normal conditions. The discharge into the wastewater , especially through personal hygiene, is estimated at around 17.8 kilograms per day in the entire European Union . There is currently a production facility for clotrimazole in the European Union with an annual production of around ten tonnes, around the same amount is imported into the EU.
Of the standards defined in the EU Technical Guidance Document (TGD), the criteria of persistence ( persistence , half-life in the environment of more than 60 days) and toxicity ( toxicity , crustaceans as the most sensitive level in the food chain ) are met, the criterion bioaccumulation ( bioaccumulation , based on the Bioconcentration Factor for Fish , BCF) is not. Clotrimazole is based on the ratio between estimated environmental concentration ( Predicted Environmental Concentration Concentration No effect (PEC) and estimated Predicted No Effect Concentration , PNEC ) not as a PBT substance classified according to the EU TGD.
Therapeutic use

Clotrimazole is generally considered to be effective and well tolerated for the treatment of fungal infections of the skin. It is equally effective against the three main groups of fungi involved in skin mycoses - dermatophytes (filamentous fungi), yeasts with the most famous representative Candida albicans and molds such as Aspergillus fumigatus , the most common pathogen causing aspergillosis . Clotrimazole does not act against dormant spores in fungi , which distinguishes it from other relevant antifungal substances such as nystatin , for example .
In addition to its main area of use against fungal infections, clotrimazole is also effective against many gram-positive bacteria, so it is used for some skin diseases caused by bacteria, especially combined infections. However, not all gram-positive bacteria are considered sensitive enough to be treated with clotrimazole. In addition, clotrimazole is effective against infections with trichomonads ( Trichomonas vaginalis ). However, it is not considered the drug of choice for this application because it is less effective than, for example, metronidazole . In addition, for an effect against trichomonads in comparison to the application against fungal infections, concentrations that are many times higher are necessary.
Its best known uses include the treatment of athlete's foot and vaginal infections . Other diseases in which clotrimazole is frequently used are, for example, erythrasma caused by bacteria and pityriasis versicolor caused by yeasts . Both cases are harmless, but cosmetically disturbing infections of the top layer of the skin.
The cure rates for treatment with clotrimazole are 85 to 90 percent, depending on the type and location of the infection. There is almost no known significant resistance of clinically relevant fungi to clotrimazole. A notable exception is evidence of resistance in Candida glabrata , a possible causative agent of vaginal infections.
Dosage and dosage forms
The most commonly used dosage forms for clotrimazole are ointments and tinctures to be applied or sprayed onto the affected areas of the skin. Both preparations contain the active ingredient in concentrations of one to two percent. The frequency of application, usually one to three times a day, depends on the severity of the infection and should be agreed with a doctor. Treatment with clotrimazole usually lasts two to four weeks until the infection has ended. Further treatment for one to two weeks is recommended even after the symptoms have subsided. An application in the form of a powder can support the treatment of infections in certain areas, since the drying effect of the powder counteracts the moist environment preferred by fungi.
Side effects and contraindications
Depending on the severity of the infection, skin reddening, itching, burning or skin irritation may temporarily occur during application. Due to certain auxiliary substances in liquid preparations, these must not be used in the area of the eyes, on mucous membranes or in the genital area . In general, clotrimazole should not be applied to open wounds.
Clotrimazole is considered to be the drug of choice for treating fungal infections during and after pregnancy . Use in the first trimester of pregnancy is contraindicated and should generally be avoided, especially in the vaginal area. The same applies to the treatment of fungal infections in the nipple area during breastfeeding .
Interactions
Clotrimazole can reduce the effect of certain other topically applied antibacterial or antifungal substances, especially amphotericin B , nystatin and natamycin . Since the active ingredient is only absorbed through the skin or the mucous membranes to an extent of less than 0.5 percent, and thus in negligibly small amounts , there is no significant absorption into the bloodstream . Relevant interactions with other drugs are therefore not known and also not expected.
Systemic application
For a previously performed systemic application in the form of orally administered tablets , clotrimazole is no longer considered suitable due to side effects in the gastrointestinal tract and a potentially liver-damaging effect. In addition, such use has effects on the cytochrome P450 enzyme complex, a family of foreign substance-degrading enzymes in the liver, in the form of a strong inhibition of certain cytochrome P450 enzymes, in particular the isoform CYP3A4. This inhibition leads to an increase in the plasma level , i.e. the concentration of active substances influenced by CYP3A4 available in the blood, which can lead to increased side effects. Other side effects described after oral ingestion are the urge to urinate and depression . Better tolerated alternatives are now available for the systemic treatment of fungal infections.
