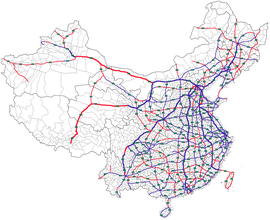
Road system in China

The old section of the S214 provincial road in Yunnan has been redesignated as the XF935 county road with a new milestone; old demolished milestone next to it, Yuxi 2016
The road system in China distinguishes between the following types of roads:
- With G , for Guódào ( Chinese 國 道 / 国 道 - "national road"), the long-distance roads are marked on a national level. The G is followed by a number - "GX" - for highways starting in Beijing ( G1 to G7 ), two numbers - "GXX" - for national highways (e.g. G30 ), three digits - "GXXX" - for national roads (e.g. . B. G318 ) and four digits - "GXXXX" - at regional and local highways (eg. G94 11 ). For Guodao include both the toll highways in China ( English National Expressway ) and the free highways in China " national roads " ( English National Highway called).
- With S , for Shengdào (
省道 - "provincial road"), the trunk roads are marked on the provincial level . The S is followed by one to four digits - "SX" to "SXXXX". In each province a new start is made at S1, i. H. there are trunk roads at the provincial level with the same standard identifier but in different provinces, e.g. B. the Shandong G61 Motorway ( 魯 高速 / 鲁 ), also called Qingdao – Liuting Airport Motorway ( 青岛 流亭 机场 高速 ) and the Guangdong Motorway G61 ( 粵高速 / 粤高速 ), also known as Maominghafen Motorway ( 茂名 港 高速 ) called. This includes both highways and provincial highways or country roads ( English Provincial Road ), which are based on the standard of the National Expressway ( German about "National Motorway " ) in China but are planned, built and maintained by the provincial government. In addition to the roads at the provincial level, there are also roads at the level of the autonomous regions , the cities directly under the government and the special administrative zones.


- With X , for Xiàndào ( 縣 道 / 县 道 - "district road"), the roads are marked on the district level . X usually followed by three digits - "XXXX" - for the county roads ( English County Road ) but it also exists differences with more numbers and letters (for example, XF935, county road at. Yuxi ). These include streets at the level of the cities, the autonomous districts , the special areas , the banners and the like. This is only followed by the street networks of the two lowest municipal levels Xiāngdào - streets of the municipality level and Cūndào - streets of the village level, the standard identifier of which is rarely shown on road maps.
- With Y for Xiāngdào ( 鄉 道 / 乡 道 - "municipal road"), the roads are marked on the municipal level of the municipalities. The Y is usually followed by three digits - "YXXX" - for "Gemeindestraßen" ( English Township Road ). This representation of the “municipal roads” is seldom seen on maps; instead, only Chinese names are shown without a standard identifier. The standard identification of the “municipal roads” only exists on the actual kilometer stones. These include ordinary municipal streets and paths in large communities , municipalities , street districts , sums or the like.
- With C for Cūndào ( 村 道 - "village street"), the roads on the village level are marked. The C usually follow three digits - "CXXX" - for the village streets ( English Village Road ). This representation of the “village streets” is seldom seen on maps; instead, only Chinese names are shown without a standard identifier. The standard identification of the “village streets” only exists on the actual kilometer stones. This includes the simplest municipal roads or routes.
The administrative responsibility of the road networks of the G, S and X series ends at the border lines of the cities and municipalities. She changes from the general administration for public roads to the local municipal administration of the public roads.