The Fiederaralien ( Polyscias ) are a genus of plants within the family of the Araliaceae (Araliaceae). The 150 to 173 species are widespread in the Paleotropic from tropical Africa to the Pacific.
description
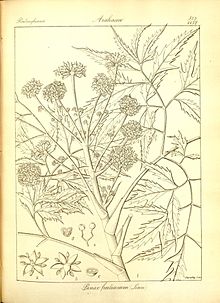
Illustration of
Polyscias fruticosa from
Icones plantarum Indiae Orientalis: or figures of Indian plants , 1843, plate 373
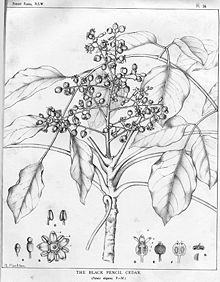
Illustration
Black Pencil Cedar, Panax elegans FvM from Joseph Henry Maiden:
Forest Flora of New South Wales , No. 23, 1904, plate 24 - synonym of
Polyscias elegans
Appearance and leaves
All Fiederaralien species are evergreen, woody plants that grow as small to large trees or shrubs . They are not reinforced and the parts of the plant above ground are often bare. In some species, the vegetative parts of the plant smell pungent aromatic.
The alternate, often heaped on the end of the branches arranged leaves are divided into petiole and leaf blade. The leaf blade is imparipinnate one to five parts. The nodes of the leaf hachis are constricted and it is articulated together with the stalks of the leaflets. The leaflets are entire to notched or serrate. The two stipules sometimes sit on the petiole (intrapetiolar) and are fused with this or form a winged petiole, are reduced to scales or are absent.
Inflorescences and flowers
The flowers are rarely hermaphroditic or mostly unisexual. If the flowers are unisexual, then the Polyscias species are either andromonocial or, less often, dioecious . The terminal, paniculate entire inflorescence is composed of dold -like , head-shaped or spike-like partial inflorescences . Some species have a terminal umbel with hermaphrodite flowers and one or more male flowers standing on the side (Andromonözisch). The flower stalk is articulated along with the base of the ovary; the flowers are rarely sessile.
The flowers are radial symmetry and four or five, rarely up to eight or more, with a double flower envelope . The four or five sepals , rarely up to 8 or more , only form a corrugated rim or four or five, rarely up to 8 or more small calyx teeth are recognizable. The four or five, rarely up to eight or more petals are valvate . There is only one circle with four or five, rarely up to 8 or more free stamens . The dust bags open with a longitudinal slit. Most four or five, rarely up to eight or more carpels are to travel for four or five, rarely up to eight or multi-chamber under constant ovary grown. The durable four or five, rarely up to 8 or more styluses are free or, more rarely, differently fused at the base.
Fruits and seeds
The stone fruits are cylindrical or laterally flattened and contain a seed. The flattened seed has a smooth endosperm .
Systematics and distribution
The genus Polyscias was established in 1775 by Johann Reinhold Forster and Georg Forster in Characteres Generum Plantarum , Volume 63, p. 32. The type species is Polyscias pinnata J.R. Forst. & G.Forst. Synonyms for Polyscias J.R. Forst. & G.Forst. are: Bonnierella R.Vig. , Botryopanax Miq. , Dipanax Seem. , Eremopanax Baill. , Eupteron Miq. , Gelibia Hutch. , Grotefendia Seem. , Indokingia Hemsl. , Irvingia F. Muell. nom. illeg., Kissodendron Seem. , Maralia Thouars , Montagueia Baker f. , Nesodoxa Calest. , Nothopanax Miq. , Oligoscias Seem. , Palmervandenbroekia Gibbs , Peekeliopanax Harms , Pterotropia W.F. Hillebr. , Sciadopanax Seem. , Shirleyopanax Domin , Tieghemopanax R.Vig. , Triplasandra Seem.
According to the publication by Lowry II & Plunkett in 2010, the species of the genera Arthrophyllum Blume , Cuphocarpus Decne. & Planch. , Gastonia Comm. ex Lam. , Munroidendron Sherff , Reynoldsia A.Gray and Tetraplasandra A.Gray also placed in the genus Polyscias .
The genus Polyscias belongs to the subfamily Aralioideae within the family of Araliaceae .
