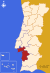
Sines
| Sines | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| Basic data | ||||||
| Region : | Alentejo | |||||
| Sub-region : | Alentejo Littoral | |||||
| District : | Setubal | |||||
| Concelho : | Sines | |||||
| Coordinates : | 37 ° 58 ′ N , 8 ° 52 ′ W | |||||
| Residents: | 13,200 (as of June 30, 2011) | |||||
| Surface: | 152.58 km² (as of January 1, 2010) | |||||
| Population density : | 87 inhabitants per km² | |||||
| politics | ||||||
| Mayor : | Carlos Manuel Jesus Salvador ( PS ) | |||||
| Address of the municipal administration: | Junta de Freguesia de Sines Largo Ramos da Costa nº 21 B 7520–159 Sines |
|||||
| Website: | www.jf-sines.pt | |||||
| Sines district | ||||||
|
||||||
| Residents: | 14,238 (as of June 30, 2011) | |||||
| Surface: | 203.3 km² (as of January 1, 2010) | |||||
| Population density : | 70 inhabitants per km² | |||||
| Number of municipalities : | 2 | |||||
| administration | ||||||
| Administration address: | Câmara Municipal de Sines Largo Ramos Costa 7520-159 Sines |
|||||
| President of the Câmara Municipal: | Nuno Mascarenhas ( PS ) | |||||
| Website: | www.sines.pt | |||||
Sines is a municipality and city in Portugal . 13,225 inhabitants live within the city (as of 2011). The place near the Cabo de Sines is located on a rock and has a historic old town with a castle. Sines is known for its oil refineries and port facilities , the city's most famous son is the seafarer Vasco da Gama (15th century).
history
The coastal area around Sines is rich in finds from the Stone Age through to settlement by the Romans . The Phoenicians , coming from Carthage , also showed their first maritime activities in the area around the Ilha do Pessegueiro and in Sines itself. In 1966, a farmer 12.5 km away from Sines in a stream valley came across the treasure trove of Gaio , which dates from this time. The pieces are now on display in the Sines Archaeological Museum. Sines possibly owes its name to the Celts , because the tribe that lived here called themselves Cinetos, from which today's Sines may have developed via Cines. Other historians see the origin of today's place name in the Latin sinus , for bay.
The Romans were the first to turn Sines into a port for the historic city of Miróbriga near what is now Santiago do Cacém . The Romans also caught fish in the area of the Ilha do Pessegueiro. In addition, a statue of Mars was unearthed in the fortress walls of the castle of Sines and the remains of a fish processing plant were found, which indicate that the present-day urban area was settled by the Romans. The entire area around the castle ruins, which are still preserved today, was inhabited during the Roman Empire. Documents from the Sines Archaeological Museum indicate that there were shipments from Sines to Mediterranean ports in the 1st century. Finds of historical anchors in the beach area of St. Torpes from the 1st and 2nd centuries point in the same direction.
The Visigoths left behind fragments of a basilica that served as a temple in Sines in the 7th century . Parts can still be seen today in the archaeological museum of Sines. The marble sculptures found in the walls of the castle during excavations also date from this period.
The Moors occupied Sines in the early 8th century, but there is little direct evidence of this period. It seems that the city of Sines has been abandoned, only the port was operated by the Arab Moors. The main activities of this period were concentrated in Santiago do Cacém and the capital of the region, Alcácer do Sal .
At the beginning of the 13th century, the area around Sines and Santiago do Cacém was conquered by the Christians during the Reconquista and became part of the Kingdom of Portugal, which had been independent since 1139 . First documents from this period show that in 1362 King Peter I. Sines granted a certain independence from Santiago do Cacém and emphasized its importance as a military fortress and port.
One of the most famous and successful sons of the city was Vasco da Gama (approx. 1469-1524). He went down in Portuguese history as a discoverer and conqueror. His greatest merit was the discovery of the sea route to India, which marked the rise of Portugal to a world power, which now controlled and comprehensively expanded the important trade with the Far East.
By 1486, the area of the medieval town expanded to the mouth of the Mira with the formation of the village of Vila Nova de Milfontes . Even then, the boundaries of today's Sines district were drawn.
The Fort of Sines, like the Fort of Setúbal, was built in the 15th century to protect the coast.
In its long history, the district of Sines has always been shaped by the maritime activities of its residents, and this condition continues to this day. In addition to handling facilities for crude oil and natural gas as well as the bulk cargo coal, there is now also an international container terminal in Sines, which is operated with the participation of the port of Singapore .
