Amomum is a plant genus in the subfamily Alpinioideae from the family of the ginger family (Zingiberaceae) that the monocots plants belongs. With up to 200 species, it is one of the two most species-rich genera in the Zingiberaceae family. Some species are used as aromatic and medicinal plants by humans.
description
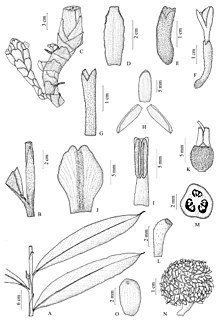
Illustration of
Amomum nilgiricum : A. Part of the pseudostem B. Ligula C. Inflorescence D.
Bract E. Bract E. Blossom G. Calyx H. Corolla lobe I. Fertile stamen J. Labellum K. Ovary with glands and style L. Scar N. fruit; from VP Thomas, M. Sabu, KM Prabhu Kumar: Amomum nilgiricum (Zingiberaceae), a new species from Western Ghats, India. 2012, doi: 10.3897 / phytokeys.8.2152

Illustration from
Indian Medicinal Plants and Drugs Wellcome by
Amomum aculeatum

Infructescence with prickly capsule fruits of
Amomum cf.
dealbatum
Vegetative characteristics
Amomum species are perennial herbaceous plants . They form widely creeping rhizomes as persistence organs.
Usually well-developed "pseudostems" are formed from mostly many, rarely only one to four leaves. The leaf sheath is long. The ligules are simple or bilobed. The leaf blades are elongated or lanceolate.
Generative characteristics
Directly from the rhizome, a terminal, racemose , spiky , paniculate inflorescence develops on a short to very long inflorescence stem covered with scale-shaped leaf sheaths, in which the flowers are close together. In many species the inflorescence looks like a cone. There is a support sheet . Each flower stands over a mostly tubular bract .
The hermaphrodite flowers are zygomorphic and threefold with double perianth . The three sepals are fused Roehrig. The three petals are fused tubular with an upright corolla lobe, which is longer, wider and more convex than the two lateral ones. Only the middle stamen of the inner circle is fertile ; it has a long, well-developed stamen . The appendages of the anthers are simple, two- or three-lobed. All other stamens are reduced to staminodes and at least one or three are missing. The two lateral staminodes of the outer circle are awl-shaped, small or absent. The middle staminodium of the outer circle is missing. The two lateral staminodes of the inner circle have grown together to form a so-called labellum ; it represents the most conspicuous part of the flower. The mostly obovate and broadly concave labellum is yellow to orange in the center, has some red veins or signs and often a white border. Three fruit leaves are a dreikammerigen ovary grown with many ovules in each ovary chamber. The thin stylus usually ends in a funnel-shaped, ciliate scar.
The irregularly shaped capsule fruits have a smooth, angular or prickly surface and contain many seeds. The rectangular or angular seeds have a fleshy or membranous aril .
Locations
The genus Amomum thrives almost only in tropical areas. Most Amomum species thrive as large, evergreen plants in moist forests, especially in clearings and on the edges of forests. There are also some epiphytes and, rarely, seasonal green, small plants in the herbaceous layer of the forests.
Systematics and distribution
The genus Amomum belongs to the tribe Alpinieae in the subfamily of the Alpinioideae within the family of the Zingiberaceae .
The genus Amomum was first established in 1753 by Carl von Linné in Monandria Monogynia with four species: Amomum zingiber , Amomum zerumbet , Amomum cardamomum and Amomum grana-paradisi . These four species belong to Aframomum K.Schum today . , Zingiber Boehm and Elettaria Maton . The current publication of the genus Amomum was made in 1820 by William Roxburgh in Plants of the Coast of Coromandel , 3, p. 75 with the type species Amomum subulatum Roxb. The generic name Amomum is derived from the Greek word ἄμωμον, amomon , which was used for an Indian species of aromatic plant. Synonyms for Amomum Roxb. are: Cardamomum Rumph. ex Kuntze , Conamomum Ridl. , Geocallis Horan. , Meistera Giseke , Paludana Giseke , Paramomum S.Q.Tong , Torymenes Salisb. nom. nud., Zedoaria Raf. , Litterbainia Giseke .
