Welzheimer forest
| Welzheimer forest | |
|---|---|
|
The Welzheimer forest south of the |
|
| Highest peak | Hagberg ( 585.2 m above sea level ) |
| location | Districts Schwäbisch Hall , Rems-Murr-Kreis and Ostalbkreis ; Baden-Württemberg |
| part of | Swabian-Franconian Forest |
| Coordinates | 48 ° 56 ' N , 9 ° 43' E |
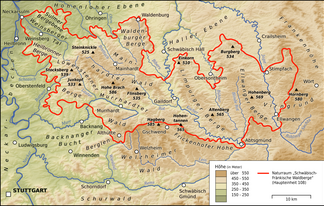
The Welzheimer forest is up to 585.2 m above sea level. NHN high, wooded ridge in the districts of Rems-Murr , Ostalb and Schwäbisch Hall in Baden-Württemberg ( Germany ). It is named after the town of Welzheim in the center of the forest area.
geography
location
The Welzheimer Wald is located almost 38 km east-northeast of Stuttgart and about 45 km southeast of Heilbronn between the Murrhardter Wald and the Kirnberger Wald in the north, the Frickenhofer Höhe in the east-northeast, the Remstal in the south and - with the side valley of the lower Wieslauf - also in the West.
The Welzheimer Wald is one of five forest regions in the Swabian-Franconian Forest Nature Park . As a natural area , however, it is not included in the Swabian-Franconian Forest Mountains bordering in the north or the foreland of the eastern Swabian Alb in the east. Rather, it forms with the Berglen (with the Buocher Höhe ) in the west beyond the Wieslauf, the Remstal (including the lower Wieslauftal) and the Schurwald south of the Rems, the main natural area group Schurwald and Welzheimer Wald .
The Welzheimer Wald is located around Welzheim, Kaisersbach and Alfdorf between Fichtenberg in the north, Gschwend in the northeast, Spraitbach and Durlangen in the east, Mutlangen and Schwäbisch Gmünd in the southeast, Lorch in the south, Plüderhausen , Urbach and Schorndorf in the southwest, Berglen in the west as well Rudersberg and Althütte in the northwest.
Surveys
The surveys of the Welzheimer Forest include - sorted according to height in meters above sea level (NHN):
- Hagberg ( 585.2 m ), with Hagbergturm ; west of Gschwend- Hagkling
- Light oaks ( 554.3 m ), north-north-west of Welzheim - Langenberg
- Hood ( 536.5 m ), directly northeast of Rudersberg - Mannenberg
- Hohbergkopf ( 498.8 m ), northeast of Plüderhausen
- Kelchenberg ( 496.1 m ), west-southwest of Pfahlbronn
- Heuberg ( 476.6 m ), northeast of Urbach
Waters
Welzheimer Forest dehydrate especially on its entire southern edge of the flowing west to the Neckar Rems and on its middle reaches from below Welzheim east to the Neckar tributary Kocher current Lein , but reaches this only beyond the landscape border. Only peripheral areas in the north-west and north are in the catchment areas of the Neckar tributary Murr and the Kocher tributary “Fichtenberger” Rot . Its largest tributary, the Wieslauf, flows to the Rems from the west of the Welzheimer Wald ; from the wide Wieslauftal onwards, smaller northern side valleys, such as those of the Urbach or Walkersbach, line up like the bones of a fish . The Lein, which never flows in the opposite direction for a long stretch north of the Rems, therefore has no tributaries from the south, its water system is comb-like. Its tributaries include the largest on the eastern border of the Welzheimer Forest, the "Gschwender" Rot , a number of smaller flowing waters, but above all another comparatively long third Rot , whose sources lie between Gschwend and Kaisersbach.
The still waters that everyone likes to visit, especially in summer, include the Ebnisee on the uppermost Wieslauf and in the tributary system of the Lein the flood retention basins Aichstruter Reservoir on the southern upper reaches, Leinecksee on the Mittellauf as well as Eisenbach , Hagerwald , Hüttenbühl , Reichenbach and Rehnenmühlsee at the tributaries.
history
By Welzheimer forest for 2005 introduces UNESCO World Heritage levied Upper German-Rhaetian Limes , of from about 150 n. Chr. Between the Danube at Kelheim and the Rhine opposite Bad Breisig a land border of the Roman Empire against the Barbarians formed. The Limes is still clearly visible in the Welzheimer Wald, especially between Lorch and Pfahlbronn and near Ebnisee.
Coming from Aalen in the east, the Limes in the Welzheimer Wald near Lorch turns north and continues via Murrhardt and Mainhardt towards Miltenberg am Main . Between Schwäbisch Gmünd and Lorch, the small Rotenbach (right tributary of the Rems ) marked the border between the Roman provinces of Raetia in the east and Upper Germany in the west. As a result, the Welzheimer forest had a share in both provinces. At Welzheim there is an archaeological park on the former Limes (east fort of the Welzheim fort ).
In 1816 Justinus Kerner published a brief description of the area in the “Morgenblatt”.
economy
Apart from wood processing, the Welzheim forest has hardly any industry. The region is of greatest importance as a local recreation area. The Schwabenpark amusement park is located south of Kaisersbach and north-northeast of Welzheim . In winter, winter sports are sometimes possible in the Welzheim forest.
Transport links
The traffic connection through state roads is good. The federal highways B 298 and B 29 affect the region. The only railway line, the Wieslauftalbahn , was discontinued in the section between Rudersberg and Welzheim in 1980 (passenger traffic) and 1988 (freight traffic). On May 8, 2010, rail traffic for tourist purposes, partly with steam trains, was resumed.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Map services of the Federal Agency for Nature Conservation ( information )
- ↑ Hansjörg Dongus : Geographical land survey: The natural spatial units on sheet 171 Göppingen. Federal Institute for Regional Studies, Bad Godesberg 1961. → Online map (PDF; 4.3 MB)
Web links
- Landscape profile of the BfN
- Schurwald and Welzheimer Wald natural area profile (107) - LUBW (PDF; 9.1 MB; information )