Envious people
| coat of arms | Germany map | |
|---|---|---|

|
Coordinates: 48 ° 35 ' N , 9 ° 34' E |
|
| Basic data | ||
| State : | Baden-Württemberg | |
| Administrative region : | Stuttgart | |
| County : | Esslingen | |
| Height : | 456 m above sea level NHN | |
| Area : | 12.62 km 2 | |
| Residents: | 1836 (December 31, 2018) | |
| Population density : | 145 inhabitants per km 2 | |
| Postal code : | 73272 | |
| Area code : | 07023 | |
| License plate : | ES, NT | |
| Community key : | 08 1 16 043 | |
| Address of the municipal administration: |
Kelterstrasse 1 73272 Neidlingen |
|
| Website : | ||
| Mayor : | Klaus Däschler | |
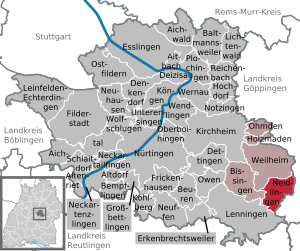
| Location of the municipality of Neidlingen in the Esslingen district | ||
Neidlingen is a municipality in the Esslingen district in Baden-Württemberg . It belongs to the Stuttgart region (until 1992 the Middle Neckar region ).
geography
Geographical location
Neidlingen is located in the central northern foreland of the Swabian Alb in the upper valley of the Lindach , east of the Randecker Maar . The next larger city is Weilheim an der Teck . Neidlingen is part of the Swabian Alb biosphere area with its entire marker .
Community structure
Apart from the village of Neidlingen, no other places belong to the municipality of Neidlingen. The lost castles Erkenberg , Burg Windeck , ruins Heimenstein , Reußenstein , Burgstall an der Lindach and Burgstall Im Hof are in the area of the municipality
Neighboring communities
Neighboring communities are in the north Weilheim an der Teck (district Esslingen), in the east Gruibingen and Wiesensteig , both district Göppingen, in the southwest Lenningen (district Schopfloch) and in the west Bissingen an der Teck (district Ochsenwang) (both district Esslingen).
Division of space
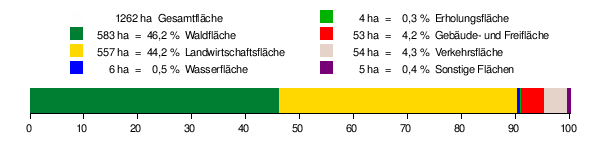
According to data from the State Statistical Office , as of 2014.
history
The place name goes back to the personal name Nidilo , the settlement was founded around 400 by the Alamanni. Neidlingen appears earlier than the majority of the other district communities as Nitlinga in written records: In 797 the place was first mentioned in a document of the Lorsch Codex . The high authorities changed several times, in 1564 the then owners, the Lords of Freyberg, were given high jurisdiction by the Kaiser , so that Neidlingen had achieved full imperial immediacy. In 1596 Neidlingen finally fell to Württemberg through inheritance . The direct imperial rule became a special Württemberg office, the Vogtei Neidlingen. In addition to the Kirchheim office, she led her own life until the 19th century.
The Lindach Valley was settled very early, as is shown by finds from the Neolithic Age . On the Butzenberg, which is also called Lichtenstein, a fortification from the Bronze Age burial mounds is suspected, on the Erkenberg one from the Hallstatt period ; a small Celtic statuette was also found in the Heimenstein cave. The road through the valley dates from Roman times.
Two moated castles from the 13th century were in the village, but have long since gone. After the younger one was destroyed in 1517, a four-wing moated castle was built a few meters north until 1536 (easy to see on the drawing by Andreas Kieser).
During the Second World War , the community was shelled by enemy fighter bombers on April 20, 1945, in which a building caught fire and two residents were killed. On April 21, the German Wehrmacht tried to prevent the Americans from climbing to the Alb at the intersection of Hepsisau-Neidlingen, but they arrived at 11:00 am with tanks, which ended the war in Neidlingen. Land consolidations took place between 1972 and 1991.
Population development
The population figures are census results (¹) or official updates from the State Statistical Office ( main residences only ).
| Deadline | population |
|---|---|
| December 3, 1834 ¹ | 891 |
| December 1, 1871 ¹ | 878 |
| December 1, 1900 ¹ | 856 |
| May 17, 1939 ¹ | 894 |
| September 13, 1950 ¹ | 1,211 |
| June 6, 1961 ¹ | 1,151 |
| May 27, 1970 ¹ | 1,387 |
| May 25, 1987 ¹ | 1,602 |
| December 31, 1995 | 1,882 |
| December 31, 2000 | 1,909 |
| December 31, 2005 | 1,908 |
| December 31, 2010 | 1,818 |
| December 31, 2015 | 1,838 |
politics
mayor
- 1962–1998 Ulrich Rieker
- 1998–2014 Rolf Kammerlander
- since 2014 Klaus Däschler.
In the election in December 2014, the detective Klaus Däschler received 58 percent of the vote, incumbent Rolf Kammerlander 38 percent. The turnout was 72 percent.
