Merenberg
| coat of arms | Germany map | |
|---|---|---|

|
Coordinates: 50 ° 31 ' N , 8 ° 11' E |
|
| Basic data | ||
| State : | Hesse | |
| Administrative region : | to water | |
| County : | Limburg-Weilburg | |
| Height : | 253 m above sea level NHN | |
| Area : | 23.09 km 2 | |
| Residents: | 3233 (Dec. 31, 2019) | |
| Population density : | 140 inhabitants per km 2 | |
| Postal code : | 35799 | |
| Primaries : | 06471, 06476 | |
| License plate : | LM, WEL | |
| Community key : | 06 5 33 012 | |
| LOCODE : | DE MBB | |
| Address of the municipal administration: |
Allendorfer Strasse 4 35799 Merenberg |
|
| Website : | ||
| Mayor : | Oliver Jung ( SPD ) | |
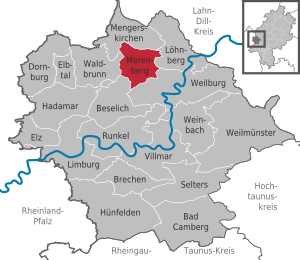
| Location of the municipality of Merenberg in the Limburg-Weilburg district | ||
The market town of Merenberg is a municipality in the central Hessian district of Limburg-Weilburg on the southern edge of the Westerwald , about five kilometers northwest of Weilburg .
geography
Merenberg borders the municipality of Mengerskirchen in the north, the municipality of Löhnberg in the east, the city of Weilburg in the south, the municipality of Beselich in the southwest , and the municipality of Waldbrunn in the west (all in the Limburg-Weilburg district).
Districts
Merenberg consists of the five districts Merenberg, Barig-Selbenhausen , Allendorf , Reichenborn and Rückershausen .
history

Settlements from the La Tène period can be found on the Almerskopf and Höhburg .
Merenberg is the ancestral castle of the Merenberg family , a noble family from the 12th to 14th centuries. In connection with this family, the place was first mentioned in 1129. In 1290 Merenberg received city rights and weekly market rights from King Rudolf I , after which a city wall was built. In 1328 the Merenberg family died out in the male line, and the fiefdom of Burg und Herrlichkeit Merenberg passed to the Nassau family through the marriage of the heir's daughter . On July 31, 1564, Albrecht von Nassau-Weilburg received the right to two annual markets in Merenberg from Emperor Maximilian II . A Jakobimarkt in connection with the Kirchweih festival has already been recorded for 1499. This existed until 1770 and is likely to have been the third annual fair in town alongside the two imperially privileged ones.
The Merenberg office existed until the end of the HRR . The castle was destroyed in 1634 and since then, as a ruin, has been Merenberg's landmark.
At the beginning of the 19th century Merenberg's town charter was withdrawn. At the end of the 19th century the House of Nassau took up the title of Herr von Merenberg , inherited in 1328, and gave the incongruous wife of Prince Nikolaus Wilhelm zu Nassau and her descendants from this marriage the title of Count of Merenberg .
In February 1902 the Merenberg volunteer fire brigade was founded . In doing so, she and other already existing volunteer fire brigades formed the Oberlahn extinguishing district in the fire brigade association for the Wiesbaden administrative region , within which she took part in the district assembly in Obertiefenbach on September 3, 1906 with a strength of 43 members.
In the course of the regional reform in Hesse , the then independent communities of the former Oberlahnkreis Allendorf, Barig-Selbenhausen, Merenberg, Reichenborn and Rückershausen merged on December 31, 1970 to form the new large community of Merenberg.