The genus Polyscias was divided into ten subgenera in 2010 ( Polyscias subg. Polyscias , Polyscias subg. Grotenfendia (Seem.) R.Vig. , Polyscias subg. Maralia (Thouars) Lowry & GMPlunkett , Polyscias subg. Arthrophyllum (Blume) Lowry & GMPlunkett , Polyscias Subg. Cuphocarpus (Decne. & Planch.) Lowry & GMPlunkett , Polyscias subg. Tetraplasandra (A.Gray) Lowry & GMPlunkett , Polyscias subg. Eupteron (Miq.) Lowry & GMPlunkett , Polyscias subg. Sciadopanax (Seem.) Lowry , Polyscias subg. Tieghemopanax (R.Vig.) Lowry & GMPlunkett , Polyscias subg. Indokingia (Hemsl.) Lowry & GMPlunkett ).
The genus Polyscias is distributed in the Paleotropic in tropical Africa , Madagascar , Southeast Asia , Australia (about ten species) and in the western Pacific region.
The genus Polyscias contains 150, since 2010 159 and since 2018 173 species:
-
Polyscias aculeata (Decne. & Planch.) Harms (Syn .: Cuphocarpus aculeatus Decne. & Planch. ): It is common in eastern Madagascar in the provinces of Antsiranana , Fianarantsoa , Toamasina and Toliara .
-
Polyscias acuminata (Wight) Seem. : It occurs in southern India and Sri Lanka .
-
Polyscias aemiliguineae Bernardi : It is endemic to Réunion . It wasratedin 1998 in the IUCN's red list of endangered speciesas “Critically Endangered”; renewed monitoring should take place.
-
Polyscias aequatoguineensis Lejoly & Lisowki : It occurs from Equatorial Guinea to Gabon .
-
Polyscias aherniana (Merr.) Lowry & GMPlunkett : It occurs in the Philippines , in northern Borneo and on the northern Moluccas .
-
Polyscias albersiana Harms : It probably only occurs in Tanzania . In 2006 it wasrated inthe IUCN's red list of endangered speciesas "Endangered". In 2006 there were only two confirmed sites in the western Usambara Mountains and at the Ngorongoro Crater ; these two locations are far too far away for the required gene exchange.
-
Polyscias alternifolia (Maingay ex Ridl.) Lowry & GMPlunkett : This endemic occurs only in Johor on the Malay Peninsula.
-
Polyscias amplifolia (Baker) Harms (Syn .: Polyscias gomphophylla (Baker) Harms ): It iswidespreadin Madagascar in the provinces of Antananarivo , Antsiranana, Fianarantsoa, Toamasina and Toliara.
-
Polyscias anacardium Bernardi : It occurs in eastern Madagascar in the provinces of Antsiranana and Toamasina.
-
Polyscias andraerum Bernardi : It occurs in eastern Madagascar in the provinces of Antsiranana and Toamasina.
-
Polyscias angustifolia (Ridl.) Lowry & GMPlunkett : This endemic occurs only in Perak on the Malay Peninsula.
-
Polyscias ariadnes Bernardi : It occurs in eastern Madagascar in the provinces of Antsiranana, Mahajanga and Toamasina.
-
Polyscias ashtonii (Philipson) Lowry & GMPlunkett : It occurs in Borneo in Sarawak and Brunei .
-
Polyscias aubrevillei (Bernardi) Bernardi : This endemic is only known from one site in Madagascar in the Antsiranana province.
-
Polyscias australiana (F.Muell.) Philipson : Of the two varieties, one occurs in New Guinea and one in northern Australia .
-
Polyscias baehniana (Bernardi) Bernardi : It is common in Madagascar in the provinces of Fianarantsoa, Mahajanga and Toliara.
-
Polyscias balansae (Baill.) Harms : It occurs only in New Caledonia .
-
Polyscias balfouriana (André) LHBailey : It occurs in New Guinea and Queensland .
-
Polyscias baretiana Bernardi : It occurs in Madagascar in the provinces of Antsiranana and Toamasina.
-
Polyscias belensis Philipson : It occurs in New Guinea.
-
Polyscias bellendenkeriensis (FMBailey) Philipson : This endemic occurs only in northeastern Queensland.
-
Polyscias bernieri (Baill. Ex Drake) R.Vig. : This endemic occurs only on Réunion .
-
Polyscias biformis (Philipson) Lowry & GMPlunkett : It was first described from New Caledonia in 2010.
-
Polyscias bipinnata (Gibbs) Philipson : This endemic occurs only in western New Guinea.
-
Polyscias bisattenuata (Sherff) Lowry & GMPlunkett : It was rated in 2015 in the IUCN's Red List of Endangered Species as “Critically Endangered”. This endemic occurs only in eastern Kauai . In 2015 only four sites were identified; the largest population has 26 flowering specimens. The stocks are continuously threatened, particularly by invasive plant species.
