Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People's Republic of China
The Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People's Republic of China ( Chinese :中华人民共和国环境保护部, including Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People's Republic of China , cast off: MEP , before 2008 State Environmental Protection Administration . Bind off SEPA ) is a Ministry and executive body of the Chinese government with the mandate to " prevent and control environmental pollution , protect nature and ecosystems , monitor nuclear safety , ensure public health and ecological safety and promote harmony between man and nature". It also funds and manages relevant research and development programs. With its 300 employees, it has about an eighth of the staff of the US Department of the Environment. It has been suggested several times to increase the agency's personnel and financial capacities.
history
- In 1972, Chinese envoys attended the first United Nations conference on the human environment in Sweden. A state “leadership group” will be convened next year.
- In 1982 an environmental protection department was established under the Ministry of Rural-Urban Construction and Environmental Protection (MURCEP).
- In 1983, the Chinese government made environmental protection a national goal with corresponding laws.
- In 1988, with the separation from MURCEP, the department becomes an independent state organization.
- In 1993 the organization received subordinate ministerial status.
- After the great floods of 1998, the organization is renamed the State Environmental Protection Administration (SEPA) and receives full ministerial status.
- In March 2008 the Chinese government followed an OECD recommendation and the SEPA became one of 27 ministries and thus part of the Chinese government .
organization
The MEP is divided into 12 staff units and 65 units . All of them have si status (ministerial status) in the government hierarchy.
-
General Administrative Office (办公厅)
- General Duty Room
- Research Office
- Office of Supervision on Administration
- Office of Public Complaints Settlement
- Office of Information Technology
- Division of Archive Management
- Division of General Meetings Service
- Division of Reception and Security
-
Department of Human Resources & Institutional Affairs (行政 体制 与 人事 司)
- Division of Institutional Restructuring
- Division One of Personnel Management
- Division Two of Personnel Management
- Division of Human Resources Development
- Office of Retired Civil Servants
-
Department of Planning and Finance (规划 与 财务 司)
- Division of General Management
- Division of Planning
- Division of Statistics
- Division of Budget
- Division of Investment Management
- Division of Financing and Accounting
-
Department of Policies, Laws and Regulations (政策 法规 司)
- Division of Environmental Policy
- Division of Laws and Regulations
- Division of Administrative Reconsideration
-
Department of Science & Technology and Standards (科技 标准 司)
- Division of Science and Technology Development
- Division of Technology Policies and Standards
- Division of Environmental Industry
- Division of Environmental Health and Monitoring
-
Pollution Control Office (污染 控制 司)
- Division of General Management
- Division of Urban Environmental Management
- Division of Water Environmental Management
- Division of Environmental Management for Major River Basins
- Division of Drinking Water Sources Protection
- Division of Marine Environmental Protection
- Division of Air and Noise Pollution Control
- Division of Solid Wastes and Toxic Chemicals Management
-
Natural Ecosystem Protection Office (自然 生态 保护 司)
- Division of General Management
- Division of Regional Ecological Environmental Management
- Division of Nature Reserves Management
- Division of Rural Environmental Protection (Division of Soil Environmental Protection)
- Office of Bio-Safety Management (Division of Biodiversity Conservation)
-
Department of Environmental Impact Assessment (环境 影响 评价 管理 司)
- Division of General Management
- Division One of Environmental Impact Assessment
- Division Two of Environmental Impact Assessment
- Division Three of Environmental Impact Assessment
- Division of Environmental Check and Acceptance of Construction Projects
-
International Cooperation Office (国际 合作 司)
- Division of General and Foreign Affairs Management
- Division of International Organizations
- Division of Bilateral Cooperation
- Division of International Cooperation on Nuclear Safety
- Division of Regional Environmental Cooperation
- Secretariat of China Council for International Cooperation on Environment and Development
-
Department of Nuclear Safety (核 安全 管理 司)
- Division of Radioactive Environment and General Management
- Division One of Nuclear Power
- Division Two of Nuclear Power
- Division of Nuclear Reactors
- Division of Nuclear Fuels Management
- Division of Radioactive Wastes Management
- Division of Radioactive Sources and Electromagnetic Radiation management
- Division of Nuclear Equipment
-
Environmental Inspection Office (环境 监察 局)
- Division of General Management
- Division of Supervision Guidance
- Division of Pollutant Discharge Fees Management
- Division of Review and Punishment
-
Department of Education and Communications
- Division of News
- Division of General Management
guide
- Minister: Chen Jining
- Deputy: Pan Yue (潘岳)
Former Minister Xie Zhenhua (解振华) resigned from office in December 2005 following an explosion at a PetroChina AG plant . Around 100 tons of carcinogenic benzene had entered the Songhua River. Weeks after the incident, the benzene concentration exceeded government guidelines by 108 times. Even at the border with Jilin and Heilongjiang, the measured values were 29 times the guide value. The water supply for around 5 million people had to be cut off for a week. His successor, Zhou Shengxian , served until February 2015.
The Deputy Minister, Pan Yue (潘岳) remained in office. In an interview in March 2005, he warned that the Chinese economic miracle would end soon if sustainable development was not achieved soon.
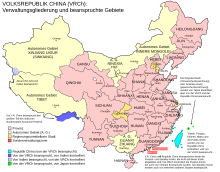
Local inspection and executive bodies
In 2006 SEPA opened five regional offices in addition to the office that had existed since 1988 in order to be able to carry out on-site inspections better:
- The MEP headquarters in Beijing is responsible for Tianjin , Hebei , Henan , Shanxi , and Inner Mongolia .
- East office: Office in Nanjing is responsible for Shanghai , Jiangsu , Zhejiang , Anhui , Fujian , Jiangxi , and Shandong .
