Akrotiri and Dekelia
| Akrotiri and Dhekelia (Western and Eastern) Sovereign Base Areas | |||||
| Akrotiri and Dekelia | |||||
|
|||||
| Official language | English , Greek | ||||
| Capital | Episkopi Cantonment | ||||
| Form of government | British overseas territory | ||||
| Head of state | Queen Elizabeth II | ||||
| Head of government | Administrator James Illingworth | ||||
| surface | 254 km² | ||||
| population | approx. 14,500 including 7,000 Cypriots and 7,500 British military personnel (estimate) |
||||
| Population density | 57 inhabitants per km² | ||||
| currency | Euro (EUR) | ||||
| founding | 1960 | ||||
| National anthem | God Save the Queen | ||||
| Time zone |
UTC + 2 UTC + 3 (March to October) |
||||
| Telephone code | +357 | ||||
| Location of Akrotiri and Dekelia (in red) | |||||
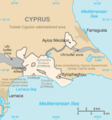
Akrotiri ( Greek Ακρωτήρι , Turkish Agrotur ) 34 ° 35 ' N , 32 ° 59' O and Dekelia ( English Dhekelia , Greek Δεκέλεια , Turkish Dikelya ) 35 ° 0 ' N , 33 ° 45' O are two British military bases on Cyprus . The bases are British territories and formally in English as Sovereign Base Areas SBA , Sovereign Base Areas' called. The administration of the military bases is located in Episkopi Cantonment , the headquarters of the SBAA (Sovereign Base Areas Administration) in Akrotiri .
description
Akrotiri, west of Limassol , covers an area of 123 km². It houses the Episkopi Garrison with an infantry battalion and the Royal Air Force Station Akrotiri military airfield with an SAR helicopter squadron (84th Squadron) and a varying number of combat aircraft. The area also includes a larger salt lake , an Orthodox monastery , a bathing beach and the port of Akrotiri .
Dekelia (east of Larnaka ) is only slightly larger than Akrotiri with 130 km². This is where the Dekelia garrison is located , which houses an infantry battalion and a second, much smaller military airfield, Kingsfield Airfield . To the south is the port of Dhekelia , which supplies the Dhekelia Power Station .
The two bases make up about three percent of the land area of Cyprus. They are subject to British jurisdiction (see Sovereign Base Areas Police ), but are not hermetically sealed from their surroundings (for example there are public road links through British territory). Akrotiri and Dekelia are estimated to be home to 1,300 military personnel and an additional 5,000 British citizens who are either military or civilian employees. As a result of the invasion of the Turkish army in Northern Cyprus in 1974 and other developments, a total of around 7,000 local civilians now live on the grounds of the bases. However, since the use contract concluded with the Republic of Cyprus in 1960 negotiated an exclusively military use (areas inhabited by civilians were excluded from the demarcation and partly form enclaves ), these residents - unlike other residents of British overseas territories - have no right to the British Citizenship . The euro replaced on 1 January 2008, the Cyprus pound as currency.
The status of the two bases was enshrined in the Zurich and London agreements between Great Britain, Greece and Turkey in 1959 : According to this, the two bases were to remain under British sovereignty even after Cyprus was granted independence .
Both bases belong to the customs area of the European Union . Since Cyprus joined the EU, EU law has also been applied in individual areas such as agriculture and the free movement of people. Otherwise, however, they were also excluded from the EU treaties during the EU membership of Great Britain and neither were any of the overseas countries and territories with association status.
history
The military airfield , the Royal Air Force Station Akrotiri, RAF Akrotiri for short, existed before 1959.
In 1957, the Royal Air Force set up the Near East Strike Wing in support of the CENTO alliance , to which four Canberra squadrons were subordinate. In addition, the 56th Squadron, equipped with Lightning , came between 1967 and 1975 . The four Canberra squadrons were replaced in 1969 by two Vulcan squadrons, which could be reinforced if necessary by two more squadrons stationed in the United Kingdom. These were also moved back to England in 1975.
Since 1972 the airfield has been the base of a Search and Rescue helicopter squadron , the 84th Squadron . She used the Whirlwind until the end of 1981 , then the Wessex and, since the beginning of 2003, the Griffin . In addition, fighter planes such as the Tornado have been operating here regularly on a rotation basis for decades .
In the winter months, the Red Arrows aerobatic team uses the airfield for training flights.
Radio reconnaissance
The two military bases play an important role in the military and intelligence service electronic reconnaissance ( SIGINT ). The British agency GCHQ has been working closely with its US counterpart , the National Security Agency (NSA), since the bases were commissioned . The cooperation is based on the UKUSA Security Agreement . The Ayios Nikolaos station already worked as a SIGINT and ELINT station during the Palestine War in 1948, then in 1956 in the Suez Crisis , during the EOKA independence conflict in Cyprus (1955-1959) and during the Bloody Christmas (1963) . In 1967 the stations in Cyprus were involved with SIGINT actions in the Six Day War and in 1973 in the Yom Kippur War . It can be assumed that the information gathered from the Middle East was transmitted to the decision-makers in London and Washington. Radoms with wiretapping technology are located in both Akrotiri and Dekelia.
Over-the- horizon radar PLUTO
The antenna systems of the PLUTO system are located near the salt lake of Akrotiri on an area of 100 m × 200 m. This is an over-the-horizon radar with a transmission power of up to one megawatt. This enables air movements to be observed beyond the horizon as far as Afghanistan , Kazakhstan and Russia. In the past, people in the area have repeatedly complained about the health effects of this system and radio amateurs perceive interference on various shortwave bands.
Transmitters
In addition to an official BBC relay station for the Middle East, there are also various military transmission systems for the medium and short wave range on the systems. It is quite likely that MI6 broadcast the Lincolnshire Poacher numbers through 2008 through the facilities. Various curtain antennas are located on the premises.
Further stations for telecommunications reconnaissance
- RAF Olympos , RAF radar system for air surveillance in the western Middle East, range 1500 to 3000 kilometers.
- CYTA Yeroskipos - Yeroskipos Submarine Cable Station , submarine cable land connection of the Cyprus Telecommunications Authority (CYTA) on the southern tip of Cyprus. The GCHQ monitors the global communication traffic via SEA-ME-WE 3 from the station .
gallery
literature
- Giorgos Georgiou: British Bases in Cyprus and Signals Intelligence. In: Etudes helléniques / Hellenic Studies. Volume 19, No. 2, 2011, p. 121 ff. ( Online ; PDF; 129 kB)
Web links
- Homepage of the SBAs in Cyprus
- CIA World Factbook: SBA Akrotiri (English)
- CIA World Factbook: SBA Dekelia (English)
- Images of the antenna systems (curtain antennas, logarithmic-periodic antennas, radomes)
- Christian Scheib, Roman Tschiedl: Aphrodite's Child - Explorations in contemporary Cyprus ( radio feature ), Radio Ö1 , April 15, 2019
Individual evidence
- ↑ Customs territory. In: Zoll.de. Federal Ministry of Finance , accessed on August 19, 2013 .
- ↑ Consolidated versions of the Treaty on European Union and the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union
- ↑ http://cryptome.org/2012/01/0060.pdf
- ↑ PLUTO II OTH Radar - Signal Identification Wiki. In: www.sigidwiki.com. Retrieved January 16, 2017 .
- ↑ "Spynumbers". Profile of The Lincolnshire Poacher http://www.spynumbers.com/profiles/index.html May 25, 2008.