Burbach (Siegerland)
| coat of arms | Germany map | |
|---|---|---|

|
Coordinates: 50 ° 45 ' N , 8 ° 5' E |
|
| Basic data | ||
| State : | North Rhine-Westphalia | |
| Administrative region : | Arnsberg | |
| Circle : | Siegen-Wittgenstein | |
| Height : | 380 m above sea level NHN | |
| Area : | 79.72 km 2 | |
| Residents: | 14,856 (Dec. 31, 2019) | |
| Population density : | 186 inhabitants per km 2 | |
| Postal code : | 57299 | |
| Area code : | 02736 | |
| License plate : | SI, BLB | |
| Community key : | 05 9 70 008 | |
| LOCODE : | DE BUH | |
| Community structure: | 9 districts | |
| Address of the municipal administration: |
Eicher Weg 13 57299 Burbach |
|
| Website : | ||
| Mayor : | Christoph Ewers ( CDU ) | |
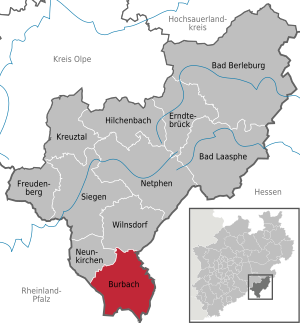
| Location of the municipality of Burbach in the Siegen-Wittgenstein district | ||
Burbach is a municipality in the Siegen-Wittgenstein district in North Rhine-Westphalia .
geography
The municipality of Burbach is located in the Siegerland between the northeastern foothills of the Westerwald and the southeastern foothills of the Rothaargebirge. It lies west of the Höh in the valley of the Heller , which is an eastern tributary of the Sieg . The municipality of Burbach is the southernmost in Westphalia . For example, mountains belong
- Walkersdorfer Berg with 526 m
- The castle with 591.4 m or
- Simberg with a height of 527.7 m .
Neighboring communities
- in the Siegen-Wittgenstein district : Wilnsdorf and Neunkirchen
- in the Lahn-Dill district : Haiger and Breitscheid
- in the Westerwaldkreis : Liebenscheid and Stein-Neukirch
- in the district of Altenkirchen (Westerwald) : Emmerzhausen and Daaden
Community structure
The community of Burbach consists of the districts of the "Upper Free Ground" :
- Burbach,
- Wahlbach ,
- Würgendorf ,
- Gilsbach
- lip
as well as from the villages of the Hickengrund :
history
Approx. 500-400 BC Celtic - Germanic tribes discovered iron ore, built the first smelting furnaces and built the hill fort on the castle hill. From around 700 the Franconian settlement took place .
The region was first mentioned in the 11th century. On April 28, 1048, a written document describes the Burbach and Neunkirchen areas as “praedium virorum liberorum”, that is, the area of free men, hence the name “Free reason”. In the 11th century one was church built and from the year 1219, the first written record dates of the name "Burbach". In 1367 the Snorrenburg was destroyed on the Römer in the center of Burbach. The dual power of Nassau and Sayn develops. The first mentioned Nassau Vogt in Burbach in 1467 was Gerhard Buckinck. Nassau and Sayn founded a joint court in Burbach in 1478, but it remained controversial. In 1530 the parish of Burbach became Lutheran and in 1568 William of Orange gathered his troops on the Ginsberger Heide. In 1584 the parish of Burbach was reformed. In 1607 Der Hickengrund, previously part of the Haiger court, was subordinated to the Burbach bailiwick.
In the Thirty Years' War , the Burbach Bailiwick had to provide workers to expand the Dillenburg castle fortifications. 1743–1806 Nassau government by the Orange Court in The Hague through the administration in Dillenburg. On July 4, 1758, more than 160 buildings fell to rubble in the great fire of Burbach, the old bailiwick remains standing. In 1760, numerous families emigrated to America. In 1774 the now dilapidated nave was demolished. Two years later the first service took place in the rebuilt but not yet completely finished church. In 1780 a new organ was purchased for the new church. In 1799 the dual rule in Freie Grund came to an end through marriage. In the same year on July 3, a fire destroyed 21 residential buildings and associated courtyards in Burbach. In 1806 the Freie Grund and the Hickengrund remained Nassau, while the rest of the Siegerland became part of the Grand Duchy of Berg .
