Apataki
| Apataki | ||
|---|---|---|
| ISS photo by Apataki | ||
| Waters | Pacific Ocean | |
| archipelago | Tuamotu Archipelago | |
| Geographical location | 15 ° 27 ′ S , 146 ° 19 ′ W | |
|
|
||
| Number of islands | 28 named | |
| Main island | Niutahi | |
| Land area | 20 km² | |
| Lagoon area | 706 km² | |
| Residents | 492 (2012) | |
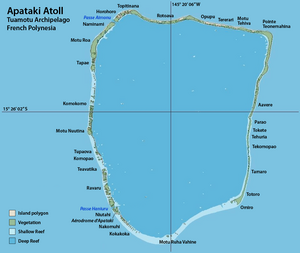
| Map of Apataki | ||
Apataki is a coral atoll in French Polynesia . Geographically, Apataki belongs to the Palliser Islands , which in turn are part of the Tuamotu Archipelago in the Pacific Ocean . Administratively, Apataki forms one of the three sub-municipalities ( Commune associée ) of the municipality of Arutua . The very large lagoon of the atoll can be reached through two passages. 350 people live on the atoll (as of 2012 census). At the 2007 census there were 492. The largest place is Niutahi on the Motu of the same name in the southwest of the atoll, with over 90 percent of the atoll population (395 of 430 at the 2002 census).
history
Apataki is a comparatively large atoll with a lagoon area of over 680 km². The land area of the numerous Motus , on the other hand, is only about 20 km².
In 1722 the atoll was discovered by the Dutchman Jakob Roggeveen . James Cook visited the island in April 1774.
At the end of April 1816 Otto von Kotzebue crossed the Palliser Islands in the northwest of the Tuamotus with the Rurik and corrected Cook's coordinates for Takapoto and Apataki, but without entering the islands.
Ludwig von Hagemeister sighted Apataki during his first circumnavigation with the Kutuzov , but did not set foot on the island. He believed himself to be the first to discover it and named it “Menschikov”, after the Russian noble family of Menshikov , who, like Hagemeister, were of German-Baltic descent. On some older maps the island can also be found under the name "Hagemeister".
Today's residents live from tourism and subsistence farming . Yams , taro , breadfruits , spiced vanilla (on some small islands) and fruit are mainly grown for personal use. In addition, copra is produced from dried coconuts . The leaves of the screw trees growing here are used to make roofs, bags and hats.
Apataki has an airfield near the capital Niutahi, which was completed in 1977 and is the basis for growing tourism. Diving and surfing are popular activities for tourists. Above all, the species-rich underwater world is remarkable. The atoll itself has only sparse vegetation due to the small land mass, which is home to insects, lizards and sea birds.
Landsat satellite image of Apataki
See also
literature
- Gilles Blanchet: L'Atoll d'Apataki et la SCEP. Office de la Recherche Scientifique et Technique Outre-Mer. Center ORSTOM de Papeete, September 1978 ( online )
Web links
- Picture and brief description of the atoll ( Memento from December 23, 2010 in the Internet Archive )
- Census 2007 ( Memento of February 29, 2008 in the Internet Archive ) (PDF, French)
- Travelogue with pictures (English)
- List of numerous motus according to location
- Map of the atoll
- better map of the atoll
- Colored map of the atoll (PDF)
Individual evidence
- ^ Glynn Barratt: Russia and the South Pacific 1696-1840. Volume 4, University of British Columbia Press, Vancouver 1988, ISBN 0-7748-0305-3 , p. 12
- ^ John Dunmore: Who's who in Pacific navigation. University of Hawaii Press, Honolulu 1991, ISBN 9780824813505 , p. 123