Oberrot
| coat of arms | Germany map | |
|---|---|---|

|
Coordinates: 49 ° 1 ' N , 9 ° 40' E |
|
| Basic data | ||
| State : | Baden-Württemberg | |
| Administrative region : | Stuttgart | |
| County : | Schwäbisch Hall | |
| Height : | 357 m above sea level NHN | |
| Area : | 37.92 km 2 | |
| Residents: | 3595 (Dec. 31, 2018) | |
| Population density : | 95 inhabitants per km 2 | |
| Postal code : | 74420 | |
| Area code : | 07977 | |
| License plate : | SHA, BK , CR | |
| Community key : | 08 1 27 062 | |
| LOCODE : | DE OOT | |
| Address of the municipal administration: |
Rottalstrasse 44 74420 Oberrot |
|
| Website : | ||
| Mayor : | Daniel Bullinger ( FDP ) | |
| Location of the municipality of Oberrot in the Schwäbisch Hall district | ||
Oberrot is a municipality in the Schwäbisch Hall district in the Franconian north-east of Baden-Württemberg . The community is a member of the Limpurger Land community administration association based in Gaildorf .
geography
Geographical location
Oberrot is located in the natural area of the Schwäbisch-Franconian Forest Mountains on the Fichtenberger Rot , about 12 km south-southwest of the district town of Schwäbisch Hall . The old center of the eponymous main village borders the right bank of the Rot and is crossed by the Fronbach, which flows here . Newer settlement areas connect to the slope and in the upward floodplain on the right. The widenings that were last made on the flatter slope on the left side of the valley are now larger than the ones on the right. Down the valley on both sides in the wide Rotaue are several large halls of an important industrial company for wood processing.
The municipality of Oberrots extends along the valley section of the Rot between its south-east bend near Schwäbisch Hall-Wielandweiler and its east bend in front of Fichtenberg and extends far into the mountains on both sides. These belong to the Mainhardt Forest and border in the southwestern part of the Murrhardt Forest . The longest extension of the municipality from northwest to southeast along the valley is almost 9 km, across it it is almost 8 km at the widest point. The Rottal, central traffic axis of the municipality, is initially quite narrow, widens in the area between the most populous settlements Oberrot and - significantly smaller - Hausen to a width of almost one kilometer, only to narrow again below Hausen. Most of the municipality is located on the edge heights, where it is west of Oberrot on the Flinsberg at 534.8 m above sea level. NN reaches its highest point; its lowest is below Hausen at the outflow of the Rot at a little below 347 m above sea level. NN . The mountains around Oberrot are noticeably crushed. In the larger side valleys, as in the main valley itself, there are several old mill locations. But the scattered settlement is not limited to the valleys, there are also farms and small hamlets on the plateaus in cleared islands. At the top, around half of the terrain is forested, while the main valley and the lower, larger side valleys are mostly open. Grassland farming dominates everywhere compared to field farming, which especially avoids the floodplains.
Community structure
The municipality of Oberrot with the municipality of Hausen an der Rot, which was independent until the municipal reform in Baden-Württemberg, includes 38 villages, hamlets, farms and houses.
Hausen an der Rot includes the village of Hausen an der Rot, the hamlets of Neuhausen, Scheuerhalden and Wiesenbach, the Völkleswald homestead and the Eitelwäldle, Greuthof and Stielberg residential areas. The village of Oberrot, the hamlets of Ebersberg, Frankenberg, Glashofen, Hohenhardtsweiler, Jaghaus, Konhalden, Kornberg, Marbächle, Marhördt, Obermühle, Seehölzle, Stiershof and Wolfenbrück, the courtyards Brennhof, Dexelhof, Ebersberger Sägmühle, Ernstenhöfle, Marhördter Mühle belong to Oberrot , Untere Kornberger Sägmühle and Ziegelhütte and the residential areas Amselhalde, Badhaus, Frankenberger Sägmühle, Hammerschmiede (Sägmühle), Marhördter Sägmühle, Neumühle, Obere Kornberger Sägmühle and Stiersbach.
In the municipality of Oberrots are the abandoned , no longer existing villages Büchelberg, Feuchtenbrunnen, Harnersberg (also Sumpfhof), Lunkenbrunnen, Satelege and Scheuren (in the area of the former municipality of Hausen an der Rot) and Burkey and Kayenberg (in the area of the municipality of Oberrot in front of the Municipal area reform).
Division of space
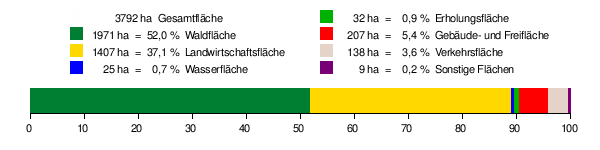
According to data from the State Statistical Office , as of 2014.
