Selz
| Selz | ||
|
Progress plan |
||
| Data | ||
| Water code | EN : 252 | |
| location |
Northern Upper Rhine Lowland
|
|
| River system | Rhine | |
| Drain over | Rhine → North Sea | |
| source | on the western edge of the Alzeyer hill country at Orbis 49 ° 41 ′ 46 ″ N , 7 ° 59 ′ 55 ″ E |
|
| Source height | 319 m above sea level NHN | |
| muzzle | at Frei-Weinheim from the left into the Rhine Coordinates: 49 ° 59 '45 " N , 8 ° 1' 33" E 49 ° 59 '45 " N , 8 ° 1' 33" E |
|
| Mouth height | 80 m above sea level NHN | |
| Height difference | 239 m | |
| Bottom slope | 3.9 ‰ | |
| length | 61 km | |
| Catchment area | 389.059 km² | |
| Discharge at the Oberingelheim A Eo gauge : 363 km² Location: 5 km above the mouth |
MNQ 1975/2002 MQ 1975/2002 Mq 1975/2002 |
267 l / s 742 l / s 2 l / (s km²) |
| Left tributaries | s. Section tributaries | |
| Right tributaries | s. Section tributaries | |
| Reservoirs flowed through | Alzeyer reservoir | |
| Medium-sized cities | Ingelheim am Rhein | |
| Small towns | Alzey , Nieder-Olm | |
| Communities | 15 local parishes | |
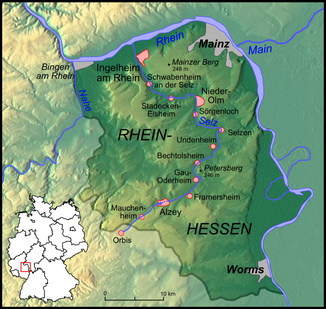
The Selz is a 61 km long, southern and left tributary of the Rhine and one of the main bodies of water in Rheinhessen . It flows in the Rheinhessen table and hill country in Rhineland-Palatinate through the Donnersbergkreis , the Alzey-Worms district and the Mainz-Bingen district .
With a discharge of only 2 l / (s · km²), the Selz , which flows in the slipstream of the North Palatinate Uplands , is one of the most arid rivers in Germany compared to the catchment area . The mean discharge is 0.77 m³ / s with a fluctuation range of 0.3 to 20 m³ / s.
geography
course
The Selz rises in the Palatinate on the western edge of the Alzeyer hill country , part of the Rheinhessen table and hill country . Your source is 319 m above sea level. NHN on the north-eastern edge of Orbis near the suture line running near the village to the northern Palatinate Bergland to the west on a field path in the extension of the residential street Weedeweg; it is signposted and freely accessible.
The Selz flows in a northeasterly direction for about 30 km. It initially passes Morschheim north and after 3 km the border between the northern Palatinate and Rheinhessen. After another 8 km stretch of river, after flowing through Mauchenheim , the confluence of the Steinbach and the first crossing under the federal motorway 63 , the Selz runs through the core of the small town of Alzey . There it first flows through the Alzeyer reservoir , then it runs through the village - mostly piped underground. Immediately afterwards it passes the federal motorway 61 .
Below Alzey, the Selz passes Schafhausen , after which the Weidas joins, Framersheim , Gau-Köngernheim and Gau-Odernheim , from where it turns a short distance to the northwest and then again to the northeast and takes in the Heimersheimer Bach . Then it passes or runs through Bechtolsheim and Friesenheim and, during a short northward section, Köngernheim , where the Goldbach joins. After about half of its walk through the Rheinhessen table and hill country, it bends towards the west-north-west near Selzen - after a U-shaped river bend.
Then the Selz Hahnheim and Wahlheimer Hof pass . Henceforth, it flows to the north and happens to run in the Saulheimer Bach , Nieder-Olm . Then, immediately after a bend to the west, it passes under the federal motorway 63 for the second and last time. Shortly afterwards, the Selz runs through Stadecken-Elsheim . Heading northwest it passes in Ingelheimer Grund Schwabenheim an der Selz , Bubenheim , Großwinternheim and Ingelheim am Rhein .