Application in veterinary medicine
In veterinary medicine , clotrimazole is also used topically, i.e. for local fungal diseases of the skin ( dermatophytosis ), for sinunasal aspergillosis and for inflammation of the oral mucosa ( stomatitis ) caused by Candida ssp. used. The active ingredient is mainly used in small animals and reptiles . It is well tolerated, local skin irritation with reddening rarely occurs , possibly also blistering , edema and itching. In these cases, the drug must be discontinued.
There are two approved veterinary drugs containing clotrimazole. On the one hand, there is Aurizon ® , which contains the active ingredient in combination with dexamethasone and marbofloxacin . On the other hand, there is Otomax ® , which contains gentamicin and betamethasone in addition to clotrimazole . Both preparations are used to treat ear infections, especially those who are involved with Malassezia pachydermatis .
However, the use of clotrimazole in food-producing animals is not permitted under pharmaceutical law, as the active ingredient is not listed in any appendix to Regulation (EEC) No. 2377/90 on maximum levels for veterinary drug residues in food .
Trade names
Aknecolor (CH), Antifungol (D), Apocanda (D), Candibene (A), Canesten (D, A, CH), Canifug (D), Cloderm (D), Clotrigalen (D), Corisol (CH), Fungiderm (D), Fungizid (D), Fungotox (CH), Gilt (D), Gromazol (CH), Gyno Canesten (CH), Imazol Paste (D, A), KadeFungin (D), Mycofug (D), Myko Cordes (D), Mykofungin (D), Mykohaug (D), Pedikurol (A), SD-Hermal (D), Undex Clotrimazol (CH), Uromykol (D), numerous generics (D, A, CH)
Baycuten (D), Fungidexan (D), Imacort (CH), Imazol (CH), Imazol Creme (D, A), Lotricomb (D), Triderm (CH)
literature
- Gerald K. McEvoy, Jane Miller, Kathy Litvak: AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Bethesda 2006, ISBN 1-58528-142-5 .
- Amber A. Kyle, Mark V. Dahl: Topical therapy for fungal infections , in: American Journal of Clinical Dermatology , 2004 , 5 (6), pp. 443-451, PMID 15663341 .
- Marianne Abele-Horn: Antimicrobial Therapy. Decision support for the treatment and prophylaxis of infectious diseases. With the collaboration of Werner Heinz, Hartwig Klinker, Johann Schurz and August Stich, 2nd, revised and expanded edition. Peter Wiehl, Marburg 2009, ISBN 978-3-927219-14-4 , pp. 255 f.
Web links
- MedlinePlus Drug Information: Clotrimazole (English)
- Entry for clotrimazole at Vetpharm, accessed July 29, 2012.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Data sheet Clotrimazole from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on October 3, 2019 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c Entry on clotrimazole in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM), accessed on June 30, 2015.
- ↑ register information of the German Patent and Trademark Office (DPMA) - Registration Number: 830991
- ↑ M. Plempel, K. Bartmann, KH Büchel, E. Regel: Experimental findings on a new, orally effective antimycotic agent with a broad spectrum of activity , in: Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift , 1969 , 94 , pp. 1356-1367, doi : 10.1055 / s -0028-1111223 .
- ↑ KH Büchel, W. Draber, E. Regel, M. Plempel: Synthesis and properties of clotrimazole and other antifungal 1-triphenylmethylimidazoles , in: Arzneimittel-Forschung / Drug Research , 1972 , 22 , pp. 1260-1272, PMID 4564742 .
- ↑ United States Patent Office: N-Trityl-Imidazoles for treating fungal infections. Inventors: Karl H. Büchel (Leverkusen) and Manfred Plempel (Wuppertal-Elberfeld) for the paint factories Bayer Aktiengesellschaft (Leverkusen). Patent number 3,660,576, issued May 2, 1972.
- ↑ United States Patent Office: N-Trityl-Imidazoles as antifungal agents. Inventors: Karl Heinz Büchel (Leverkusen), Erich Regel (Wuppertal-Kronenberg) and Manfred Plempel (Wuppertal-Elberfeld) for the paint factories Bayer Aktiengesellschaft (Leverkusen). Patent number 3,660,577, issued May 2, 1972.
- ^ IJ Sud, DS Feingold: Mechanisms of action of the antimycotic imidazoles , in: Journal of Investigative Dermatology , 1981 , 76 (6), pp. 438-441, PMID 7017013 .
- ^ OSPAR Commission: Hazardous Substances Series: OSPAR background document on clotrimazole. OSPAR Publication 2005/199, 2005, ISBN 1-904426-38-7 (pdf, English; 184 kB) ( Memento from June 10, 2015 in the Internet Archive ).