-
Polyscias boivinii (Seem.) Bernardi : It occurs in Madagascar in the provinces of Antsiranana, Fianarantsoa, Mahajanga and Toliara.
-
Polyscias borbonica Marais : This endemic occurs only on Réunion.
-
Polyscias borneensis Philipson : It occurs from northern Borneo to Palawan .
-
Polyscias botryophora Harms : It occurs only in New Caledonia.
-
Polyscias bracteata (R.Vig.) Lowry : It occurs only in New Caledonia.
-
Polyscias briquetiana (Bernardi) Lowry & GMPlunkett : It occurs in Madagascar in the provinces of Antsiranana, Fianarantsoa, Mahajanga and Toamasina.
-
Polyscias carolorum Bernardi : It occurs in Madagascar in the provinces of Antsiranana, Fianarantsoa, Toamasina and Toliara.
-
Polyscias cenabrei (Merr.) Lowry & GMPlunkett : This endemic occurs only on the Philippine island of Cebu .
-
Polyscias chapelieri (Drake) Harms ex R.Vig. (Syn .: Polyscias tennantii Bernardi ): It occurs in Madagascar in the provinces of Antsiranana, Fianarantsoa, Toamasina and Toliara.
-
Polyscias cissiflora (Baker) Harms : This endemic occurs in Madagascar only in the Toamasina province.
-
Polyscias cissodendron (C.Moore & F.Muell.) Harms : It occurs from the Santa Cruz Islands to New Caledonia and on Lord Howe Island.
-
Polyscias collina (Philipson) Lowry & GMPlunkett : It occurs in Borneo.
-
Polyscias compacta Lowry & GMPlunkett : Only five localities of this endemic are known in Madagascar in the Antsiranana province.
-
Polyscias confertifolia (Baker) Harms : It occurs in Madagascar in the provinces of Fianarantsoa and Toliara.
-
Polyscias coriacea Marais : This endemic occurs only on Réunion.
-
Polyscias corticata Gibbs : This endemic occurs only in Fiji .
-
Polyscias crassa (Hemsl.) Lowry & GMPlunkett : This endemic occurs only in the Seychelles. It wasrated inthe IUCN's Red List of Endangered Speciesas "Vulnerable".
-
Polyscias crenata (Pancher & Sebert) Frodin : It is only found in New Caledonia. It wasrated inthe IUCN's Red List of Endangered Speciesas "Vulnerable".
-
Polyscias culminicola A.C.Sm. : This endemic occurs only on the island of Viti Levu .
-
Polyscias cumingiana (C.Presl) Fern.-Vill. : It occurs from the Philippines to the islands of the southwestern Pacific.
-
Polyscias cussonioides (Drake) Bernardi : It is only known from one site in Madagascar only in the province of Fianarantsoa.
-
Polyscias cutispongia (Lam.) Baker : This endemic occurs only on Réunion.
-
Polyscias dichrostachya Baker : It was rated in 1998 in the IUCN's red list of endangered speciesas “Endangered”. It thrives with a few specimens in the remaining dry forests on Mauritius.
-
Polyscias dioica (Vieill. Ex Pancher & Sebert) Harms : It occurs only in New Caledonia.
-
Polyscias diversifolia (flower) Lowry & GMPlunkett : It occurs from Indochina to western and central Malesia.
-
Polyscias duplicata (Thouars ex Baill.) Lowry & GMPlunkett : It occurs in the Comoros and Madagascar in the provinces of Antananarivo, Antsiranana, Toamasina and Toliara.
-
Polyscias elegans (C.Moore & F.Muell.) Harms : It occurs from southern New Guinea to eastern Australia.
-
Polyscias elliptica (flower) Lowry & GMPlunkett : It occurs on the island of Java and maybe also on Sumatra.
-
Polyscias engganoense (Philipson) Lowry & GMPlunkett : This endemic occurs only in southern Sumatra .
-
Polyscias farinosa (Delile) Harms : It occurs in Ethiopia .
-
Polyscias felicis Bernardi : It occurs in the Comoros.
-
Polyscias filicifolia (C. Moore ex E. Fourn.) LHBailey : It occurs in New Guinea and New Caledonia.
-
Polyscias floccosa (Drake) Bernardi : This endemic occurs in northern Madagascar only in the Antsiranana province.
-
Polyscias florosa Philipson : This endemic occurs only on the island of Luzon .