Then the Selz crosses under the Bundesautobahn 60 to flow 2.3 kilometers below it in the northern Ingelheim district of Frei-Weinheim (Ingelheim-Nord) at a height of about 80 m into the Rhine coming there from the east-northeast .
Tributaries
The following tributaries of the Selz are recorded with the river code number:
| Surname | page | Length [km] |
EZG [km²] |
Mouth on km |
Mouth | GKZ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Four acre ditch | right | 0.54 | 0.92 | 1.43 | northwest of Morschheim | 252-112 |
| Hahlbach | Left | 1.11 | 1.56 | 1.81 | north-north-west of Morschheim | 252-12 |
| Gersborn | Left | 2.46 | 2.05 | 4.71 | in Mauchenheim | 252-14 |
| Steinbach | Left | 3.38 | 12.06 | 8.05 | east of Weinheim | 252-16 |
| Ditch | Left | 1.48 | 0.78 | 12.64 | in the east of Alzey | 252-18 |
| Weidas | right | 11.07 | 36.81 | 15.00 | below Alzeys | 252-2 |
| Framersheim Bach | right | 2.69 | 1.66 | 15.77 | northwest of Framersheim | 252-32 |
| Haaggraben | right | 5.26 | 19.86 | 18.82 | opposite Gau-Odernheims | 252-34 |
| Heimersheimer Bach | Left | 10.16 | 24.87 | 21.46 | opposite Biebelnheims | 252-4 |
| Bach from Petersberg | right | 1.26 | 0.99 | 23.11 | immediately below Bechtolsheims | 252-5112 |
| Dolgesheimer flood ditch | right | 3.96 | 7.08 | 24.54 | below Bechtolsheims | 252-512 |
| Weinolsheimer flood ditch | right | 3.21 | 5.35 | 25.92 | between Bechtolsheim and Friesenheim | 252-52 |
| Ditch | Left | 3.48 | 5.87 | 27.18 | above Friesenheim | 252-532 |
| Dalheimer flood ditch | right | 4.95 | 9.95 | 28.62 | in Friesenheim | 252-54 |
| Goldbach | Left | 6.24 | 14.85 | 29.65 | at Undenheim | 252-552 |
| Maze | right | 0.32 | 2.18 | 30.21 | Koengernheim | 252-5532 |
| Reizengalgenbach (Mörtelgraben) | right | 1.11 | 1.73 | 32.12 | immediately above Selzens | 252-554 |
| Langenbacher Graben (barrage ditch) | right | 0.97 | 1.82 | 32.45 | Selzen | 252-55992 |
| Sand ditch | right | 1.75 | 2.25 | 33.22 | opposite Hahnheim | 252-55994 |
| Schornsheimer Graben | Left | 5.76 | 6.52 | 34.23 | below Hahnheims | 252-56 |
| Bach from Wahlheimer Hof | right | 1.86 | 1.78 | 34.64 | below Hahnheims | 252-5712 |
| Wilhelmsgrundbach (Udenheimer Graben) | Left | 4.24 | 5.35 | 35.09 | below Hahnheims | 252-572 |
| Oil trench | Left | 0.88 | 0.47 | 36.42 | south of Sorgeloch | 252-5792 |
| Udenheim Bach | Left | 3.02 | 3.34 | 37.20 | east of Udenheim | 252-58 |
| Saulheim Bach | Left | 8.63 | 24.36 | 40.75 | above Nieder-Olms | 252-6 |
| Haybach (Selz) | right | 3.21 | 8.31 | 43.39 | below Nieder-Olms | 252-72 |
| Essenheim Bach | right | 2.44 | 5.07 | 44.65 | southeast of Essenheim | 252-74 |
| Saubach | Left | 6.58 | 21.49 | 48.65 | in Stadecken-Elsheim | 252-8 |
| Effengraben | right | 1.79 | 2.42 | 49.33 | Stadecken-Elsheim | 252-9 |
| Engelstädter Bach (Engelstädter Graben) | Left | 2.96 | 5.41 | 51.30 | above Schwabenheim | 252-92 |
| Schwabenheimer Bach (Schwabenheimer Graben) | right | 2.56 | 10.72 | 52.98 | in Schwabenheim | 252-94 |
| Großwinternheimer Bach (moat Schloßbergstraße) | right | 1.54 | 2.14 | 55.02 | Großwinterheim | 252-96 |
| Source in the sour earth | Left | 0.88 | 0.15 | 55.22 | 252-972 | |
| Source in the duck pond | Left | 0.88 | 0.70 | 55.74 | 252-976 | |
