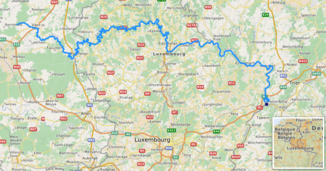
Sour (Moselle)
|
Sauer Sûre |
||
|
Course of the Sauer ( interactive map ) |
||
| Data | ||
| Water code | EN : 262 | |
| location |
Ardennes
Belgium (B) Germany (D) Luxembourg (L) |
|
| River system | Moselle | |
| Drain over | Moselle → Rhine → North Sea | |
| Headwaters | in the Ardennes in the municipality of Libramont-Chevigny at the Planchipont farm ( B ) | |
| Source height | approx. 510 m | |
| muzzle | between Wasserbilligerbrück ( D ) and Wasserbillig ( L ) in the Moselle Coordinates: 49 ° 42 ′ 49 ″ N , 6 ° 30 ′ 24 ″ E, 49 ° 42 ′ 49 ″ N , 6 ° 30 ′ 24 ″ E |
|
| Mouth height | approx. 133 m above sea level NHN | |
| Height difference | approx. 377 m | |
| Bottom slope | approx. 2.2 ‰ | |
| length | 173 km | |
| Catchment area | 4259 km² | |
| Discharge at the Bollendorf A Eo gauge: 3,221.8 km² |
NNQ (Jul 27, 1964) MNQ 1959–2007 MQ 1959–2007 Mq 1959–2007 MHQ 1959–2007 HHQ (Jan 3, 2003) |
2.6 m³ / s 7.06 m³ / s 40.9 m³ / s 12.7 l / (s km²) 417 m³ / s 895 m³ / s |
| Outflow A Eo : 4259 km² at the mouth |
MQ Mq |
53.8 m³ / s 12.6 l / (s km²) |
|
The Sauer in Echternach |
||
The Sauer ( French Sûre ) is a 173 km long left tributary of the Mosel in Belgium , Luxembourg and Germany .
The very winding and important river of the southern Ardennes , called Ösling in Luxembourg , is the largest left tributary of the Moselle with a water flow of almost 54 m³ / s on average. Its catchment area is 4259 km².
geography
course
The Sûre rises as Sûre in the south-east of Belgium ( province of Luxembourg ) in the Ardennes, the western part of the Rhenish Slate Mountains . Its source area is in the eastern municipality of Libramont-Chevigny , east of the Planchipont farm and around 7 km (as the crow flies ) north of the A26 and A4 motorway triangle at an altitude of around 510 m .
From there the Sauer flows eastwards and crosses the Belgian-Luxembourg border at Martelange . On its way through the mountainous north of Luxembourg (the Ösling ) it runs through the Obersauer reservoir west of Esch -Sûre (French Esch-sur-Sûre) in the center of the Obersauer Nature Park .
Below Erpeldingen the Alzette flows into the Sauer, on which lies just above the Ettelbrück estuary , which forms the small Nordstad region with the district capital Diekirch and the surrounding communities .
In Walldorf (about 30 km southwest of Bitburg ) opens the Our to the sour. The German-Luxembourg border is formed north of this confluence by the Our and south of the Sauer on about 50 km of flow to Wasserbillig . There, in the southern Eifel , the German-Luxembourgish nature park stretches across borders . Part of it is the Luxembourgish Switzerland near Echternach . At Ralingen , 6 km east of Echternach, the main direction of the strongly winding river turns south. The largest tributary of the Sauer, the Prüm, flows into this area from the left .
Finally, the Sauer flows between Wasserbillig ( canton Grevenmacher ; Luxembourg) in the west and Wasserbilligerbrück ( Rhineland-Palatinate ; Germany) in the east at about 133 m above sea level in the Rhine tributary Moselle , which from there, viewed upstream, is part of the German to the southwest -Luxembourg border is. Beyond the estuary lies Oberbillig (Rhineland-Palatinate) on the banks of the Moselle .