-
Polyscias flynnii (Lowry & KRWood) Lowry & GMPlunkett : It was rated in 2015 in the IUCN's Red List of Endangered Species as “Critically Endangered”. This endemic occurs only in Kaua'i . In 2015 seven sites were identified with a total of only 30 flowering specimens; in the largest population there are only five flowering specimens. The populations are continuously threatened, especially by invasive plant species.
-
Polyscias fraxinifolia (Baker) R.Vig. : It occurs in Madagascar in the provinces of Antananarivo, Antsiranana, Fianarantsoa , Mahajanga, Toamasina and Toliara.
-
Polyscias fruticosa (L.) Harms : It occurs in Malesia , New Guinea, New Caledonia, in the Bismarck Archipelago and in Queensland.
-
Polyscias fulva (Hiern) Harms : It occurs in tropical Africa and on the southwestern Arabian Peninsula .
-
Polyscias gracilis Marais : It was rated "Critically Endangered" in the IUCN's 1998 red list of endangered species; renewed monitoring should take place. This endemic occurs only at three localities on Mauritius . In 1998 only 10 flowering specimens were found.
-
Polyscias gruschvitzkii Bernardi : It was first described in 1971 and is only known of the type material that originates in Madagascar from the Toamasina province.
-
Polyscias guilfoylei (W.Bull) LHBailey : It occurs in eastern Malesia, New Guinea, the Bismarck Archipelago, New Caledonia, Vanuatu and the Santa Cruz Islands .
-
Polyscias gymnocarpa (Hillebr.) Lowry & GMPlunkett : It was rated “Critically Endangered” in the IUCN's 1998 red list of endangered species; renewed monitoring should take place. This endemic occurs only in the Koolau Mountains on Oahu . In 1998 only 16 sites were identified, each with a few flowering specimens. The populations are continuously threatened, especially by invasive plant species.
-
Polyscias havilandii (Ridl.) Lowry & GMPlunkett : This endemic occurs only in Sabah .
-
Polyscias hawaiensis (A.Gray) Lowry & GMPlunkett : It is found in Hawaii.
-
Polyscias heineana Bernardi : Fewer than five sites are known of this endemic from Madagascar only from the Toamasina province.
-
Polyscias humbertiana (Bernardi) Lowry & GMPlunkett : Fewer than five locations are known of this endemic from Madagascar only from the province of Antsiranana.
-
Polyscias jackiana (G.Don) Lowry & GMPlunkett : It occurs from the Andaman and Nicobar Islands to western and central Malesia. Bis
-
Polyscias jacobsii Philipson : It occurs in Papua New Guinea .
-
Polyscias javanica Koord. & Valeton : It occurs from eastern Java to the Lesser Sunda Islands .
-
Polyscias joskei Gibbs : It occurs in Fiji.
-
Polyscias kalabenonensis Lowry & Callm. : It was first described in 2009. This rare endemic occurs in Madagascar only from the Antsiranana province.
-
Polyscias kavaiensis (H.Mann) Lowry & GMPlunkett : It occurs in Hawaii.
-
Polyscias kikuyuensis Summerh. : It occurs in Kenya . It wasrated inthe IUCN's Red List of Endangered Speciesas "Vulnerable".
-
Polyscias kivuensis Bamps : It occurs only in the eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo .
-
Polyscias kjellbergii (Philipson) Lowry & GMPlunkett : This endemic occurs only in southeastern Sulawesi .
-
Polyscias lancifolia (Drake) R.Vig. : Less than five locations are known of this endemic from Madagascar only from the province of Fianarantsoa.
-
Polyscias lantzii (Drake) R.Vig. : Less than five sites are known in Madagascar in the provinces of Fianarantsoa and Toamasina.
-
Polyscias lanutoensis ( upper right ) Lowry & GMPlunkett : This endemic occurs only in Samoa .
-
Polyscias leandriana (Bernardi) Lowry & GMPlunkett : Fewer than five locations are known of this endemic from Madagascar only from the province of Antsiranana.
-
Polyscias lecardii (R.Vig.) Lowry : It occurs only in New Caledonia.
-
Polyscias ledermannii Harms : It occurs in New Guinea.
-
Polyscias letestui C. Norman : It occurs from Gabon to Angola .
-
Polyscias lionnetii (F.Friedmann) Lowry & GMPlunkett In 2011 it was rated “Critically Endangered” in the IUCN's red list of endangered species. This endemic occurs only on the island of Mahé , which belongs to the Seychelles. In 2011 only one location was determined, there are only two flowering specimens. The population is continuously threatened, especially by invasive plant species.