| Source in the Eschloch | right | 0.28 | 0.33 | 56.14 | 252-978 | |
| Bach von der Ingelheimer Döll (water rose) | right | 1.55 | 2.79 | 56.41 | above Ingelheims | 252-98 |
| Source on the upper Rheinweg | Left | 0.27 | 0.36 | 56.79 | above Ingelheims | 252-99112 |
| Source at the raft meadow | right | 0.14 | 1.02 | 56.94 | above Ingelheims | 252-99114 |
| Source large meadow | Left | 0.22 | 0.26 | 59.14 | Ingelheim South | 252-99192 |
| Coin pit | right | 3.60 | 8.02 | 62.25 | below Ingelheims | 252-992 |
| Old sand pool | right | 2.82 | 0.55 | 62.51 | below Ingelheims | 252-994 |
Adjacent surveys
On its way through Rheinhessen, the Selz flows below Alzeys past various elevations on the right-hand side of the northern Rheinhessen table and hill country, which protrude 100 to 150 m above the level of the valley floodplain and some of which are part of the watershed between the Selz and the 10 bis 16 km east of the Rhine flowing past. This includes:
- Petersberg ( 245.6 m ) between Gau-Odernheim and Bechtolsheim
- Selzer Berg ( 237.1 m ) between Selzen and Sörgenloch
- Mühlberg ( 242.9 m ) between Mainz-Ebersheim and Nieder-Olm
- Mainzer Berg ( 249.1 m ) near Schwabenheim and Ingelheim- Großwinternheim
history
Written occupies the Selz as part of is Veronese donation , with the June 14, 983 Emperor Otto II. In Verona his Lord Chancellor , the Mainzer archbishop Willigis , the city Bingen and the associated landscape gave that "on this side of the Rhine from the bridge extends over the Selzbach to Heimbach, on the other side of the Rhine but from the point where the Elzbächlein flows into it to the little village of Caub. "
In 1909, the so-called Selztalstellung with Fort Muhl was built near Zornheim as an important line of defense and an advanced bulwark of the German Empire against France, as from here there is a view of more than 30 km over Rheinhessen.
On Good Friday, April 20, 1962, after heavy rainfall, the Selz near Mauchenheim overflowed the bank and flooded the lower part of the village. The house of the Anhäuser Mühle was under water up to the ceiling and had to be demolished. The road to Alzey was also so covered with mud that the course was no longer recognizable.
The Selz and its floodplains have been renatured piece by piece since 1992 . Wetlands were created, the banks flattened and fall trees introduced so that the Selz can find a new path. Many amphibians, water birds and insects can be seen again since then. One of the first renatured sections is between Hahnheim and Sörgenloch.
Source at Orbis
... near Frei-Weinheim (Ingelheim-Nord)
Economical meaning
bridges
137 bridges cross the Selz; if distributed evenly, the watercourse could be crossed every 460 m. Most of the crossings are only intended for agricultural traffic on the dirt roads . Road bridges for general motor traffic are mainly in or near the places through which the water flows. The largest of these is the Weinheim Viaduct .
Selztal cycle path
From the source near Orbis through Alzey to Ingelheim am Rhein , a signposted hiking and cycling path , the Selztalweg or Selztal-Radweg , leads along the Selz . It runs partly on or next to the former “Amiche” and “Zuckerlottche” railway lines .