At the beginning of the 20th century, the population lived from agriculture and fishing. In addition, the cork industry was of greater importance, and fish canning factories were located in the city area. At the time of the authoritarian Salazar regime in the 1950s, tourism was added, due to the particular beauty of the beaches around Sines.
At the beginning of the 1970s, the government of Marcelo Caetano decided to set up a large port and industrial complex in the vicinity of Sines. In addition to the production of energy from coal, several petrochemical factories and refineries were established, which still shape the area around Sines today. They also wanted to service the mines in the hinterland of the Alentejo with pyrite deposits via Sines. Thanks to the relatively high draft, a deep-water port was built in which large tankers and bulk carriers can also be handled.
The industrialization of Sines profoundly changed the composition of the local population. While in the 1950s and 1960s there was still a large rural exodus to the metropolises, industrialization from 1972 to 1981 resulted in a strong increase in the population of the place (92% increase). In 1976 Sines still had 7,000 inhabitants while in 1984 it was already 10,500. A larger colony of African Cape Verdians (former Portuguese colony ), who settled in Sines, also dates from this period .
The downside of industrialization was the increase in pollution around Sines. To this day, this is a major point of contention between the local population and industry in the region. In some localities around the industrial settlements there was and is always a high rate of cancer. The fact that around 30% of all cork trees in the near and far region are sick or have already died has not yet been scientifically clarified.
The fishermen were also at war with the petrochemical industry. In the 1980s there were several tanker accidents (such as MT Campeón off Sines on August 15, 1980 and the leakage of crude oil from MT Marão in July 1989, and another case in 1990). These had a major impact on the ecological situation of the protected coastal region and on the local population. There were boycotts by fishermen and the first “green” strikes in Portugal. Since 1976 , local governments led by the CDU have been fighting for a “greener” Sines with more environmental friendliness.
The nearby Morgavel dam has existed since 1980.
The previous small town ( Vila ) Sines was elevated to a town ( Cidade ) in 1997 .
Culture and sights
Events and museums
Since the 1990s, the municipality of Sines has been holding a summer cultural festival of world music FMM Festival, the Musicas do Mundo, at the beginning of August, which is highly regarded at home and abroad. Every year, artists from all over the world come together here to create this extraordinary cultural festival within the walls of the old castle.
In addition to the archeology and city museum Museu de Sines , the city has a cultural center, the Centro de Artes de Sines , which opened in 2005 , which has galleries, multimedia libraries and an auditorium for 191 guests, and which also houses the city's historical archive. The museum was designed by the architecture firm Atelier Aires Mateus & Associados of the two architects Francisco and Manuel Mateus and made it into the final selection for the European Architecture Prize in 2007 .
Also worth mentioning is the Centro Cultural Emmerico Nunes , which is dedicated to the painter, illustrator and caricaturist Emmerico Nunes (1888–1968). He lived and worked in Sines, belonged to the first generation of modernist artists in Portugal, and is also considered a pioneer of comic drawing. He worked u. a. for the Meggendorfer-Blätter in Germany, for which he created over 500 drawings.
Historic Buildings
- Ermida de Nossa Senhora das Salas (was expanded by Vasco da Gama)
- Matriz de São Salvador Church (built in the 17th century)
- Church of Espírito Santo ou da Misericórdia (functioned as a hospital church for several centuries and is now a cultural center)
- Ermida from São Bartolomeu
- São Sebastião Chapel (built in the 15th century, served as the castle's soldiers' church)
- Igreja de Nossa Senhora da Soledade (in Porto Covo , a neighboring town)
- Castle of Sines (was extended by King Peter I and is probably the birthplace of Vasco da Gama)
- Fort do Revelim (used to defend Sines, along with the castle)
- Forte do Pessegueiro (was built in the 17th century and is located outside of Sines in front of the Ilha do Pessegueiro, historically a strategic point of the area)
Nature reserve - Parque Natural do Sudoeste Alentejano e Costa Vicentina
The area around Sines is rich in natural beauty. The unique coastline with its beaches, natural dunes and rocky coasts should be mentioned in particular. This coastal landscape was incorporated into the Southeast Alentejo and Costa Vicentina Natural Park . The lake of Sancha, whose banks are also under nature protection, is less quickly accessible for visitors. In addition to the coastal areas, there is the Serra do Cercal in the east , which is of volcanic origin and whose highest point is the summit of Monte Chaos.