The previous division of the genus into two sub-genera can be found in Yong-Mei Xia et al. 2004 cannot be confirmed, and a division into sections is not possible with the current results from the molecular genetic investigations; well-confirmed clades are shown, but further investigation is required to clearly show the relationships.
The main distribution area is Southeast Asia . Individual species occur from the Himalayas through Southeast Asia to northern Australia and to the central Pacific region . There are 39 species in China , 29 of them only there.
The genus Amomum contains 150 to 200 species (new species are constantly being added):
-
Amomum aculeatum Roxb. (Syn .: Cardamomum ciliatum (flower) Kuntze , Amomum ciliatum flower , Amomum aurantiacum . Ridl , Amomum flavum . Ridl , Amomum hatuanum Náves , Amomum aculeatum . Var gymnocarpum Valeton , Amomum aculeatum var. Macrocarpum Valeton ): It is used in Thailand , Myanmar , Vietnam and from the Andamans to New Guinea .
-
Amomum acuminatum Thwaites : This endemic occurs in Sri Lanka only in the Ratnapura district.
-
Amomum agastyamalayanum V.P. Thomas & M. Sabu : It wasfirst describedin 2012 from the Indian state of Kerala .
-
Amomum alborubellum K.Schum. & Lauterb. : It occurs only in Papua New Guinea .
-
Amomum andamanicum V.P. Thomas, Dan & M. Sabu : It wasfirst describedby the Andamans in 2010.
-
Amomum angustipetalum S. Sakai & Nagam. : Sarawak .
-
Amomum anomalum R.W.Sm. : Borneo.
-
Amomum apiculatum K.Schum. : Sumatra.
-
Amomum aquaticum Raeusch. : Sri Lanka.
-
Amomum argyrophyllum Ridl. : Southern Thailand.
-
Amomum aromaticum Roxb. : Nepal to Bangladesh.
-
Amomum benthamianum Trimen : This endemic occurs in Sri Lanka only in the Kalutara district.
-
Amomum bicorniculatum K.Schum. : Kalimantan .
-
Amomum bicornutum Ridl. : Western New Guinea.
-
Amomum biflorum Jack : Malay Peninsula to Sumatra.
-
Amomum bilabiatum S. Sakai & Nagam. : It wasfirst describedin 1998 from Sarawak .
-
Amomum blumeanum Valeton : This endemic occurs only on the island of Java .
-
Amomum borealiborneense I.M. Turner (Syn .: Amomum sylvestre Ridl. Nom. Illeg., Amomum ridleyi R.M.Sm. nom. Illeg.): The valid name was published in 1998. The species is only found in Sarawak.
-
Amomum borneense (K.Schum.) RMSm. : It only occurs in Sarawak.
-
Amomum botryoideum Cowley : It wasfirst describedin 2000 from Brunei .
-
Amomum bulusanense Elmer : It only occurs on Luzon .
-
Amomum burttii R.M.Sm. : Sarawak.
-
Amomum calcaratum Lamxay & MFNewman : It wasfirst describedfrom Laos in 2012.
-
Amomum calcicolum Lamxay & MFNewman : It was first described from Laos in 2012.
-
Amomum calyptratum S. Sakai & Nagam. : It was first described in 1998 from Sarawak.
-
Amomum cannicarpum (Wight) Benth. ex Baker : Southwest India.
-
Amomum capsiciforme S.Q.Tong : It was first described in 1989. This endemic thrives in forests at altitudes of around 1400 meters only in Yingjiang County in western Yunnan.
-
Amomum carnosum V.P. Thomas & M. Sabu : It wasfirst describedin 2012 from Nagaland in Assam.
-
Amomum celsum Lamxay & MFNewman : It was first described in 2012. It occurs in Laos and Vietnam.
-
Amomum centrocephalum A.D.Poulsen : Northern Sumatra.
-
Amomum cephalotes Ridl. : Malay Peninsula.
-
Amomum cerasinum Ridl. : Western and Central Sumatra and Sarawak.