Mills
Most of the once 40 mills on the Selz are no longer in operation.
Use in culture
Alexandre Dumas the Elder has his novel The Council of the Magician set in the Selz region. In the introduction he describes the water in detail.
Original French text:
Introduction I - Le mont Tonnerre
Sur la rive gauche du Rhin, à quelques lieues de la ville impériale de Worms, vers l'endroit où prend sa source la petite rivière de Selz , commencent les premiers chaînons de plusieurs montagnes dont les croupes hérissées paraissent s'enfuir vers le nord, comme un troupeau de buffles effrayés qui disparaîtrait dans la brume. [...]
[…] Seule au milieu de ce silence, la petite rivière dont nous avons déjà parlé, le Selzbach , comme on l'appelle dans le pays, poursuit son cours mystérieux sous les sapins de la rive; et quoique ni jour ni nuit ne l'arrêtent, car il faut qu'elle se jette dans le Rhin qui est son éternité à elle, quoique rien ne l'arrête, disons-nous, le sable de son lit est si frais, ses roseaux sont si flexible, ses roches si bien ouatées de mousses et de saxifrages, que pas un de ses flots ne bruit de Morsheim, où elle commence, jusqu'à Freiwenheim, où elle finit. [...]
German translation:
Introduction I - The Donnersberg
Above the left bank of the Rhine, several miles away from the imperial city of Worms in the direction where the river Selz rises, the foothills of several mountain ranges begin, the rugged peaks of which seem to flee to the north like a herd of startled buffalo disappearing in the fog. [...]
[...] In the midst of this silence, the river, of which we have already spoken, the Selzbach , as it is called in this country, takes its mysterious course under the fir trees on its bank; and although there is no stopping day and night, because the Selz, as it is their eternal destination, has to pour into the Rhine, although nothing can stop them, as I said, the sand in its stream bed is so fresh, the reeds are so flexible , their rocks are so padded with moss and saxifrage that not one of their current noises can be heard as far as Morschheim, where it begins, or to Freiweinheim, where it ends. [...]
literature
- Werner Lang: The Selz . In: Heimatbuch Landkreis Mainz . Printed by Wilhelm Traumüller, Oppenheim am Rhein 1967, p. 186-192 .
Web links
- SGD Süd : Implementation of the EU Water Framework Directive. Selz pilot project (October 2006; PDF; 3.2 MB)
- Expedition home - on the way in the Selztal , from November 10, 2013, on programm.ard.de
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Map service of the landscape information system of the Rhineland-Palatinate nature conservation administration (LANIS map) ( notes )
- ↑ a b c GeoExplorer of the Rhineland-Palatinate Water Management Authority ( information )
- ↑ Proof of catchment area and location of the gauge: RLP - Structure and Approval Directorate South ( Memento of July 14, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) (PDF; 3.2 MB).
- ↑ Water hiking trails on the Selz , Ministry for Environment and Forests Mainz (PDF; 3.4 MB).
- ↑ 61 long kilometers to the mouth of the Rhine . In: Allgemeine Zeitung . Mainz February 17, 2007.
- ↑ With km the Selz- are km downstream from the source meant.
- ↑ Enemy visibility over 30 kilometers. Fort Muhl has a prominent position as the largest fortification in the Selzstellung. In: Rhein Main Presse . Mainz August 10, 2009.
- ↑ AM: History (s) of our homeland . In: News bulletin of the Alzey-Land association . April 19, 2012, p. 17.
- ↑ Selztal-Radweg , on wikivoyage.org.
- ↑ Selztalradweg (State Office for Surveying and Geographic Base Information Rhineland-Palatinate) on lvermgeo.rlp.de.
- ↑ Erich Hirsch: The Selz as a literary outflow . Orbis: setting for the novel "The Council of the Magi" by Alexandre Dumas. In: The Rhine Palatinate . Ludwigshafen July 11, 2001 (quoted at huegelland.net, accessed February 21, 2012).