Municipal council
The local council in Neidlingen has 10 members. The local elections on May 25, 2014 led to the following official final result. The municipal council consists of the elected voluntary councilors and the mayor as chairman. The mayor is entitled to vote in the municipal council.
| Parties and constituencies |
% 2014 |
Seats 2014 |
% 2009 |
Seats 2009 |
Local election 2014
% 60 50 40 30th 20th 10
0
53.82%
46.18%
WUB
NWV
Gains / losses
compared to 2009
% p 4th 2
0
-2 -4 + 2.72 % p.p.
-2.72 % p.p.
WUB
NWV
|
|
| WUB | Voter association of independent citizens for Neidlingen | 53.82 | 5 | 51.1 | 5 | |
| NWV | Neidlinger voter association | 46.18 | 5 | 48.9 | 5 | |
| total | 100.0 | 10 | 100.0 | 10 | ||
| voter turnout | 61.15% | 62.1% | ||||
coat of arms
The coat of arms shows in a split shield a green oak branch with 3 acorns above in silver, below in green a silver N (for envious people). The coat of arms has been in use since 1669. Between 1807 and 1952 the municipality had a different coat of arms. In 1952 the coat of arms from 1669 was adopted again.
Economy and Infrastructure
Bike paths
Neidlingen is located on the Swabian Alb Cycle Path , a long-distance cycle path that leads from Lake Constance to Nördlingen across the entire Swabian Alb.
education
Neidlingen has its own small primary school .
Culture and sights
- The cherry blossom in the Neidlinger Tal is known throughout the region: More than 20,000 cherry trees grow on the fertile and climatically favorable slopes of the Alb.
- At the back of the valley is the Pfannenberg forest , which has been left to its own devices for over 100 years.
- One of the last (according to information on their homepage, the last producing) ball mills in Germany is located on Seebach in Neidlingen . Here balls are made from the rocks in the area.
Buildings
-
Neidlingen's landmark is the Reußenstein castle ruin, which crowns a rock dominating the valley . The castle, which was built at the end of the 13th century and whose owners changed several times, was inhabited until the 16th century and then fell into disrepair.
 Neidlinger Tal with meadows and orchards, in the background the Reußenstein castle ruins .
Neidlinger Tal with meadows and orchards, in the background the Reußenstein castle ruins .
- The historic parish barn in the village was saved from demolition in the 1970s and is now used as the parish hall.
- The Protestant parish church was rebuilt in the palace garden in 1746.
Natural monuments
- The Neidlinger waterfall, idyllically situated in the wooded steep slope of the Albtraufs , directly below the Reußenstein ruins, is considered the origin of the Lindach (see also: List of waterfalls in Germany ).
- In the home cave should according to the legend of Wilhelm Hauff , the giant home have come to expect from Home Stone before he Reußenstein the castle had built.
Sports
Neidlingen is also known as a flight area among hang-gliders and paragliders. The launch site is on a western slope east of Neidlingen (270 meters difference in altitude).
The gymnastics club 1910 Neidlingen operates football, athletics, winter sports and inline skating and, according to its own information, has almost half of the population as members.
Other sports clubs are the Schützenverein Neidlingen 1873 e. V. and the tennis club Neidlingen e. V. 1981 .
Regular events
- Zwetschgenmarkt (grocer's market, annually on September 21)
- Zwetschgenmarktfest (village festival, on the weekend before or after the plum market)
- Advent market (Saturday before the first Advent )
Personalities
Sons and daughters of the church
- Johannes Hepperle (born March 10, 1882 in Neidlingen, † February 28, 1976 in Kirchheim unter Teck), carpenter and harmonium maker, owner of the Teck Harmonium company in Kirchheim unter Teck
Personalities who have worked in Neidlingen
- Heinrich Seufferheld (1866–1940), painter, professor at the University of Tübingen, lived in Neidlingen during the summer
- Konrad Widerholt (1598–1667), Württemberg commander, received rule over Neidlingen in 1650
literature
- Hans Schwenkel : Home book of the Nürtingen district. Volume 2. Würzburg 1953, pp. 668-691.
- The district of Esslingen - published by the Baden-Württemberg State Archives. V. with the district of Esslingen, Jan Thorbecke Verlag, Ostfildern 2009, ISBN 978-3-7995-0842-1 , Volume 2, pages 214-225.
- Christoph J. Drüppel: Neidlingen: history of the rule, bailiwick and community under the Reußenstein [Hrsg .: community Neidlingen]. - Neidlingen: Neidlingen community, 1997. ISBN 3-925589-16-3 .
Web links
- Official website of the community of Neidlingen
- Data and map service of the State Institute for the Environment, Measurements and Nature Conservation , query option for natural monuments, accessed on December 3, 2015
Individual evidence
- ↑ State Statistical Office Baden-Württemberg - Population by nationality and gender on December 31, 2018 (CSV file) ( help on this ).
- ^ The state of Baden-Württemberg. Official description by district and municipality. Volume III: Stuttgart District, Middle Neckar Regional Association. Kohlhammer, Stuttgart 1978, ISBN 3-17-004758-2 , pp. 251-252.
- ↑ State Statistical Office, area since 1988 according to actual use for Neidlingen.
- ↑ http://www.neidlingen.de/portal/index.php?page=316 History of Neidlingen
- ↑ Ulrich Stolte: Commissioner overthrows mayor. Stuttgarter Zeitung , December 1, 2013, accessed June 5, 2014 .
- ^ Election information from the Stuttgart municipal data center
- ↑ http://www.kugelmuehle-neidlingen.de/39994.html
- ^ TVN portrait , accessed December 27, 2015.