- South Office: Office in Guangzhou is responsible for Hunan , Hubei , Guangdong , Guangxi , and Hainan .
- Northwest location: Office in Xi'an is responsible for Shaanxi , Gansu , Qinghai , Xinjiang , and Ningxia .
- Southwest Office: Office in Chengdu is responsible for Chongqing , Sichuan , Guizhou , Yunnan , and Tibet .
- Northeast location: Shenyang office is responsible for Liaoning , Jining , and Heilongjiang .
Assignments and publications
The MEP sets standards and monitors them in the areas of water, soil and air quality, waste, noise and radioactivity. It has published its results annually since 1999 in the report On the State of the Environment In China (SOE). The authority has been issuing its own bulletin every year since 2003 on the environmental impact of the Three Gorges Dam project . In addition, a statistical yearbook is published in collaboration with other authorities.
It also administers the meanwhile 11th five-year plan for national environmental protection (2006-2010), the purpose of which is to “identify central goals and private and public (political) fields of action, to define the responsibilities and tasks of the government and environmental protection authorities, and private participation Sector and civil society to lead and mobilize an environmentally friendly society. ”The plan puts the public expenditure for the project at € 75 billion per annum or 1.35% of the respective GDP . A further € 8 billion is to be borne by the private sector according to the polluter pays principle . With subsidies and fiscal concessions one also wants to create incentives for (especially development) banks to invest. Further funds are being made available by international donors. However, the SEPA White Paper on environmental protection eight times as much as the actual means that would be necessary to implement the project. An evaluation of the individual projects is planned for the end of 2008 and 2010. The goals of previous plans could not be realized. The main reasons for this are the lack of interaction between environmental and economic policy and underfunding of the targeted programs.
Challenges for future action
After the failure of the 10th five-year plan for national environmental protection , solutions for the problem of air pollution must be found and soot and SO 2 emissions must be sustainably reduced. The current five-year plan provides for a 10% cut by 2010 compared to 2006 levels, when 43.4% of the cities tested had air quality that is “harmful to health”. Acid rain incidence exceeded 5% in 32.6% of the cities tested .
Another key point of the MEP work will be water pollution . In 2006, three of the four rivers tested were found to have “harmful” water quality. Only two of the 27 lakes tested showed an "acceptable" quality. Cancer-related death rates from water pollution are estimated at 64 cases per 100,000 population. In addition to the health effects, high economic losses are also reported due to agricultural irrigation with polluted wastewater; As a result, roughly half of the 2003 rice harvest failed to meet food standards.
Web links
- Information text from the Federal Agency for Civic Education ( Sternfeld 2006)
- Position text ( memento from June 14, 2008 in the Internet Archive ) from the German Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development on environmental policy in China and German-Chinese cooperation .
- goethe.de/china - Article on the topic of environmental protection in China on the website of the Goethe-Institut China (in German, English, Chinese)
Individual evidence
- ↑ Official mandate on the website: “ Prevent and control environmental pollution, protect nature and ecology, supervise nuclear safety, safeguard public health and environmental safety, and promote the harmony between man and nature. ”
- ↑ Article in China Dialogue on February 5, 2007
- ↑ a b ( page no longer available , search in web archives: paper ) by Jianguo Liu and Jared Diamond January 2008
- ↑ a b c Environmental Performance Reviews: China (2007) OECD , July 2007
- ^ Organization chart ( Memento from April 14, 2008 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ China punishes river's polluters on BBC News Friday November 24, 2006
- ↑ Toxic water of polluted river reaches Harbin at China Daily Thursday, November 24, 2005
- ↑ Andreas Lorenz: The miracle will soon end . In: Der Spiegel . No. 10 , 2005, pp. 149 f . ( online - March 7, 2005 ).
- ^ Official announcement by SEPA (Chinese source) July 8, 2006
- ^ Publications of the MEP ( Memento of March 15, 2018 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ a b c d e f China National Environmental Protection Plan in the Eleventh Five-Years (2006-2010) ( Memento of April 14, 2008 in the Internet Archive ) (PDF; 278 kB), No. 39 document of the State Council 2005
- ↑ Wording in the document: “ … aims at expounding the objectives, tasks investment focuses and key policy measures in the field of environmental protection during the 11th Five-Year Plan period, identifying the responsibility and tasks of people's government and environmental protection departments at all levels , guiding and mobilizing the participation of enterprises and civil society and striving for environment-friendly society. ”
- ↑ The calculations are based on the BIP- IMF data and an exchange rate of US $ to € 0.68. Other sources assume stronger growth and put the GDP share correspondingly lower.
- ↑ a b Research paper (PDF; 1 MB) from Deutsche Bank on the “growth market” of the environmental sector in China, FRANK 2006
- ↑ Environmental Objectives and Investment Requirements for China 10th Five-Year Plan ( Memento of October 12, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) of the US Embassy in November 2000 for the 10th Five-Year Plan for National Environmental Protection , into which USD 4 billion flowed from international donors.
- ↑ i. e. 10% of GDP. See Environmental Protection in China (1996-2005) ( Memento from February 21, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) (PDF; 106 kB) Information Office of the State Council of the People's Republic of China, Beijing in June 2006
- ↑ The China Syndrome ( memento of November 19, 2008 in the Internet Archive ) by State Secretary Matthias Machnig , published on August 29, 2006 in the Handelsblatt
- ↑ a b c Cost of Pollution in China (PDF; 6.1 MB) joint report by the World Bank and SEPA, 2007
- ↑ SOE 2006 Atmospheric Environment, SEPA, 2006
- ↑ a b c d SOE 2006 Water Environment, SEPA 2006