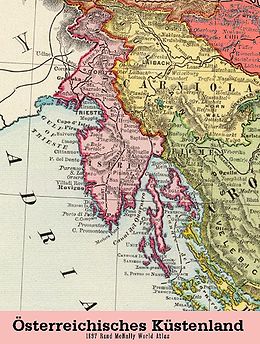
Austrian coastal country
The Austrian coastal lands (mostly plural, also known as Latin Litorale , Italian Litorale Austriaco , Slovenian Avstrijska Primorska , Croatian Austrijsko Primorje , Hungarian Tengermellék ) had been the Habsburg possessions on the upper Adriatic since the 14th century .
From 1849–1861 the Austrian coastal land was its own crown land in the Austrian Empire , until 1918 the Austrian-Irish coastal land the collective name for the three Austrian crown lands, cisleithan after 1867
- Margraviate of Istria ,
- Gorizia and Gradisca and princely counties
- The imperial city of Trieste and its territory
until the break-up of Austria-Hungary in 1918.
history
The individual countries and individual regions came under Habsburg rule at very different times: in 1335 the Carniola as hinterland, then from 1366 to 1476 Duino and Fiume (Rijeka) on the Adriatic, 1374 Istria , 1382 Trieste , 1500 the Inner County of Gorizia , 1717 Gradisca , last in 1797 on the west coast of Istria. Until 1849, the coastal regions were part of the Austrian administrative unit, Kingdom of Illyria, created in the post-Napoleonic period .
In 1849 the coastal land was formally crowned with Trieste as its capital.
With the imperial constitution of 1861, the three constituent parts of the coastal land acquired their status as independent crown lands with a state parliament, state committee and governor appointed by the emperor , but the common imperial governor (state chief) for the Austro-Irish coastal state in Trieste and the common state law gazette (not common Laws, joint publication only) received until 1918.
At the end of the First World War , the coastal area was occupied by the Italian army in early November 1918; in the Treaty of Saint Germain (September 10, 1919) it was granted to Italy under international law. After the Second World War it fell to Yugoslavia (excluding Gorizia and Trieste) .
Today, Istria is largely part of Croatia and the northernmost part of Slovenia . The term coastal land lives on today in the Slovenska Primorska region and the formerly Transleithan bordering Hrvatsko Primorje .
| Quartered, at the top split diagonally in silver and red and a golden lion for Gorizia, and the anchor cross of Gradisca, at the bottom in front double-headed eagle and glaive for Trieste, behind Istria billy goat . Above the Illyrian serrated crown (heathen crown, crown of David) |
geography
The coastal land had a size of about 8,000 km² and in 1910 around 900,000 inhabitants. Almost half of the population were Italians , a quarter Slovenes , a fifth Croatians and 5% Germans .
As the largest sea and trading port of the Danube monarchy, Trieste had enormous economic importance for the monarchy; the opening of the Vienna-Trieste railway line in 1857 was correspondingly important.
Due to the emerging tourism, the coast of Gorizia and Istria - north and south of Trieste and around Abbazia - was nicknamed the Austrian Riviera .
Administrative division (1868–1918)
Gorizia and Gradisca, Princely County
- Districts
- Judicial districts
Istria, margraviate
- Districts
- Judicial districts
Trieste, imperial city, with its territory
- Trieste , own jurisdiction
See also
Web links
- Meyers Konversations-Lexikon: Coastal country, Austrian-Illyrian
- Flag lexicon
- E. Oberegger, Brief Railway History of the Austrian Coastal Country (2017)
Individual evidence
-
↑ 1366 land near San Giovanni di Duino after the submission of Haug (Hugo) von Tybein / Duino ; cf. Andreas Helmedach: The transport system as a modernization factor: roads, post office, haulage and trips to Trieste and Fiume from the beginning of the 18th century to the age of the railways . tape 107 of Southeast European Works . Oldenbourg Wissenschaftsverlag, 2002, footnote 438, p. 147 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
In 1466 the ownership of the Walsee on the Quarnerobusen with Fiume, Castau , Veprinac and Moschenitz came to the Habsburgs.
1472 (Declaration of inheritance from Reinprecht V. March 12, 1472 in favor of Emperor Frederick; † May 19, 1483) the legacy of the Tybeiners followed: Duino (lordship of Upper and Lower Tibein), Bremp and Senosetsch ; compare also Franz von Krones: Walsee, Eberhard v . In: Allgemeine Deutsche Biographie (ADB). Volume 41, Duncker & Humblot, Leipzig 1896, pp. 5-16. (Family item)
- ↑ Land ordinance and Landtag election ordinance, Appendix II i to the Imperial Constitution 1861, RGBl. No. 20/1861 (= p. 69, supplement: p. 198)
- ↑ State law gazettes for Trieste and the coastal area