-
Polyscias lucens (Craib) Lowry & GMPlunkett : It occurs in Thailand .
-
Polyscias lydgatei (Hillebr.) Lowry & GMPlunkett : This endemic occurs only on the Hawaiian island of Oahu.
-
Polyscias macgillivrayi (Benth.) Harms : It occurs from New Guinea to the islands of the western Pacific.
-
Polyscias mackeei Lowry & GMPlunkett : It only occurs in New Caledonia.
-
Polyscias macrantha (Philipson) Lowry & GMPlunkett : It occurs in New Guinea.
-
Polyscias macrocarpa (Philipson & Bui) Lowry & GMPlunkett : It occurs in Laos .
-
Polyscias madagascariensis (Seem.) Harms : It occurs in Madagascar in the provinces of Antananarivo, Fianarantsoa and Toamasina.
-
Polyscias maraisiana Lowry & GMPlunkett : It wasfirst describedin 2010 from Mauritius .
-
Polyscias maralia (Schult.) Bernardi : It occurs in Madagascar in the provinces of Antsiranana, Fianarantsoa and Toamasina.
-
Polyscias marchionensis (F.Br.) Lowry & GMPlunkett : It is only found in the Marquesas Islands .
-
Polyscias mauritiana Marais : It wasratedin 1998 in the IUCN's red list of endangered speciesas "Endangered". This endemic occurs only in Mauritius .
-
Polyscias mayottensis Lowry, O. Pascal & Labat : This endemic occurs only on the Comoros island of Mayotte .
-
Polyscias meliifolia (Craib) Lowry & GMPlunkett : It occurs in Thailand .
-
Polyscias microbotrys (Baill.) Harms : It occurs only in New Caledonia.
-
Polyscias mollis (Benth.) Harms (Syn .: Polyscias macdowallii (F.Muell.) Domin ): This endemic occurs only in northeastern Queensland.
-
Polyscias montana (Ridl.) Lowry & GMPlunkett : It occurs only on the Malay Peninsula .
-
Polyscias multibracteata (Baker) Harms (Syn .: Polyscias bakeriana (Drake) R.Vig. ): It occurs in Madagascar in the provinces of Antananarivo, Antsiranana, Fianarantsoa , Mahajanga, Toamasina and Toliara.
-
Polyscias multijuga (A.Gray) Harms : It occurs from Norfolk Island to islands in the southwestern Pacific.
-
Polyscias muraltiana Bernardi : This endemic occurs in Madagascar in the provinces of Antsiranana and Toamasina.
-
Polyscias murrayi (F.Muell.) Harms : It occurs in the Australian states of eastern Queensland, New South Wales and Victoria .
-
Polyscias myrsine Bernardi : It occurs in Madagascar in the provinces of Antananarivo, Antsiranana, Fianarantsoa, Mahajanga, Toamasina and Toliara.
-
Polyscias neraudiana (Drake) Harms ex R.Vig. : It was rated in 1998 in the IUCN's Red List of Endangered Species as “Critically Endangered” = “threatened with extinction”; renewed monitoring should take place. This endemic occurs only in Mauritius . In 1998 only one location was determined, there are said to be fewer than 15 flowering specimens. The population is continuously threatened, especially by invasive plant species.
-
Polyscias nodosa (flower) Seem. : It occurs from Java to the Solomon Islands and northeast Queensland.
-
Polyscias nossibiensis (Drake) Harms (Syn .: Polyscias hildebrandtii (Drake) Harms , Polyscias lokobensis (Drake) Harms ex R. Vig. ): It occurs in northern Madagascar in the provinces of Antsiranana and Mahajanga.
-
Polyscias nothisii Lowry : It was rated in 2007 in the IUCN's red list of endangered speciesas "Endangered". This endemic occurs only in New Caledonia . Only five isolated sites with only a few flowering specimens are known.
-
Polyscias oahuensis (A.Gray) Lowry & GMPlunkett : It is found in Hawaii.
-
Polyscias obtusifolia Frodin : It was described in 2004 using a cultivated specimen that comes from Java.
-
Polyscias ornifolia (Baker) Harms : It occurs in Madagascar in the provinces of Antananarivo, Antsiranana, Fianarantsoa, Mahajanga, Toamasina and Toliara.
-
Polyscias otopyrena (Baill.) Lowry & GMPlunkett : It occurs only in New Caledonia.
-
Polyscias pachypedicellata Lowry & Callm. : It was first described in 2009 from Madagascar from the Antsiranana province.