Neighboring communities
Neighboring towns and municipalities in Oberrot are ( clockwise , starting in the northwest): Mainhardt , Schwäbisch Hall , Rosengarten , Gaildorf , Fichtenberg (all Schwäbisch Hall district ), Murrhardt and Großerlach (both Rems-Murr district ).
history
Oberrot is one of the oldest communities in the Limpurger Land and probably dates back to a Franconian foundation around the year 650. The place was first mentioned in a document on the occasion of a donation to the Lorsch Monastery in 788 in the Lorsch Codex as “Raodhaha” in Kochergau in the Westheim district. The place name Oberrot is derived from the then Rottach, later called Rot, the name of which refers to an earlier Frankish clearing. It can therefore be assumed that a representative of the Westheimer Königshof cleared and settled and then settled in Oberrot himself. The well-known noble family von Rot goes back to this first Franconian local lord, whose seat must first have been in the village.
It seems that in its beginnings, the family of the Lords of Red, which can be traced back to before 1100, was dependent on the Counts of Comburg . In the legacy of the Comburgers, the Reds came to the Staufer . After they lost the German throne in 1254 and died out completely in 1268, the Lords of Rot entered the service of the Limpurg taverns . The Limpurg taverns had a great influence on the decisions and thus the development of the community for a long time. It was different in today's town of Hausen, where the Comburg monastery was in charge at the time .
For several centuries Oberrot was ruled by these Lords of Red. After the destruction of the castle on the Schlossbuckel around 1290, the lords of the castle took their seat in Oberrot again in a medieval building. The building was burned down during the city war (1449 to 1450). In its place, a stately two-storey plastered half-timbered building was built in 1550 by the Limpurgian Vogt zu Oberrot. In 1571 it became the property of the Haller Senfft von Sulburg and from 1634 to 1707 it was owned by the Senfft von Ellrichshausen family branch .
From 1738 onwards, the building was called the Altes Amtshaus and in later years until 2005 the Zehntscheuer. When researching the building in 2005, the State Monuments Office determined that it was the former free aristocratic seat. Next to it is a baroque plastered building from 1738, which was built under Countess Wilhelmina Christina zu Solms-Assenheim. Countess of Limpurg was built as a stately office building.
The life of the ordinary citizens of the two places Oberrot and Hausen was always determined by forestry and forestry. Nevertheless, there were some excursions into more exotic branches of the economy, for example many people from Oberroter and Hausener tried to grow wine in the 15th and 16th centuries. The attempt was unsuccessful, however, the noble "drink" had to be heavily sweetened with honey and sugar. Also on the hop -growing is tried.
With the dissolution of the German Empire in 1806, the political independence of the County of Limpurg also ended. Oberrot fell under the sovereignty of Württemberg and came to the Oberamt Gaildorf, which was formed in 1807 . Around 1810, the first forerunners of today's municipal councils, the so-called courts, appeared in Oberrot and Hausen. In 1819, the municipalities' right of self-administration was laid down in the Württemberg constitution, and the courts were therefore replaced by municipal councils who were subordinate to a mayor . The Oberamt Gaildorf, formed in 1807, was dissolved in 1938, and the community came to the Backnang district .
In December 1969 the municipal councils of Oberrot and Hausen voted to merge their previously independent municipalities. The merger was the first community association in the Backnang district. During the district reform in 1973 , the Backnang district was split up, and Oberrot became part of the Schwäbisch Hall district. The old schoolhouse in the center of Oberrot serves as the town hall today.
politics
coat of arms
Before the union with Hausen an der Rot on January 1, 1970, Oberrot carried the coat of arms of the local aristocracy as the legally valid municipal coat of arms. The coat of arms of Hausen an der Rot showed a house and a wavy beam under a deer pole. When Hausen was incorporated, it was agreed to create a new coat of arms that represented both Oberrot and Hausen. On October 14, 1971, the Baden-Württemberg Ministry of the Interior awarded the municipality the current coat of arms and the flag in the colors "white and red".
Blazon : "In a split shield in front four times divided by red and silver (white), behind in blue a golden (yellow) lion head with a golden (yellow) rafter in its mouth."
The front half of the shield shows the coat of arms of the local nobility, the Lords of Rot, who owned both Oberrot and the suburb of Hausen. The back field contains the coat of arms of the monastery or monastery Comburg, which after 1248 appears next to the Lords of Rot as owners of Hausen.
 Upper red old |
 Hausen old |
 Oberrot new |
|---|
mayor
Daniel Bullinger (* 1985) was elected as the new mayor in 2012 with 88.45% of the votes.