Territorial history and administration
The following list gives an overview of the territories in which Merenberg was located and the administrative units to which it was subordinate:
- before 1806: Holy Roman Empire , County / Principality of Nassau-Weilburg , Merenberg Office
- from 1806: Duchy of Nassau , Weilburg office
- from 1816: German Confederation , Duchy of Nassau , Weilburg office
- from 1849: German Confederation, Duchy of Nassau, Hadamar District Office
- from 1854: German Confederation, Duchy of Nassau, Weilburg office
- from 1867: North German Confederation , Kingdom of Prussia , Province of Hessen-Nassau , Administrative Region of Wiesbaden , Oberlahnkreis
- from 1871: German Empire , Kingdom of Prussia, Province of Hessen-Nassau, administrative district of Wiesbaden, Oberlahnkreis
- from 1918: German Empire, Free State of Prussia , Province of Hessen-Nassau, Administrative Region of Wiesbaden, Oberlahnkreis
- from 1944: German Empire, Free State of Prussia, Nassau Province , Oberlahnkreis
- from 1945: American zone of occupation , Greater Hesse , Wiesbaden district, Oberlahn district
- from 1949: Federal Republic of Germany , State of Hesse , Wiesbaden district, Oberlahnkreis
- from 1968: Federal Republic of Germany, State of Hesse, administrative district Darmstadt , Oberlahnkreis
- from 1974: Federal Republic of Germany, State of Hesse, administrative district Darmstadt, district Limburg-Weilburg
- from 1981: Federal Republic of Germany, State of Hesse, Gießen district, Limburg-Weilburg district
population
Population development
| Merenberg: Population from 1834 to 2015 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| year | Residents | |||
| 1834 | 656 | |||
| 1840 | 669 | |||
| 1846 | 729 | |||
| 1852 | 721 | |||
| 1858 | 677 | |||
| 1864 | 710 | |||
| 1871 | 693 | |||
| 1875 | 680 | |||
| 1885 | 676 | |||
| 1895 | 680 | |||
| 1905 | 671 | |||
| 1910 | 635 | |||
| 1925 | 714 | |||
| 1939 | 614 | |||
| 1946 | 884 | |||
| 1950 | 895 | |||
| 1956 | 803 | |||
| 1961 | 807 | |||
| 1967 | 923 | |||
| 1970 | 2,320 | |||
| 1972 | 2,373 | |||
| 1976 | 2,308 | |||
| 1984 | 2,591 | |||
| 1992 | 3,013 | |||
| 2000 | 3,500 | |||
| 2010 | 3,331 | |||
| 2015 | 3,200 | |||
| Data source: Historical municipality register for Hesse: The population of the municipalities from 1834 to 1967. Wiesbaden: Hessisches Statistisches Landesamt, 1968. Further sources:; 1972 :; 1976 :; 1984 :; 1992 :; 2000, 2015 :; 2010: From 1970 including the towns incorporated into Hesse as part of the regional reform . | ||||
Religious affiliation
Source: Historical local dictionary
| • 1885: | 637 Protestant (= 94.23%), 24 Catholic (= 3.55%) and 15 Jewish (= 2.22%) residents |
| • 1961: | 673 Protestant (= 83.40%), 117 Catholic (= 14.50%) residents |
politics
Community representation
The local elections on March 6, 2016 produced the following results, compared to previous local elections:
| Parties and constituencies | % 2016 |
Seats 2016 |
% 2011 |
Seats 2011 |
% 2006 |
Seats 2006 |
% 2001 |
Seats 2001 |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPD | Social Democratic Party of Germany | 48.8 | 11 | 47.5 | 11 | 39.7 | 9 | 43.3 | 10 | |
| CDU | Christian Democratic Union of Germany | 37.5 | 9 | 34.4 | 8th | 39.7 | 9 | 36.0 | 8th | |
| GREEN | Alliance 90 / The Greens | 13.7 | 3 | 9.1 | 2 | 6.0 | 2 | 3.3 | 1 | |
| BM / FWG | Citizens List / Free Voting Community Merenberg | - | - | 9.0 | 2 | 14.6 | 3 | 17.3 | 4th | |
| total | 100.0 | 23 | 100.0 | 23 | 100.0 | 23 | 100.0 | 23 | ||
| Voter turnout in% | 51.3 | 48.8 | 54.7 | 57.3 | ||||||
mayor
After the Hessian municipal constitution is Mayor Chairman of the Municipal Board , the volunteer in the market town Merenberg next to the mayor six Associate members. Oliver Jung (SPD) has been mayor since May 11, 2016. His directly elected predecessors were
- 2004 to 2016 Reiner Kuhl (independent)
- 1998 to 2004 Gerald Born (SPD)
coat of arms
In September 1950 the municipality of Merenberg was granted the right to use a coat of arms by the Hessian State Ministry.
The coat of arms was approved on July 5, 1973 by the Hessian Ministry of the Interior .
Blazon : "In green a golden tray , accompanied by three golden crosses in every corner."
The community carries the coat of arms of the Lords of Merenberg, which was also included in the coat of arms of the former Oberlahnkreis (seat: Weilburg).
Buildings
Economy and Infrastructure
In addition to the local trade and craft, there are some medium-sized industrial companies on site. The main industries are mechanical and plant engineering , metal and plastics processing and automation technology . The best-known company from Merenberg is the record label ZYX Music .
Facilities
- Daycare center Villa Kunterbunt Merenberg
- Kindergarten Tigerente Barig-Selbenhausen
- Merenberg volunteer fire brigade , founded in 1902 (including youth fire brigade since July 7, 1990)
- Allendorf volunteer fire brigade, founded in 1926 (including youth fire brigade since July 7, 1990)
- Barig-Selbenhausen volunteer fire brigade, founded in 1925 (including youth fire brigade since July 7, 1990)
- Reichenborn volunteer fire brigade, founded in 1925 (including youth fire brigade since July 7, 1990)
- Rückershausen volunteer fire brigade, founded in 1934 (including youth fire brigade since July 7, 1990)
- A children's fire brigade has been running for the market town since April 14, 2007 .
education
In Merenberg there is a primary and secondary school, the Albert Wagner School . It was inaugurated in 1958 as the first Hessian center school . The school was named after the administrator and politician Albert Wagner . Merenberg belongs to the catchment area of the secondary and secondary school Westerwaldschule in Mengerskirchen-Waldernbach. Furthermore, students attend secondary schools in Weilburg .
traffic
The municipality is located on federal highway 49 , which is currently (September 2014) being expanded to four lanes between Limburg and Wetzlar . Merenberg is thus connected to the trunk road network.