On October 26, 1816, Prussia took possession of the Burbach area as a result of the Congress of Vienna for the reorganization of Europe after the Napoleonic era. A year later than the rest of the Siegerland, Burbach came to Prussia and was initially ruled from Koblenz . In 1817 the Siegen district was formed within Westphalia . In 1844, the Burbach office was created from the mayor offices of Dresselnorf , Neunkirchen and Burbach, which were formed 30 years earlier . In 1848 the district court and today's medical center was built on Jägerstrasse.
In 1860 a connection to today's B 277 was built. On July 1, 1861, the Betzdorf-Burbach railway line and on January 12, 1861, the Burbach-Dillenburg railway line were added. The Burbach Voluntary Fire Brigade was founded in 1876 and electricity came to Burbach from 1905. In the same year, today's town hall was occupied. In 1907 the Peterszeche , the largest mine in the municipality, stopped mining. During the Second World War, air raids took place in 1944 and on March 29, 1945, Burbach was captured by the Americans.
By the local government reform in the winning country of was due to the Second Law on the restructuring of the district wins the greater community of Burbach on 1 January 1969 by a summary of the previously independent and the Office Burbach member municipalities Burbach, Gilsbach, Holzhausen, Lippe, Lützeln, Niederdresselndorf, Oberdresselnorf, Wahlbach and Würgendorf. In 1976 the district court was closed. In 1982 the Alte Vogtei, the oldest half-timbered house in Burbach, was restored. From 1983 to 1989 the “Living and Working in Burbach” museum was set up and set up in the former tithe barn of the Bailiwick. In 1986 the Bürgerhaus Burbach was inaugurated.
Between 1994 and 1998 the Herbig house, which dates back to the 17th century, was acquired by the “Alte Vogtei” local history association. The building was restored in accordance with a listed building. In 1999 the bypass road through the Leimkaute, north of the center of Burbach, was built.
Population development
Official population of the municipality of Burbach since its foundation
|
|
|
|
|
Core town of Burbach
Population of the core town of Burbach
|
|
|
Numbers of houses in the core town of Burbach
| year | 1447 | 1548 | 1589 | 1698 | 1704 | 1706 | 1725 | 1788 | 1810 | 1846 | 1850 | 1867 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Houses | 20th | 48 | 48 | 60 | 71 | 71 | 75 | 81 | 81 | 110 | 112 | 127 |
politics
Municipal council
After the local elections on May 25, 2014, the 32 seats of the municipal council are distributed as follows:
| CDU | SPD | GREEN | total | |
| 2014 | 19th | 10 | 3 | 32 |
The FDP, which previously had three seats, has left the municipal council.
mayor
Mayor is Christoph Ewers (* 1962) (CDU). He was elected mayor in 2003 and re-elected in 2009 and 2014. His predecessors included Hermann-Josef Droege, Volkmar Klein and Hartmut Hering, who was elected on October 19, 1989 (all CDU).
Coat of arms and banner
coat of arms
The municipality was granted the right to use a coat of arms and a flag (banner shape) with a certificate from the District President Arnsberg dated July 20, 1970.
Blazon : “Split by blue and gold; in front an upright, red-armored, golden lion accompanied by six golden clapboards, behind three stake-like, butting, upright black diamonds. "
The lion stands for the Princely House of Nassau-Siegen. The three diamonds come from the Lords of Seelbach, who controlled the community in the Middle Ages.
banner
Description of the banner: "From yellow to blue striped lengthways with the municipal coat of arms in the shield in the upper half."
Town twinning
There has been an official twinning with the Czech city of Tanvald since 2007 , after a declaration of friendship between the two cities had already been made in 1995.
Culture and sights
- The Evangelical Reformed Church is worth seeing
Buildings
Natural monuments
Economy and Infrastructure
traffic
The A 45 motorway (Sauerland line) runs through the municipality in the northeast . In addition, the municipality in the east is opened up by the B 54 , which runs from Siegen in the direction of Limburg an der Lahn .
The community is connected to the Deutsche Bahn AG network via the Hellertalbahn (RB96) from Betzdorf to Haiger . In Haiger there are connections in the direction of Siegen and Gießen / Frankfurt am Main and in Betzdorf in the direction of Siegen and Cologne . The station is served by the RB 96 Betzdorf – Dillenburg line of the Hessian State Railway . Freight traffic is carried out through the Siegen-Wittgenstein circular railway .
There are bus connections through the VGWS to all neighboring communities, which are operated by the VWS . The central transfer point is the Burbach Post stop , which is linked to the Burbach train station (Kr Siegen) .