-
Polyscias pacifica (Philipson) Lowry & GMPlunkett : It occurs in Maluku and in the Bismarck Archipelago, including the Admiralty Islands within the Lord Howe Archipelago.
-
Polyscias palmervandenbroekii Bernardi : This endemic occurs only in western New Guinea.
-
Polyscias pancheri (Baill.) Harms : It occurs only in New Caledonia.
-
Polyscias paniculata (DC.) Baker It was rated in the IUCN's Red List of Endangered Species in 2000 as “Critically Endangered”; renewed monitoring should take place. This endemic occurs only in Mauritius . In 2000, only one site was determined, there are said to be fewer than 50 flowering specimens. There are no recent reports from the further described site. The stocks are continuously threatened, particularly by invasive plant species.
-
Polyscias papyracea (Philipson) Lowry & GMPlunkett : This endemic occurs only in eastern Sumatra.
-
Polyscias pentamera (Baker) Harms : It occurs in Madagascar in the provinces of Antananarivo and Toamasina.
-
Polyscias philipsonii Bernardi : This endemic occurs only in western New Guinea.
-
Polyscias pinnata J.R. Forst. & G.Forst. : It is native to islands in the southwestern Pacific. It is a neophyte in some tropical areas.
-
Polyscias pleiosperma (A.Gray) Lowry & GMPlunkett : This endemic occurs only in Samoa .
-
Polyscias prolifera (Philipson) Lowry & GMPlunkett : It was rated in 1998 in the IUCN's red list of endangered speciesas "Vulnerable"; renewed monitoring should take place. It is only known from two collections in the Kuper Mountain Range in the Morobe Province of Papua New Guinea.
-
Polyscias pulgarensis (Elmer) Lowry & GMPlunkett : It was rated in 1998 in the IUCN's red list of endangered speciesas "Vulnerable"; renewed monitoring should take place. This endemic occurs only at altitudes above 1200 meters in the upper area of Mt. Pulgar on the island of Palawan .
-
Polyscias purpurea C.T.White : It is only found in Queensland.
-
Polyscias quintasii Exell : It was rated in 1998 in the IUCN's red list of endangered speciesas "Endangered". This endemic occurs only on the islands of Sao Tomé and Principe . Only a few sites are known.
-
Polyscias racemosa (CNForbes) Lowry & GMPlunkett : It was rated in 2016 in the IUCN's Red List of Endangered Species as “Critically Endangered”. This endemic occurs only on the Hawaiian island of Kaua'i at altitudes of 142 to 450 meters. Eleven sites were identified in 2016; Most sites contain only one or two, in the largest population 45 flowering specimens; In 2016 there were 110 flowering specimens. The stocks are continuously threatened, particularly by invasive plant species.
-
Polyscias rainaliorum Bernardi : There are only five known sites in Madagascar in the provinces of Fianarantsoa and Toliara.
-
Polyscias reineckei Harms : This endemic occurs only in Samoa.
-
Polyscias repanda (DC.) Baker : It occurs on islands in the western Indian Ocean.
-
Polyscias revoluta Lowry & GMPlunkett : It was first described in 2010 and occurs in Sarawak and Kalimantan on Borneo.
-
Polyscias richardsiae Bamps : It occurs in Tanzania .
-
Polyscias rivalsii Bernardi : This endemic occurs only on the island of Réunion .
-
Polyscias rodriguesiana (Marais) Lowry & GMPlunkett : It was rated in 1998 in the IUCN's red list of endangered speciesas “Critically Endangered”; renewed monitoring should take place. This endemic occurs only on the island of Rodrigues , which belongs to Mauritius. In 1998 fewer than 50 flowering specimens were found. Young plants were successfully planted in suitable habitats.
-
Polyscias roemeriana Harms : It occurs in New Guinea.
-
Polyscias royenii Philipson : It occurs in Papua New Guinea.
-
Polyscias rubiginosa (Ridl.) Lowry & GMPlunkett : This endemic occurs only in Sarawak .
-
Polyscias rufosepala (Ridl.) Lowry & GMPlunkett : This endemic occurs only in Sarawak.
-
Polyscias sambucifolia (Sieber ex DC.) Harms : It is common in the Australian states of eastern New South Wales , southeastern Queensland , eastern and southern Victoria and Tasmania .
-
Polyscias samoensis (A.Gray) Harms : It occurs in Vanuatu, Samoa and Tonga.
-
Polyscias sandwicensis (A.Gray) Lowry & GMPlunkett : It is found in Hawaii.
-
Polyscias schmidii Lowry : This endemic occurs only in Vanuatu .
