Leinzell
| coat of arms | Germany map | |
|---|---|---|

|
Coordinates: 48 ° 51 ' N , 9 ° 53' E |
|
| Basic data | ||
| State : | Baden-Württemberg | |
| Administrative region : | Stuttgart | |
| County : | Ostalbkreis | |
| Height : | 400 m above sea level NHN | |
| Area : | 2.11 km 2 | |
| Residents: | 2041 (Dec. 31, 2018) | |
| Population density : | 967 inhabitants per km 2 | |
| Postal code : | 73575 | |
| Area code : | 07175 | |
| License plate : | AA, GD | |
| Community key : | 08 1 36 040 | |
| Address of the municipal administration: |
Mulfinger Strasse 2 73575 Leinzell |
|
| Website : | ||
| Mayor : | Ralph Leischner | |
| Location of the community of Leinzell in the Ostalb district | ||
Leinzell is a municipality in Baden-Württemberg and belongs to the Ostalb district . It belongs to the East Wuerttemberg region and the edge zone of the European metropolitan region of Stuttgart .
geography
Geographical location
Leinzell lies at an altitude of 400 to 460 meters in the foreland of the eastern Swabian Alb on the Lein , a small tributary of the Kocher , about ten kilometers northeast of Schwäbisch Gmünd . The community has a comparatively very small community area that does not even extend to the edge of the Leintal.
Neighboring communities
The community borders Göggingen in the north and east , Iggingen in the south and Täferrot in the west .
Community structure
The community of Leinzell includes the village of Leinzell and the hamlet of Ölhäuser as well as the abandoned villages of Pulvermühle and Schafhaus.
Division of space

According to data from the State Statistical Office , as of 2014.
history
Leinzell was first mentioned in a document in 1259 under the name Cella . In 1409 the place was under the name cell at the Lyn , 1426 as Lynzelle mentioned. In the 15th century, the Ellwangen Abbey was converted into the Prince Provost of Ellwangen , and Leinzell was given as a fief. From 1360 to 1483 Leinzell (with a short interruption) was given to the Gmünder Taler family . Rosina Taler, the widow of the last Taler, married Rudolf von Westerstetten; In 1484 he took over the rule of the village under the suzerainty of Albrecht Propst zu Ellwangen. In 1530 Leinzell came to the von Horkheim family, in 1604 to Jörg Christoph von Ursenbeck and in 1612 to Hans Burkhard von Fauber auf Randegg.
In 1636 (in the middle of the Thirty Years War ) Valentin von Lang, who had initially worked in the administration of the Archdiocese of Bremen, was enfeoffed with Leinzell. The Lang family lived in Leinzell and determined village life for 170 years until the time of the Imperial Knights came to an end and during the course of secularization in 1806, Leinzell fell to the Kingdom of Württemberg , where it was assigned to the Oberamt Gmünd . In 1810 Leinzell became an independent municipality. The compulsory labor of the citizens of Leinzeller was not regulated until 1842 by a redemption contract, the Baron von Lang received the last installment in 1874; From this point on, the citizens of Leinzeller were exempt from all compulsory labor. In 1938, as part of a regional reform in Württemberg during the Nazi era , Leinzeill was assigned to the district of Gmünd, which from 1941 was officially called the district of Schwäbisch Gmünd . With the district reform in 1973 , Leinzell became part of the new Ostalb district .
Population development
|
|
|
| date | Total number | male | female |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dec 31, 2005 | 2217 | 1075 | 1142 |
| Dec 31, 2006 | 2186 | 1052 | 1134 |
| Dec 31, 2007 | 2194 | 1054 | 1140 |
| Dec 31, 2008 | 2172 | 1029 | 1143 |
| Dec 31, 2009 | 2130 | 1008 | 1122 |
| Dec 31, 2010 | 2084 | 997 | 1087 |
Religions
The construction of the Catholic Church in Leinzell in its current form began in 1776. Before that, the church was particularly noticeable due to its lack of structural substance and minor furnishings. The church was completed in 1783 and the altars were finally erected in 1805. The painted ceiling, which shows the assumption of Mary into heaven, is by Johann Nepomuk Nieberlein , who among other things designed the station chapels of the Stations of the Cross to the Schönenbergkirche in Ellwangen .
It was not until 1971 that the construction of a Protestant parish hall began because a hall for church events, youth rooms and a vicar's apartment were urgently needed. In 1980 the parish of Eschach was separated and the parish of Göggingen-Leinzell became independent. Church services alternate weekly in Leinzell and Göggingen.
politics
Administrative association
The municipality is the seat of the Leintal-Frickenhofer Höhe municipal administration association, to which the municipalities of Eschach , Göggingen , Iggingen , Leinzell, Obergröningen and Schechingen belong.