-
Amomum chaunocephalum K.Schum. : Papua New Guinea.
-
Amomum chevalieri Gagnep. ex Lamxay : Vietnam.
-
Amomum chinense W.Y.Chun : It thrives in forests in Hainan , Thailand, Cambodia, Laos and Vietnam.
-
Amomum chryseum Lamxay & MFNewman : Laos.
-
Amomum compactum Sol. ex Maton (Syn: Amomum cardamomum Willd. sensu auct., Amomum kepulaga Sprague & Burkill ): It is native to Sumatra and western Java . It is used as a medicinal plant.
-
Amomum conoideum (Ridl.) Elmer : Philippines.
-
Amomum coriaceum R.M.Sm. : Sarawak.
-
Amomum coriandriodorum S.Q.Tong & YMXia : It thrives in forests at altitudes of 1300 to 1500 meters in southern Yunnan and northern Thailand.
-
Amomum cylindraceum Ridl. : Malay Peninsula to Sumatra.
-
Amomum dallachyi F. Muell. : Northern Queensland.
-
Amomum dampuianum V.P. Thomas , M. Sabu & Lalramngh. : It wasfirst describedin 2013 from Mizoram in Assam.
-
Amomum dealbatum Roxb. : It occurs in Yunnan, Bangladesh , India, Sikkim , Thailand , Laos, Cambodia, Myanmar, Vietnam, in eastern Nepal and maybe also on Sumatra.
-
Amomum deorianum D.P.Dam & N.Dam : It occurs in the Indian state of Meghalaya .
-
Amomum deuteramomum K.Schum. : Northern Sulawesi.
-
Amomum dictyocoleum K. Schum. : Sarawak.
-
Amomum dimorphum M.F.Newman (Syn .: Alpinia polycarpa K.Schum. , Amomum polycarpum (K.Schum.) RMSm. Nom. Illeg.): The valid name was published in 2001. This endemic occurs only in Sarawak.
-
Amomum dolichanthum D.Fang : This endemic thrives in forests only in Longzhou Xian in southwestern Guangxi. It is used as a medicinal plant.
-
Amomum durum S. Sakai & Nagam. : Sarawak.
-
Amomum echinatum Willd. : India and Sri Lanka.
-
Amomum echinocarpum Alston : Sri Lanka, Laos, Java, Sulawesi, New Guinea and Bismarck Archipelago.
-
Amomum elegans Ridl. : Philippines.
-
Amomum elephantorum Pierre ex Gagnep. : Thailand, Cambodia, Laos and Vietnam.
-
Amomum epiphyticum R.M.Sm. : Sarawak.
-
Amomum flavidulum Ridl. : Sarawak.
-
Amomum flavoalbum R.M.Sm. : Sarawak.
-
Amomum flavorubellum K.Schum. & Lauterb. : Papua New Guinea.
-
Amomum fragile S.Q.Tong : It was first described in 1989. This endemic thrives in forests only in Menghai County in southwestern Yunnan.
-
Amomum fulviceps Thwaites : It occurs in Sri Lanka and southwest India.
-
Amomum gagnepainii T.L.Wu, K.Larsen & Turland (Syn .: Amomum thyrsoideum Gagnep. Non Ruiz & Pavón ): It was first described in 2000. It occurs in southwest Guangxi and northern Vietnam.
-
Amomum garoense S.Tripathi & V.Prakash : It wasfirst describedin 1999 from Assam .
-
Amomum ghaticum K.G.Bhat : Southwest India.
-
Amomum glabrifolium Lamxay & MFNewman : It was first described from Laos in 2012.
-
Amomum glabrum S.Q.Tong : It was first described in 1989. This endemic thrives in forests at altitudes of around 700 meters only in Mengla Countyin southwestern Yunnan and in Laos.
-
Amomum globba J.F. Gmel . : Thailand.
-
Amomum gracile flower : Western Sumatra to Java.
-
Amomum gramineum Wall. ex Baker : Myanmar.
-
Amomum graminifolium Thwaites : Sri Lanka.