The climate of the area can be described as particularly mild despite the great influence of the Atlantic. Because of the high humidity, fog and haze often form. In the area of the Costa Vicentina Natural Park (which extends beyond the district of Sines to Zambujeira do Mar ) there are a number of rare, protected bird species and the barren coastal vegetation under protection. At the Lake of Sancha there is a plant variety - ionopsidium acaule - which is only found in this coastal region.
economy
Sines is an important deep-water port, which is of particular importance for the handling of oil and natural gas. There are various refineries in the surrounding area, which form the heart of southern Portuguese fuel production and storage. From 2004 a container terminal was also created, which is operated by the Singapore port company in cooperation with a Portuguese company. In 2015, 1.332 million TEU ( containers ) were handled here. There is still a sizeable fishing fleet in Sines.
Since 1970, Sines was the location of a large transmission system for short wave of Deutsche Welle . The most distinctive antenna supports were three rotatable V-shaped antennas. The facility was demolished in early 2013.
traffic
The Ramal de Sines railway connected the city to the country's rail network until 1990 . Today there is no longer any passenger traffic, and it is only in operation up to the Repsol refinery. The port is connected to the railway network via the Linha de Sines .
The N261-5, which has been converted into an expressway, leads to the beaches and lakes north of the city. The IP8, which has also been converted into an expressway, surrounds the town and later merges with the IC33 to the east. This means that Sines is connected to the A2 motorway (here also European route 1 ) with the 55 distant connection at Grândola .
Sines Airport , which is currently closed, is also close to the city .
administration
circle
Sines is the administrative seat of a district of the same name ( concelho ) in the Setúbal district . On June 30, 2011, the district had 14,238 inhabitants on an area of 203.3 km². Sines belongs to the statistical sub-region of the Alentejo Littoral .
The neighboring areas are (starting clockwise in the north): Santiago do Cacém, Odemira and the Atlantic Ocean.
The district of Sines consists of only two parishes ( Freguesias ):
| local community | Population (2011) |
Area km² |
Density of population / km² |
LAU code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Porto Covo | 1,038 | 50.72 | 20th | 151302 |
| Sines | 13,200 | 152.58 | 87 | 151301 |
| Sines district | 14,238 | 203.30 | 70 | 1513 |
Population development
| Population in Sines County (1801–2011) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1801 | 1849 | 1900 | 1930 | 1960 | 1981 | 1991 | 2001 | 2011 | |
| 1 766 | 2,632 | [1] | 7 666 | 8 866 | 12 075 | 12 347 | 13 577 | 14 238 | |
[1]: incorporated in the district of Santiago do Cacém
Municipal holiday
- November 24th
Town twinning
-
 Cape Verde : Santa Cruz , Santiago Island
Cape Verde : Santa Cruz , Santiago Island
-
 Portugal : Nisa
Portugal : Nisa
-
 Portugal : Vidigueira
Portugal : Vidigueira
-
 Portugal : Évora
Portugal : Évora
-
 Mozambique : Pemba
Mozambique : Pemba
sons and daughters of the town
- Vasco da Gama (1469–1524), navigator and explorer
- Cláudia de Campos (1859–1916), writer and English scholar
- Arlete Argente Guerreiro (1905–1940), writer
- Rui Pereira (* 1963), journalist, university lecturer and author
- Jorge Manuel Amador Galufo (* 1978), football player
- Ricardo Miguel da Silva Pereira (* 1978), international roller hockey player
Web links
- Map of the Freguesia Sines at the Instituto Geográfico do Exército
Individual evidence
- ↑ www.ine.pt - indicator resident population by place of residence and sex; Decennial in the database of the Instituto Nacional de Estatística
- ↑ a b Overview of code assignments from Freguesias on epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu
- ↑ a b www.ine.pt - indicator resident population by place of residence and sex; Decennial in the database of the Instituto Nacional de Estatística
- ^ João Fonseca: Dicionário do Nome das Terras . 2nd edition, Casa das Letras, Cruz Quebrada 2007, p. 243f ISBN 978-972-46-1730-5
- ^ Festival website (Portuguese and English), accessed on December 3, 2013
- ^ Website of the architectural office , accessed on December 3, 2013
- ↑ Page on architecture ( Memento of the original from December 6, 2013 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link has been inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. on the museum's website, accessed December 3, 2013
- ↑ Page on the exhibition of Nunes' drawings for the Meggendorfer Blätter ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. from the Gulbenkian CAM website , accessed December 3, 2013
- ↑ Sender photos Sines. DXaktuell, accessed on January 6, 2019.
- ↑ Sines station demolished. Radio Eins, February 6, 2013 ( Memento from April 12, 2013 in the web archive archive.today ).
- ↑ www.anmp.pt , accessed on February 3, 2013