Municipal council
The town council in Oberrot has 18 members. The local elections on May 26, 2019 led to the following official final result:
| Parties and constituencies |
% 2019 |
Seats 2019 |
% 2014 |
Seats 2014 |
Local elections 2019
% 60 50 40 30th 20th 10
0
55.54%
44.46%
Free
Independent |
|
| Free | Free citizen list Oberrot | 55.54 | 8th | k. A. | k. A. | |
| Independently | Independent citizen list | 44.46 | 6th | k. A. | k. A. | |
| total | 100.0 | 14th | k. A. | k. A. | ||
| voter turnout | 59.33% | k. A. | ||||
Community partnerships
The municipality of Oberrot has maintained partnership relationships with the municipality of Zweisimmen in Switzerland since 1991 .
Tourism and sightseeing
The Protestant Bonifatius Church is over 1200 years old. It was rebuilt in the historicist style by the Württemberg architect Heinrich Dolmetsch in 1887 for its 1100th anniversary . It has rich ornamentation on the two-story gallery and the pointed gable ceiling and biblical scenes in the wooden vault of the choir .
Also the former free aristocratic seat and the former office building in Oberrot as well as the St. Michaelskirche and the Stielberg chapel with the historical Stations of the Cross in Hausen an der Rot are worth seeing.
At the lower course of the Mühlbach, less than 500 meters from its confluence with the Rot, is the Marhördter Sägmühle (!), Which seven farmers from the neighboring villages of Marhördt, Morbach and Ofenberg built in 1856. The mill was in operation until 1975. In October 1981 the municipality of Oberrot bought the old mill building together with the water rights and in 1983 set up the sawmill museum. Equipment for wood processing as well as carts and sleds for transporting wood are exhibited.
The Way of St. James runs directly through Oberrot . The Limes hiking trail runs near Oberrot along the UNESCO World Heritage Site. In Ebersberg is the Flinsberg natural monument with its flint blocks.
In addition to restaurants and accommodation, there is a tennis facility, two golf courses, a campsite, well-signposted hiking and cycling trails of over 50 km in length and cross-country ski trails in winter.
Economy and Infrastructure
Established businesses
- Campsite Zum Offenberg and restaurant, Moll GbR
- Dreher BBQ Heroes
- Prefabricated house white
- Gasthof Krone
- Farrenstall restaurant
- Häfner Gewichte GmbH
- Klenk Holz AG
- Landhaus Noller
- Micronisierungs-Kontor Oberrot GmbH
- Margarete retirement home
education
There is a primary and secondary school in Oberrot.
societies
The FC Oberrot 1928 eV is the largest club in town with around 850 members. It was founded as a football club in 1928 and has evolved over time into a multi-discipline club. In addition to football, other sports such as table tennis , gymnastics, jazz gymnastics, downhill and karate are offered.
Personalities
Sons and daughters of the church
- Christian Kausler (1761–1822), Oberamtmann of Württemberg
- Hermann Frasch (1851–1914), German / American chemist, honored with a mausoleum in Gaildorf
- Albert Schüle (1890–1947), politician (NSDAP)
- Karl Hermann Häuser (1920–2008), economist and university professor
- Kurt Oesterle (* 1955), journalist and writer
Web links
- Map of the municipality of Oberrot on: State Institute for the Environment Baden-Württemberg (LUBW) ( information )
- Map of the village of Oberrot on: Geoportal Baden-Württemberg ( information )
literature
- Gerhard Fritz, Hans Peter Müller, Rolf Schweizer, Andreas Zieger: 1200 years of Oberrot. From the history of the Rottal communities Hausen and Oberrot. Wegra-Verlagsgesellschaft, Stuttgart 1987, ISBN 3-921546-25-7 .
References and comments
- ↑ State Statistical Office Baden-Württemberg - Population by nationality and gender on December 31, 2018 (CSV file) ( help on this ).
- ↑ Natural areas of Baden-Württemberg . State Institute for the Environment, Measurements and Nature Conservation Baden-Württemberg, Stuttgart 2009
- ^ The state of Baden-Württemberg. Official description by district and municipality. Volume IV: Stuttgart district, Franconian and East Württemberg regional associations. Kohlhammer, Stuttgart 1980, ISBN 3-17-005708-1 . Pp. 474-477
- ↑ State Statistical Office, area since 1988 according to actual use for Oberrot.
- ↑ Minst, Karl Josef [trans.]: Lorscher Codex (Volume 1), Certificate 13, June 7, 788 - Reg. 2037. In: Heidelberger historical stocks - digital. Heidelberg University Library, p. 69 , accessed on September 19, 2018 .
- ^ Election information from the Stuttgart municipal data center .
- ^ Evangelical church district Gaildorf: History of the Bonifatius Church at a glance. Retrieved on September 16, 2017 (German).
- ↑ The Marhördter Sägmühle should not be confused with the Marhördter Mühle , which is about a kilometer further west and up in the valley, with the Lower Kornberger Sägmühle less than a hundred meters from the mouth of the stream.
- ↑ campsite
- ↑ Event service
- ↑ weights
- ^ Restaurant, hotel, golf club
- ↑ pharmaceutical company
- ↑ FC Oberrot
- ↑ Homepage of FC Oberrot