-
Amomum gymnopodum K.Schum. : South Sulawesi.
-
Amomum gyrolophos R.M.Sm. : Western Sumatra and Sarawak.
-
Amomum hansenii R.M.Sm. : Sarawak.
-
Amomum hastilabium Ridl. : Thailand, Malaysia and Sumatra.
-
Amomum hedyosmum I.M. Turner (Syn .: Amomum trilobum Ridl. Nom. Illeg.): The valid name was published in 2000. The species occurs in the Philippines.
-
Amomum hirticalyx K.Schum. : It only occurs in Thailand.
-
Amomum hochreutineri Valeton : Java.
-
Amomum holmesii K.Schum. : Southwest India.
-
Amomum hypoleucum Thwaites : Southern India, Sri Lanka and Malay Peninsula.
-
Amomum irosinense (Elmer) Merr. : Luzon.
-
Amomum jainii S. Tripathi & V. Prakash : It was first described in 1999. This endemic occurs in Assam only in Meghalaya .
-
Amomum jingxiense D.Fang & DHQin : It was first described in 1989. This endemic thrives in forests at altitudes of around 1300 meters only in Jingxi County in western Guangxi .
-
Amomum kinabaluense R.M.Sm. : It wasfirst describedin 1987 from Sabah .
-
Amomum kingii Baker : It only occurs in Sikkim.
-
Amomum koenigii J.F. Gmel. (Syn .: Amomum corynostachyum Wall. ): It occurs in Assam , Bangladesh, Thailand, Myanmar, Laos, Vietnam and in the Chinese provinces of Guangxi and Yunnan.
-
Amomum kwangsiense D.Fang & XXChen : It thrives in forests at altitudes of 600 to 700 meters in the Chinese provinces of Guangxi and Guizhou . It is used as a medicinal plant.
-
Amomum lacteum Ridl. : Southeast Vietnam.
-
Amomum lambirense R.M.Sm. : Sarawak.
-
Amomum laoticum Gagnep. : Laos.
-
Amomum lappaceum Ridl. : Thailand, Malaysia, Sumatra, Java.
-
Amomum laxisquamosum K.Schum. : Sumatra, Sarawak.
-
Amomum lepicarpum Ridl. : Philippines.
-
Amomum ligulatum R.M.Sm. : Borneo.
-
Amomum linearifolium Elmer : Luzon.
-
Amomum loheri K. Schum. : Luzon.
-
Amomum longiligulare T.L.Wu : It thrives in forests in Hainan and from Guangdong to Thailand, Laos and Vietnam. It is grown as a medicinal plant.
-
Amomum longipedunculatum R.M.Sm. : Sabah.
-
Amomum longipes Valeton : Sumatra.
-
Amomum longipetiolatum Merr. : It thrives in forests at altitudes of 400 to 600 meters in the Chinese province of Guangxi and in northern Vietnam.
-
Amomum lophophorum (Ridl.) Elmer : Philippines.
-
Amomum luteum R.M.Sm. : Sarawak.
-
Amomum luzonense Elmer : Philippines.
-
Amomum macrodons Scort. : Malay Peninsula.
-
Amomum macroglossa K.Schum. : Malay Peninsula and Sarawak.
-
Amomum masticatorium Thwaites : Sri Lanka.
-
Amomum maximum Roxb. : It occurs in tropical and subtropical Asia. It is used as a medicinal plant.
-
Amomum meghalayense V.P. Thomas, M. Sabu & Sanoj : It wasfirst describedin 2016 from Meghalaya in Assam.
-
Amomum menglaense S.Q.Tong :: It was first described in 1991. This endemic thrives in forests at altitudes of around 1800 meters only in Mengla Countyin southern Yunnan.
-
Amomum mengtzense H.T.Tsai & PSChen : It occurs in southern Yunnan.
-
Amomum mentawaiense A.J.Droop : It wasfirst describedin 2014 from Sumatra .
-
Amomum micranthum Ridl. : Malay Peninsula.
-
Amomum microcarpum C.F.Liang & D.Fang : This endemic thrives in dense forests at altitudes of 300 to 500 meters only in Dongxing Countyin southern Guangxi and in Laos and Vietnam. It is used as a medicinal plant.