- RB96 Betzdorf - Herdorf - Neunkirchen - Burbach - Würgendorf - Haiger - Dillenburg
- R24 / R22 to Neunkirchen / Siegen ZOB and Hbf. , Connection with Abellio Rail NRW to Hagen / Essen
- In Neunkirchen there is also a connection to Herdorf and Daaden with the R23 line and with the Hellertalbahn to Betzdorf
- R25 to Haiger-Kalteiche - Wilnsdorf - Siegen ZOB and Hbf, connection with Abellio Rail NRW to Hagen / Essen
- SB4 to Wahlbach - Gilsbach - Oberwilden - Wilnsdorf - Siegen ZOB and Hbf, connection with Abellio Rail NRW to Hagen / Essen
- L220 Würgendorf - Holzhausen - Niederdresselnorf - Oberdresselnorf - Lützeln
- L221 Wahlbach - Gilsbach
- L222 Lippe / Siegerland Airport
- BBB1 Burbach, local traffic
- BBB2 Burbach – Gilsbach – Wahlbach
- BBB3 Burbach – Lippe
The Citizen Bus Burbach has been running since 2007.
Siegerland Airport is located in the south of the municipality .
Personalities
Sons and daughters of the community who were born or worked in Burbach
- Wilhelm Killing (1847–1923), mathematician
- Werner Kolb (1895–1975), engineer and major general of the reserve
- Ewald Sahm (1904–1979), mayor, community director, district member, entrepreneur, holder of the Federal Cross of Merit
- Hermann Schmidt (1917–1983), politician
- Ulrich Eibach (born October 16, 1942), former professor for systematic theology and ethics at the Evangelical Theological Faculty of the University of Bonn and until the end of 2007 clinic pastor and representative of the Evangelical Church in the Rhineland for further training and questions of ethics in biology and medicine .
- Falk Heinrichs (* 1960), politician
- Markus Hering (* 1960), actor and ensemble member at the Vienna Burgtheater
- Volkmar Klein (* 1960), politician
- Dirk Müller (* 1975), German racing car driver
- Cem İslamoğlu (* 1980), German-Turkish soccer player
- Christian Dünnes (* 1984), German national volleyball player and participant in the 2012 Olympic Summer Games
See also
literature
- Kurt Becker: Our fathers - the miners of the Bautenberg mine between Gilsbach and Wilden, Dill and Westerwald , Dillbrecht 1994
Web links
- Website of the municipality of Burbach
- Burbach in the Westphalia Culture Atlas
Individual evidence
- ↑ Population of the municipalities of North Rhine-Westphalia on December 31, 2019 - update of the population based on the census of May 9, 2011. State Office for Information and Technology North Rhine-Westphalia (IT.NRW), accessed on June 17, 2020 . ( Help on this )
- ↑ Siegen Document Book Volume I, Siegen , 1887, p. 8, no. 7.
- Jumped back ... , Siegener Zeitung of July 30, 2011, p. 43
- ↑ Martin Bünermann: The communities of the first reorganization program in North Rhine-Westphalia . Deutscher Gemeindeverlag, Cologne 1970, p. 69 .
- ↑ State database NRW
- ↑ 700 years of Neunkirchen , Otto Braun Verlag, Neunkirchen 1988
- ^ Otto Schaefer: The district of Siegen , Siegen 1968
- ^ A b c Michael Rademacher: German administrative history from the unification of the empire in 1871 to reunification in 1990. City and district of Siegen. (Online material for the dissertation, Osnabrück 2006).
- ↑ Westfälisches Gemeindelexikon 1897, pp. 110/111
- ↑ gemeindeververzeichnis.de: District of Siegen
- ↑ Heinrich Gamann: history of free reason , pressure of the West German publishing house, Neunkirchen 1925, p. 6
- ↑ genealogy.net: Office Burbach
- ↑ Martin Bünermann, Heinz Köstering: The communities and districts after the municipal territorial reform in North Rhine-Westphalia . Deutscher Gemeindeverlag, Cologne 1975, ISBN 3-555-30092-X , p. 173 .
- ↑ Rolf Betz: Burbach ( Memento of the original from November 25, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (PDF; 7.4 MB) , approx. 1995
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l E. Weidenbach: History of the County of Sayn and the components of the same , print E. Weidenbach, Dillenburg 1874, p. 287.
- ^ Burbach, Council election
- ^ "Siegerland Chronicle from September 1, 1989 to August 31, 1990", Siegerländer Heimatkalender 1991, pp. 173, 174, 66th edition, published by Siegerländer Heimat- und Geschichtsverein e. V., publishing house for local literature
- ↑ Main statute of the municipality of Burbach, § 2. Accessed on January 31, 2013 .