-
Polyscias schultzei Harms : It occurs from the Moluccas to New Guinea.
-
Polyscias scopoliae (Baill.) Lowry : It occurs only in New Caledonia.
-
Polyscias scutellaria (Burm. F.) Fosberg : It occurs on the Moluccas, in New Guinea, on the Solomon Islands, on the Santa Cruz Islands and in Vanuatu.
-
Polyscias Sechellarum Baker : It wasratedin 2007 in the IUCN's red list of endangered speciesas "Vulnerable". It occurs only in Seychelles on the islands of Mahé , Silhouette , Praslin , La Digue , Curieuse and Félicité .
-
Polyscias serratifolia (Miq.) Lowry & GMPlunkett : It occurs on Sumatra, Borneo, Java, the Moluccas, Philippines, the Lesser Sunda Islands, Sulawesi, New Guinea and the Solomon Islands.
-
Polyscias sessiliflora Marais : This endemic occurs only on Réunion.
-
Polyscias sleumeri Philipson : This endemic occurs only in western New Guinea.
-
Polyscias sorongensis Gibbs : This endemic occurs only in western New Guinea.
-
Polyscias spectabilis (Harms) Lowry & GMPlunkett (Syn .: Gastonia spectabilis (Harms) Philipson , Gastonia boridiana Harms ): This new combination took place in 2010. It occurs from Papuasia to the Santa Cruz Islands and northeastern Queensland.
-
Polyscias stonei (A.-L.Lim) Lowry & GMPlunkett : It occurs on the Malay Peninsula.
-
Polyscias stuhlmannii Harms : It wasratedin 2006 in the IUCN's red list of endangered speciesas "Endangered". It occurs in Tanzania in seven to eight isolated sites, each with a relatively large number of specimens. There are three collections from southern Kenya, but it has not been found there since 1953.
-
Polyscias subcapitata Kaneh. : This endemic occurs only on the Carolines .
-
Polyscias tafondroensis (Drake) R.Vig. : It occurs in Madagascar in the provinces of Antsiranana and Toamasina.
-
Polyscias tahitensis (Nadeaud) Harms : It was rated in 1998 in the IUCN's red list of endangered species as "Critically Endangered". It only occurs on the Society Islands of Raiatea and Tahiti .
-
Polyscias terminalia Bernardi : There is only one known site of this endemic in Madagascar in the Antsiranana province.
-
Polyscias thailandica Lowry & GMPlunkett : It occurs in Thailand.
-
Polyscias tripinnata Harms : It occurs in Madagascar in the provinces of Antananarivo, Fianarantsoa, Mahajanga, Toamasina and Toliara.
-
Polyscias verrucosa (Seem.) Lowry & GMPlunkett : This endemic occurs only in Tahiti .
-
Polyscias verticillata B.C. Stone : It occurs from the Bismarck Archipelago to the Solomon Islands.
-
Polyscias vieillardii (Baill.) Lowry & GMPlunkett : The two varieties are only found in New Caledonia .
-
Polyscias vogelkopensis Philipson : This endemic occurs only in western New Guinea.
-
Polyscias waialealae (Rock) Lowry & GMPlunkett : It was rated in 2016 in the IUCN's Red List of Endangered Speciesas “Endangered”. This endemic occurs only on the Hawaiian island of Kaua'i. In 2016, a total of around 33,500 flowering specimens were found at the only five sites.
-
Polyscias waimeae (Wawra) Lowry & GMPlunkett : It was rated in 2016 in the IUCN's red list of endangered speciesas "Endangered". This endemic occurs only on the Hawaiian island of Kaua'i. In 2016, a total of around 18,000 flowering specimens were found at the only three sites.
-
Polyscias weinmanniae (Baill.) Harms : It occurs only in New Caledonia.
-
Polyscias willmottii (F.Muell.) Philipson : This endemic occurs only in northeastern Queensland.
-
Polysciaswohlhauseri Lowry & Callm. : This endemic is known from at most five localities and occurs in Madagascar only in the Antsiranana province. It is rated as "Critically Endangered".
-
Polyscias zanthoxyloides (Baker) Harms : It occurs in Madagascar in the provinces of Antananarivo, Fianarantsoa, Toamasina and Toliara.
-
Polyscias zippeliana (Miq.) Valeton : It occurs in New Guinea (including the Aru Islands) and from the northern Australian Northern Territory to northern and northeastern Queensland.
|
use
Polyscias species are used in traditional medicine in Southeast Asia . Polyscias filicifolia , for example, is described in the official Vietnamese pharmacopoeia as a stimulant and agent for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Polyscias fruticosa is cultivated in China and used as a medicinal plant.