-
Amomum microcheilum (Ridl.) Merr. : Philippines.
-
Amomum mindanaense Elmer : Mindanao.
-
Amomum mizoramense M. Sabu , VP Thomas & Vanchh. : It was first described in 2013 from Mizoram in Assam.
-
Amomum molle Ridl. (Syn .: Amomum rivale Ridl. ): Thailand and Malay Peninsula.
-
Amomum muricarpum Elmer : It occurs in the Philippines, in the Chinese provinces of Guangdong and Guangxi as well as in Laos and Vietnam. It is used as a medicinal plant.
-
Amomum muricatum Bedd. : Southern India.
-
Amomum nemorale (Thwaites) Trimen : Sri Lanka.
-
Amomum neoaurantiacum T.L.Wu, K.Larsen & Turland (Syn .: Amomum aurantiacum H.T.Tsai & SWZhao nom. Illeg. Non Ridl. ): The valid name was published in 2000. The species thrives in forests at altitudes of around 600 meters in southern Yunnan. It is used as a medicinal plant.
-
Amomum newmanii M.Sabu & VPThomas : It wasfirst describedin 2012 from the Indian state of Kerala .
-
Amomum nilgiricum V.P. Thomas & M. Sabu : It was first described in 2012 from the Indian state of Kerala.
-
Amomum nimkeyense M.Sabu, Hareesh, Tatum & AK That : It wasfirst describedin 2018 from the Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh .
-
Amomum ochreum Ridl. : Malay Peninsula to Sumatra.
-
Amomum odontocarpum D.Fang : It thrives in sparse forests at altitudes of around 1500 meters in Guangxi, but also in Laos and Vietnam.
-
Amomum oliganthum K.Schum. : Borneo.
-
Amomum oligophyllum AJDroop : It wasfirst describedfrom Sumatra in 2014.
-
Amomum palawanense Elmer : Palawan .
-
Amomum paratsaoko S.Q.Tong & YMXia : It was first described in 1988. It thrives in forests at altitudes of around 1,600 meters in the Chinese provinces of Guangxi, Guizhou and Yunnan.
-
Amomum pauciflorum Baker : It occurs in Meghalaya in Assam.
-
Amomum paucifolium R.M.Sm. : Sarawak.
-
Amomum pellitum Ridl. : Western New Guinea.
-
Amomum petaloideum (SQTong) TLWu (Syn .: Paramomum petaloideum S.Q.Tong ): This new combination took place in 1997. This endemic thrives in forests at altitudes of 500 to 600 meters in Mengla Countyin southern Yunnan and northwestern Laos.
-
Amomum pierreanum Gagnep. : Thailand and Cambodia.
-
Amomum plicatum Lamxay & MFNewman : It was first described from Laos in 2012.
-
Amomum prionocarpum Lamxay & MFNewman : It was first described from Laos in 2012.
-
Amomum propinquum Ridl. : Philippines.
-
Amomum pterocarpum Thwaites : Southern India and Sri Lanka.
-
Amomum pubescens (Ridl.) Merr. : Philippines.
-
Amomum pubimarginatum Elmer : Mindanao .
-
Amomum pungens R.M.Sm. : Sarawak.
-
Amomum purpureorubrum S.Q.Tong & YMXia : It was first described in 1988. This endemic thrives in forests at altitudes of 1,600 to 1,700 meters only in Menghai County in southwestern Yunnan.
-
Amomum putrescens D.Fang : This endemic thrives in forests at altitudes of around 300 meters only in Dongxing Countyin southern Guangxi.
-
Amomum quadratolaminare S.Q.Tong : It was first described in 1989. It thrives in forests at altitudes of around 800 meters only in southern Yunnan.
-
Amomum queenslandicum R.M.Sm. : New Guinea to northern Queensland.
-
Amomum repoeense Pierre ex Gagnep. : It occurs in Cambodia , Thailand, Laos, Vietnam and southern Yunnan.