Tributaries
The tributaries of the Sauer include - viewed downstream:
- Syrbach ( left ), 4.4 km
- Wiltz ( left ), 45.0 km
- Alzette ( right ), 73.0 km
- Blees ( left ), 20.2 km
- White Ernz ( right )
- Our ( left ), 96.1 km
- Gaybach ( left ), 23.2 km
- Black Ernz ( right )
- Prüm ( left ), 95.0 km
Localities

Villages on the Sauer are - viewed downstream:
- Vaux-sur-Sûre (B)
- Strainchamps (Sauerfeld) (B)
- Bodange (Bödingen) (B)
- Wisembach (Wiesembach) (B)
- Radelange (Rädelingen) (B)
- Martelange (Martelingen) (B)
- Rombach-Martelingen (L)
- Greimelingen (L)
- Insenborn (L)
- Bonnal (L)
- Lultzhausen (L)
- Esch-Sauer (L)
- Dirbach (L)
- Michelau (L)
- Erpeldingen an der Sauer (L)
- Ingeldorf (L)
- Diekirch (L)
- Gilsdorf (L)
- Bettendorf (L)
- Möstroff (L)
- Reisdorf (L)
- Wallendorf (D)
- Wallendorferbrück (L)
- Grundhof (L)
- Dillingen (L)
- Bollendorf (D)
- Bollendorferbrück (L)
- Laufenwehr (D)
- Weilerbach (D)
- Fölkenbach (D)
- Echternach (L)
- Echternacherbrück (D)
- Minden (D)
- Steinheim (L)
- Edingen (D)
- Godendorf (D)
- Rosport (L)
- Ralingen (D)
- Wintersdorf (D)
- Menhir (L)
- Born (L)
- Metzdorf (D)
- Moersdorf (L)
- Mesenich (D)
- Langsur (D)
- Wasserbillig (L)
- Wasserbilligerbrück (D)
history
After the Ardennes offensive of the Wehrmacht , which began in mid-December 1944, collapsed during World War II - due to a lack of fuel and other supplies , among other things - Allied troops carried out a counter-offensive through the Ardennes from January 3 to 28. During the fighting, the Sauer was at times part of the front line.
various
On its way between Wallendorf and Wasserbillig, the Sauer, as well as the Our further north and the Moselle further south , is a condominium under the name Common German-Luxembourgish Territory , that is, the river belongs to the territory of the Federal Republic of Germany over its entire width as well as the territory of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg.
The Sauer often led to floods , which caused great damage in neighboring towns, e. B. 1993, 1995 and early 2003.
In the southern area, the Sauer was flanked by a branch line on each bank: on the Luxembourg side it was the Diekirch – Echternach – Wasserbillig section of the Ettelbrück – Grevenmacher line and on the German side the Nims-Sauertal Railway from Erdorf via Bitburg and Irrel to Igel. Both railways were shut down and demolished in the 1960s.
tourism
The Sauer is important for tourism. The 60 km long Sauer Valley cycle path connects over a dozen villages between Wasserbillig and Ettelbrück. You can go down the Sûre with canoes that can be rented on site. Tours start, for example, in Bollendorf and end in Echternacherbrück .
See also
literature
- Johann Baptist Keune : Sura 4a . In: Paulys Realencyclopadie der classischen Antiquity Science (RE). Volume IV A, 1, Stuttgart 1931, Col. 961 f.
References and comments
- ↑ Map services of the Federal Agency for Nature Conservation ( information )
- ↑ For the height of the mouth of the Sauer, see the height information on / next to the Moselle in the individual record of the map services of the Federal Agency for Nature Conservation : "133.7" just above and "132.2" just below the mouth of the Sauer
- ↑ Level data , at the State Office for the Environment Rhineland-Palatinate (LfU)
- ↑ Added level data from Bollendorf (Sauer), Prümzurlay (Prüm) and Alsdorf-Oberecken (Nims), increased by the remaining catchment area (199 km²) with a low estimated mq of 10, at the State Office for the Environment Rhineland-Palatinate (LfU)
- ↑ Chapter II, Victory in the Ardennes (Summary Report on the Counteroffensive of the Americans), on ibiblio.org (English)
- ^ The last offensive. Chapter VI: Bitburg and the Vianden Bulge (American description of the river crossing), on ibiblio.org (English)
- ↑ Border communities mobilize against floods with EU help , from April 11, 2014, accessed on March 28, 2016, at eu-info.de
Web links
- Map / aerial photo of the Sauer
- Flood warning services:
- Luxembourg , on inondations.lu
- Flood reports for Moselle / Saar / Sauer , on hochwasser-rlp.de
- Sauer , information for anglers, on anglermap.de
Information about the railway on the Sauer:
- The railways in and around Luxembourg , on rail.lu
- The Nims-Sauertalbahn , on nims-sauertal-bahn.de