Municipal council
The local elections on May 26, 2019 led to the following result with a turnout of 61.38%:
| Political party | percent | Seats |
|---|---|---|
| CDU | 43.79% | 5 |
| SPD / Free Voters Leinzell | 39.19% | 5 |
| Civil election proposal (BWV) | 17.02% | 2 |
mayor
- ? –1808: Hansjörg Stegmaier
- 1808–1813: Josef Rieger
- 1813-1821: Michael Funk
- 1821–1824: Georg Stegmaier
- 1824–1825: Melchior Müller
- 1825–1832: Bernhard Schmid
- 1832–1844: Johannes Riegg
- 1844–1849: Josef Dolderer
- 1849–1856: Johann Aigeldinger
- 1856–1883: August Reichle
- 1883–1897: Josef Schock
- 1897–1921: Josef Rist
- 1921–1934: August Ohnewald
- 1934–1945: Anton Lang
- 1945–1946: Anton Ströbel
- 1945–1968: Gustav Vogt
- 1968–1974: Klaus Pick
- 1974–2006: Günter Nesper
- Since 2006: Ralph Leischner
Partnerships
Since 1989, Leinzell has had a partnership with the French community of Danjoutin near Belfort .
Culture and sights
The Leinzeller Castle was built by the Lang family around 1650 on the ruins of a fortification that was destroyed in the Thirty Years' War. Even after the Lang family lost power, the castle remained in their possession and was only sold in 1990 from the possession of Baroness Brigitte von Lang. The conversion into a hotel failed due to the concerns of the Baden-Württemberg State Monuments Office , after all, the castle was used as a residence for asylum seekers for several years. Today the castle is privately owned again and is inhabited and renovated by the owners Helmut and Sylvia Wickleder.
Sports
Leinzell has three sports fields, a swimming pool, a sports hall, a culture hall, a shooting club and a ski slope with a ski lift. There are also numerous sports clubs that offer tennis, ice stock sport, football and Jiu Jitsu , among other things .
Economy and Infrastructure
education
In Leinzell there is a primary and a technical secondary school as well as a secondary school . The special school for children with learning disabilities was closed at the end of the 2012 school year. The next secondary schools are in Schwäbisch Gmünd .
For the youngest citizens there is a Catholic and a Protestant kindergarten ; they are open to all denominations.
Personalities
Sons and daughters of the church
- Wilhelm Beißwenger (1871–1942), member of the state parliament ( WBWB ) and district farmer leader
- Alois Lang (1940–1994), local politician, Lord Mayor of Ditzingen
Others
After the Thirty Years' War, many homeless people settled in Leinzell who earned their living as wandering traders. These traders brought the Yenish language to Leinzell, which is still spoken here and there today.
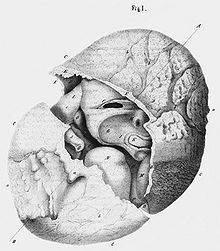
In 1720 a lithopedion was discovered in the body of a 90-year-old inhabitant of Leinzell , which she had carried with her for 46 years. The Steinkind von Leinzell is considered to be one of the best preserved Lithopaedia. The personal physician of King George I , Johann Georg Steigerthal , wrote a first description of the find . In 1854 the stone child was the subject of a dissertation by W. Kieser. Today the Steinkind von Leinzell is in the collection of the University of Tübingen.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ State Statistical Office Baden-Württemberg - Population by nationality and gender on December 31, 2018 (CSV file) ( help on this ).
- ^ The state of Baden-Württemberg. Official description by district and municipality. Volume IV: Stuttgart district, Franconian and East Württemberg regional associations. Kohlhammer, Stuttgart 1980, ISBN 3-17-005708-1 , pp. 739-740.
- ↑ State Statistical Office, area since 1988 according to actual use for Leinzell.
- ^ Deed of donation in the Ludwigsburg State Archives B 177 U 1508.
- ↑ Source: www.leinzell.de.
- ^ Frank Raberg : Biographical handbook of the Württemberg state parliament members 1815-1933 . On behalf of the Commission for Historical Regional Studies in Baden-Württemberg. Kohlhammer, Stuttgart 2001, ISBN 3-17-016604-2 , p. 48 .
- ↑ See the Tübingen national economic dissertation by Kurt Seidel (typed 1953): http://d-nb.info/480444943 .
- ↑ http://www.unimuseum.uni-tuebingen.de/38dinge/dinge15.html