-
Amomum riwatchii M. Sabu & Hareesh : It wasfirst describedin 2018 from the Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh .
-
Amomum robertsonii Craib : Myanmar.
-
Amomum roseisquamosum Nagam. & S.Sakai : Sarawak.
-
Amomum rubidum Lamxay & NSLý : It was first described from Vietnam in 2012.
-
Amomum sabuanum V.P. Thomas , Nissar & U.Gupta : It wasfirst describedin 2014 from Sikkim .
-
Amomum sahyadricum V.P. Thomas & M. Sabu : It was first described in 2013 from southwest India.
-
Amomum scarlatinum H.T.Tsai & PSChen : It thrives in damp locations, roadsides at altitudes of around 900 meters in Yunnan.
-
Amomum sceletescens R.M.Sm. : Borneo.
-
Amomum schlechteri K. Schum. : Papua New Guinea.
-
Amomum schmidtii (K.Schum.) Gagnep. : Thailand, Cambodia, Laos, Vietnam.
-
Amomum sericeum Roxb. : It occurs from Sikkim to southern Yunnan, in Thailand, Myanmar, Cambodia, Laso and Vietnam.
-
Amomum siamense Craib : Thailand.
-
Amomum somniculosum S. Sakai & Nagam. : Borneo.
-
Amomum spiceum Ridl. : Malay Peninsula.
-
Amomum squarrosum Ridl. : Malay Peninsula.
-
Amomum staminidivum Gobilik, ALLamb & ADPoulsen : It wasfirst describedin 2004 from Borneo .
-
Amomum stenocarpum Valeton : Sumatra.
-
Amomum stephanocoleum Lamxay & MFNewman : It was first described in Laos in 2012.
-
Amomum subcapitatum Y.M.Xia : It was first described in 1997. This endemic thrives in forests at altitudes of around 900 meters in Yingjiang County in western Yunnan, but also in Thailand, Laos and Vietnam.
-
Black cardamom ( Amomum subulatum Roxb. ): It is common from northern India, Bangladesh, Nepal , Assam, Bhutan, Sikkim, Myanmar and Tibet to the Chinese provinces of Guangxi and Yunnan.
-
Amomum tenellum Lamxay & MFNewman : It was first described in 2012. It occurs in Laos and Vietnam.
-
Amomum tephrodelphys K.Schum. : Northern Sumatra.
-
Amomum terminale Ridl. : Bismarck Archipelago .
-
Amomum testaceum Ridl. : Southern China to the Malay Peninsula and Sabah.
-
Amomum thysanochililum S.Q.Tong & YMXia : It was first described in 1988. It thrives in forests at altitudes of around 800 meters only in southern Yunnan.
-
Amomum tomrey Gagnep. : It occurs in two varieties in Thailand, Cambodia, Laos and Vietnam.
-
Amomum trianthemum K.Schum. : Northern Sulawesi.
-
Amomum trichanthera Warb. : Papua New Guinea.
-
Amomum trichostachyum Alston : Sri Lanka.
-
Amomum tsao-ko Crevost & Lem. (Syn .: Amomum hongtsaoko C.F. Liang & D.Fang ): It thrives in light forests at altitudes of 1100 to 1800 meters in Yunnan, Laos and Vietnam. It is used as a medicinal plant.
-
Amomum tuberculatum D.Fang : It thrives in forests at altitudes of 1500 to 1800 meters in Guangxi.
-
Amomum vermanum S. Tripathi & V. Prakash : It was first described in 2000 from Assam.
-
Amomum verrucosum S.Q.Tong : It was first described in 1989. It thrives in forests at altitudes of around 800 meters in southern Yunnan.
-
Amomum verum Blackw. : Thailand, Cambodia, Vietnam and Sumatra.
-
Amomum vespertilio Gagnep. : Northern Vietnam.
-
Amomum villosum Lour. : There have been three varieties since 2014:
-
Amomum villosum Lour. var. villosum (Syn .: Amomum echinosphaera K.Schum. ): It occurs from Bangladesh to Thailand, Cambodia, Laos and Vietnam and is grown at altitudes of 100 to 600 meters in the Chinese provinces of Fujian, Guangdong, Guangxi and Yunnan.