Sons and daughters of the church
- Antonius Jacobus Henckel , (born October 27, 1668 in Merenberg, † August 12, 1728 in Springfield), theologian and, after emigrating to the United States, reformer of the Lutheran Church in Pennsylvania .
- Wilhelm Dörr , (born February 9, 1921 in Merenberg, † December 13, 1945 (executed) in Hameln). SS Oberscharführer , deputy camp leader in the Kleinbodungen satellite camp
literature
- Literature about Merenberg in the Hessian Bibliography
- Search for Merenberg in the archive portal-D of the German Digital Library
Web links
- Merenberg, Limburg-Weilburg district. Historical local dictionary for Hessen. In: Landesgeschichtliches Informationssystem Hessen (LAGIS).
- Information on the community of Merenberg. In: Hessisches Gemeindelexikon. HA Hessen Agentur GmbH , 2016.
- Link catalog on the subject of Merenberg at curlie.org (formerly DMOZ )
Individual evidence
- ↑ Hessian State Statistical Office: Population status on December 31, 2019 (districts and urban districts as well as municipalities, population figures based on the 2011 census) ( help ).
- ↑ Franz-Josef Sehr : Fire Department District Days around the turn of the century . In: Yearbook for the Limburg-Weilburg district 2000 . The district committee of the district of Limburg-Weilburg, Limburg-Weilburg 1999, ISBN 3-927006-29-7 , p. 187-189 .
- ↑ Amalgamation of the communities of Allendorf, Barig-Selbenhausen, Merenberg, Reichenborn and Rückershausen in the Oberlahnkreis to form the community of "Merenberg" on January 5, 1971 . In: The Hessian Minister of the Interior (ed.): State Gazette for the State of Hesse. 1971 No. 3 , p. 111 , point 117a ( online at the information system of the Hessian state parliament [PDF; 5.5 MB ]).
- ↑ a b c Merenberg, Limburg-Weilburg district. Historical local dictionary for Hessen. (As of May 24, 2018). In: Landesgeschichtliches Informationssystem Hessen (LAGIS).
- ^ Michael Rademacher: German administrative history from the unification of the empire in 1871 to the reunification in 1990. State of Hesse. (Online material for the dissertation, Osnabrück 2006).
- ^ Local elections 1972; Relevant population of the municipalities on August 4, 1972 . In: The Hessian Minister of the Interior (ed.): State Gazette for the State of Hesse. 1972 No. 33 , p. 1424 , point 1025 ( online at the information system of the Hessian state parliament [PDF; 5.9 MB ]).
- ↑ Local elections 1977; Relevant population figures for the municipalities as of December 15, 1976 . In: The Hessian Minister of the Interior (ed.): State Gazette for the State of Hesse. 1976 No. 52 , p. 2283 , point 1668 ( online at the information system of the Hessian state parliament [PDF; 10.3 MB ]).
- ^ Local elections 1985; Relevant population of the municipalities as of October 30, 1984 . In: The Hessian Minister of the Interior (ed.): State Gazette for the State of Hesse. 1984 No. 46 , p. 2175 , point 1104 ( online at the information system of the Hessian state parliament [PDF; 5.5 MB ]).
- ↑ local elections 1993; Relevant population of the municipalities as of October 21, 1992 . In: The Hessian Minister of the Interior (ed.): State Gazette for the State of Hesse. 1992 No. 44 , p. 2766 , point 935 ( online at the information system of the Hessian state parliament [PDF; 6.1 MB ]).
- ^ Municipal data sheet : Merenberg. (PDF; 222 kB) In: Hessisches Gemeindelexikon. HA Hessen Agency GmbH
- ↑ The population of the Hessian communities on June 30, 2010. (PDF; 552 kB) Hessisches Statistisches Landesamt, p. 11 , archived from the original on February 7, 2018 ; accessed on March 20, 2018 .
- ^ Result of the municipal election on March 6, 2016. Hessian State Statistical Office, accessed in April 2016 .
- ^ Hessian State Statistical Office: Result of the municipal elections on March 27, 2011
- ^ Hessian State Statistical Office: Result of the municipal elections on March 26, 2006
- ^ Hessian State Statistical Office: direct elections in Merenberg
- ↑ Delivery of the certificate of appointment to Mayor Reiner Kuhl for the term of office from May 11, 2010 to May 10, 2016 ( memento of August 2, 2016 in the Internet Archive ), accessed on August 2, 2016
- ↑ Granting of the right to use a coat of arms to the community of Merenberg, Oberlahnkreis, Wiesbaden administrative district on September 21, 1950 . In: The Hessian Minister of the Interior (ed.): State Gazette for the State of Hesse. 1950 No. 40 , p. 406 , point 759 ( online at the information system of the Hessian state parliament [PDF; 2.2 MB ]).
- ^ Burgruine Merenberg - a facility of the Administration of State Palaces and Gardens Hesse ( Memento from January 26, 2017 in the Internet Archive )
- ^ Antonius Jacobus Henckel in the personal database of the state bibliography of Baden-Württemberg