Some Polyscias species, for example Polyscias cumingiana , Polyscias filicifolia , Polyscias fruticosa , Polyscias guilfoylei , Polyscias nodosa , Polyscias scutellaria , and their varieties are used in tropical areas as ornamental plants in parks and gardens, for example as a hedge. Some species, for example Polyscias balfouriana , Polyscias filicifolia , Polyscias scutellaria , Polyscias guilfoylei, and Polyscias fruticosa and their varieties, are used as indoor plants . Some varieties of Polyscias balfouriana and Polyscias fruticosa can tolerate light frost (around −1 ° C).
The resin from Polyscias sambucifolia is used.
swell
- Qibai Xiang, Porter P. Lowry: Araliaceae. : Polyscias , p. 472 - online with the same text as the printed work , In: Wu Zheng-yi, Peter H. Raven, Deyuan Hong (ed.): Flora of China. Volume 13: Clusiaceae through Araliaceae , Science Press and Missouri Botanical Garden Press, Beijing and St. Louis 2007, ISBN 978-1-930723-59-7 .
- Gregory M. Plunkett et al .: The phylogenetic status of Polyscias (Araliaceae) based on nuclear its sequence data. In: Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden , Volume 88, 2001, pp. 213-230.
Individual evidence
-
↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n
Qibai Xiang, Porter P. Lowry: Araliaceae. : Polyscias , p. 472 - online with the same text as the printed work , In: Wu Zheng-yi, Peter H. Raven, Deyuan Hong (ed.): Flora of China. Volume 13: Clusiaceae through Araliaceae , Science Press and Missouri Botanical Garden Press, Beijing and St. Louis 2007, ISBN 978-1-930723-59-7 .
-
^ A b c d e f
MJ Henwood, RO Makinson: Polyscias in: New South Wales Flora Online . (English)
-
↑ a b c d Polyscias at Tropicos.org. In: Araliaceae . Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louis
-
↑ Polyscias at Tropicos.org. Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louis, accessed April 18, 2015.
-
^ A b c Polyscias in the Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN), USDA , ARS , National Genetic Resources Program. National Germplasm Resources Laboratory, Beltsville, Maryland. Retrieved April 18, 2015.
-
↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc bd be bf bg bh bi bj bk bl bm bn bo bp bq br bs bt bu bv bw bx by bz ca cb cc cd ce cf cg ch ci cj ck cl cm cn co cp cq cr cs ct cu cv cw cx cy cz da db dc dd de df dg dh di dj dk dl dm dn do dp dq dr ds dt du dv dw dx dy dz ea eb ec ed ee ef eg eh ei ej ek el em en eo ep eq er es et eu ev ew ex ey ez fa fb fc fd fe ff fg fh fi fj fk fl fm fn fo fp fq fr fs Rafaël Govaerts (Ed.): Polyscias. In: World Checklist of Selected Plant Families (WCSP) - The Board of Trustees of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew . Retrieved May 1, 2018.
-
↑ a b c
Porter Prescott Lowry II, Gregory M. Plunkett: Recircumscription of Polyscias (Araliaceae) to include six related genera, with a new infrageeric classification and a synopsis of species. In: Plant Diversity and Evolution. Volume 128, No. 1–2, 2010, pp. 55–84, DOI: 10.1127 / 1869-6155 / 2010 / 0128-0003 , PDF file. ( Memento of the original from March 4, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
 @1@ 2Template: Webachiv / IABot / www.uhh.hawaii.edu
@1@ 2Template: Webachiv / IABot / www.uhh.hawaii.edu
-
↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao Polyscias at Tropicos.org. In: Catalog of the Vascular Plants of Madagascar . Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louis
-
↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad Search for “Polyscias” in the IUCN's Red List of Endangered Species .
-
↑
Kee-Yoeup Paek, Hosakatte Niranjana Murthy, Jian-Jiang Zhong: Production of Biomass and Bioactive Compounds Using Bioreactor Technology . Springer, 2014, p. 709 ( full text in Google Book Search).
-
↑ a b
Gordon Cheers (Ed.): Botanica. The ABC of plants. 10,000 species in text and images . Könemann Verlagsgesellschaft, 2003, ISBN 3-8331-1600-5 (therein page 696).
-
↑ Some Polyscias species and varieties used as ornamental plants at Dave's Garden . (English)
-
↑ Polyscias sambucifolia in Plants For A Future
Web links




