-
Amomum villosum var. Xanthioides (Wall. Ex Baker) TLWu & SJChen : It occurs originally in Myanmar and in the Chinese provinces of Guangxi and Yunnan.
-
Amomum villosum var. Zeylanicum Karun. & Yakand. : It was first described from Sri Lanka in 2014.
-
Amomum warburgianum K.Schum. & Lauterb. : Papua New Guinea.
-
Amomum warburgii (K.Schum.) K.Schum. : Mindanao.
-
Amomum xanthophlebium Baker : Malaysia, Sumatra and Sarawak.
-
Amomum yingjiangense S.Q.Tong & YMXia : It was first described in 1989. This endemic thrives in forests at altitudes of around 1700 meters only in Yingjiang County in western Yunnan.
-
Amomum yunnanense S.Q.Tong : It was first described in 1990. This endemic thrives in forests at altitudes of around 1200 meters only in Yingjiang County in western Yunnan.
For example, no longer belongs to the genus Amomum :
|
use
Many Amomum species (see species list above for examples) are used in traditional Chinese medicine. Amomum tsaoko is a food crop in China. Black cardamom ( Amomum subulatum ) is used as a spice.
swell
- Delin Wu, Kai Larsen: Zingiberaceae. : Amomum , p. 347 - the same text online as the printed work , In: Wu Zheng-yi, Peter H. Raven (Ed.): Flora of China. Volume 24: Flagellariaceae through Marantaceae , Science Press and Missouri Botanical Garden Press, Beijing and St. Louis, 2000, ISBN 0-915279-83-5 . (Section description)
- Yong-Mei Xia, W. John Kress, Linda M. Prince: Phylogenetic Analyzes of Amomum (Alpinioideae: Zingiberaceae) Using ITS and matK DNA Sequence Data , In: Systematic Botany , Volume 29, Issue 2, 2004, pp. 334-344 : doi : 10.1600 / 036364404774195520 (sections systematics and distribution)
- Amomum at e-monocot.org .
Individual evidence
-
^ A b William Roxburgh: Plants of the Coast of Coromandel , 3, 1820, p. 75 scanned at biodiversitylibrary.org.
-
↑ Amomum in the Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN), USDA , ARS , National Genetic Resources Program. National Germplasm Resources Laboratory, Beltsville, Maryland.
-
↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc bd be bf bg bh bi bj bk bl bm bn bo bp bq br bs bt bu bv bw bx by bz ca cb cc cd ce cf cg ch ci cj ck cl cm cn co cp cq cr cs ct cu cv cw cx cy cz da db dc dd de df dg dh di dj dk dl dm dn do dp dq dr ds dt du dv dw dx dy dz ea eb ec ed ee ef eg eh ei ej ek el em en eo ep eq er es et eu ev ew ex ey ez fa fb fc fd fe ff fg fh fi fj fk fl fm fn fo fp fq fr fs ft fu fv fw fx fy fz ga gb gc gd ge gf gg gh gi gj gk gl gm gn go gp gq gr gs gt gu gv gw gx gy
Rafaël Govaerts (Ed.): Amomum. In: World Checklist of Selected Plant Families (WCSP) - The Board of Trustees of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew . Retrieved August 14, 2018.
-
↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap
Delin Wu, Kai Larsen: Zingiberaceae . : Amomum , p. 347 - the same text online as the printed work , In: Wu Zheng-yi, Peter H. Raven (Ed.): Flora of China. Volume 24: Flagellariaceae through Marantaceae , Science Press and Missouri Botanical Garden Press, Beijing and St. Louis, 2000, ISBN 0-915279-83-5 .
Web links
Paul Wagler : Amomon . In: Paulys Realencyclopadie der classischen Antiquity Science (RE). Volume I, 2, Stuttgart 1894, Sp. 1873 f.
This article is about a health issue. It is
not used for self-diagnosis and
does not replace a diagnosis by a doctor. Please
note the information
on health issues !

























